What Is Surface Analysis?

What is surface analysis?
Surface analysis is an analytical technique to elucidate elemental composition, chemical state, and micro
structure from material surface layer (several nm to several µm).
As phenomena such as corrosion, wear, adhesion, and reactions that impact performance and reliability occur
primarily on the surface, surface analysis is vital for material evaluation, quality control, and failure
analysis.
For analysis, it is necessary to select the most suitable method, according to the sample state(target point, size, material, etc.) and analysis purpose.
What information we want to know? What is the material of the sample?
What is the range of information that we want to know? How deep?
Is it water-soluble? Does it react with solvents? Pre-treatment needed?

It is important to select the analytical method suitable for the purpose
Types and features of surface analysis instruments
The figure below shows the comparison of typical surface analysis methods from various points of view, such as excitation source, detection signal, quantitativeness, whether the chemical state can be analyzed or not, sensitivity, handling of an insulator, and analysis capability of depth direction. It is important to understand the feature of each method and properly select the analysis method according to the purpose.
| Analytical methods | EPMA (WDS)/SXES/EDS | AES | XPS | XRF | SIMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excitation source | Electron beam | Electron beam | X-ray | X-ray | Ion |
| Signal | Characteristic X-ray | Auger electron | Photoelectron | Fluorescence X-ray | Secondary ion |
| Detectable element | Be ~ (WDS, EDS) Li (SXES, Windowless EDS) |
Li ~ | Li ~ | C ~ | H~ |
| Quantitative analysis | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | × |
| Chemical state | △ | ○ | ○ | × | Organic compound |
| Detection depth | Several µm | Several nm | Several nm | Several mm | Several nm |
| Sensitivity | Several ten ppm (Mass concentration) |
Several thousand ppm (Atomic concentration) |
Several thousand ppm (Atomic concentration) |
Several ten ppm (Mass concentration) |
Several ppm (Atomic concentration) |
| Insulator | ○ (Conductive coating) | △ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Depth analysis | △ | ○ | ○ | × | ○ |
| Strength |
Qualitative analysis Quantitative analysis Wide area ~ micro area analysis |
Micro area analysis Chemical bonding state analysis Depth profile analysis |
Insulator analysis Chemical bonding state analysis Depth profile analysis |
Qualitative analysis Thin film analysis Trace element analysis |
Organic substance analysis Trace element analysis |
| Challenge |
Chemical bonding state analysis (Strong at SXES) Organic substance analysis |
Wide area analysis Insulator analysis Organic substance analysis |
Micro area analysis Trace element analysis |
Micro area analysis |
Qualitative analysis Quantitative analysis |
In this column, we explain surface analysis instruments that JEOL offers, such as XPS (photoelectron
spectrometer), AES (Auger microprobe) , XRF (X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometer) , EPMA(Electron Probe
Microanalyzer) with *standard wavelength-dispersive X-ray spectrometer, SEM+EDS(Scanning Electron
Microscope+Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectrometer), and SXES(soft X-ray emission spectrometer) that can be
installed to EPMA(WDS) and SEM.
We clearly explain each mechanism, its strengths and weaknesses in analysis, and key points for selecting the instrument.
Surface analysis instruments by JEOL
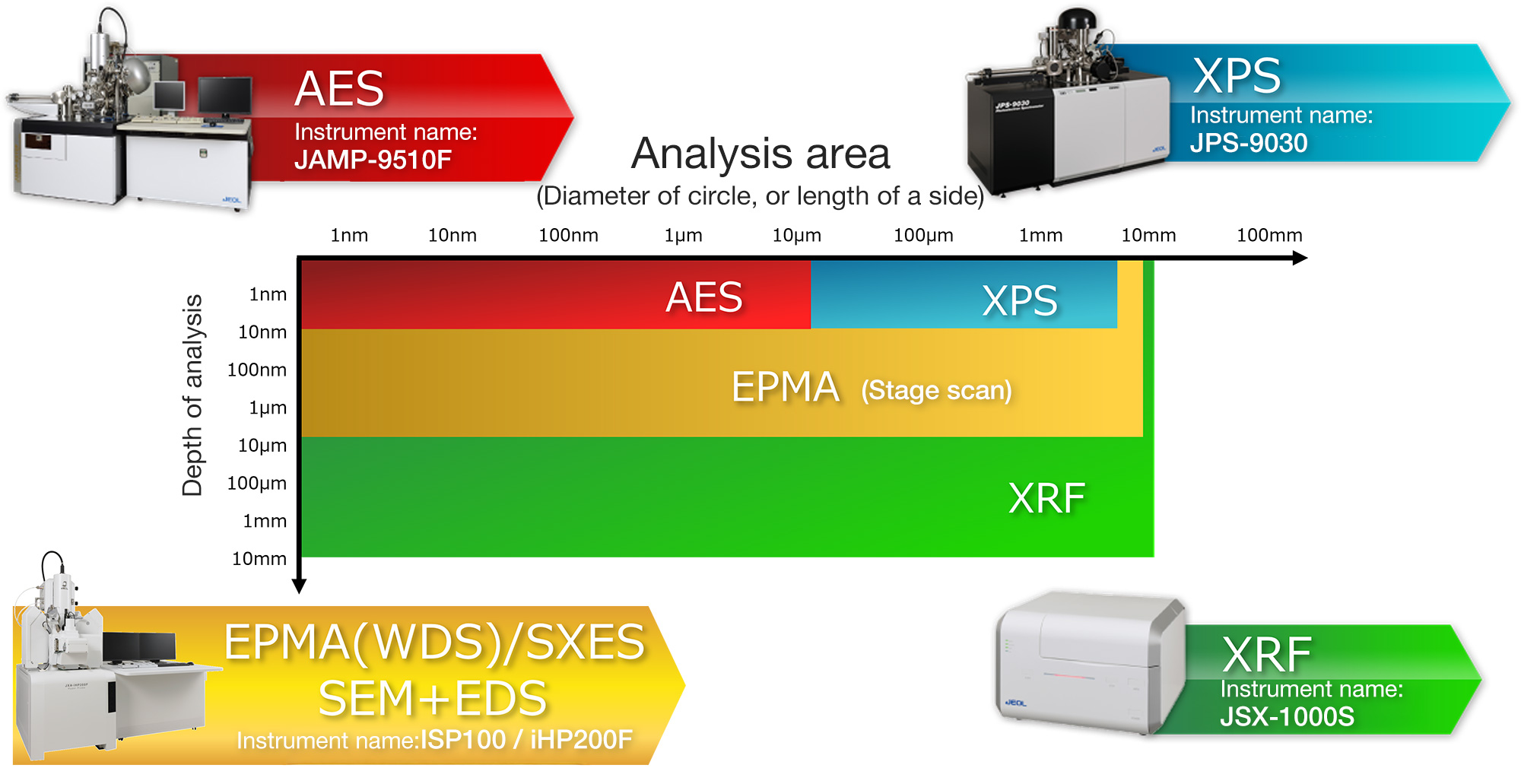
Difference of analysis area/depth according to surface analysis instrument
XRF enables elemental analysis in the deepest and widest region. It is suitable for understanding the average composition of the entire bulk material and is utilized in qualitative/quantitative analysis in a wide field of view.
On the other hand, SEM + EDS and EPMA(WDS) can investigate the local elemental distribution by detecting x-rays that are generated in a local area of about several micrometers. SEM+EDS enables simultaneous evaluation of morphology and elemental analysis, while EPMA provides superior capabilities in more precise quantitative analysis and area analysis.
Soft X-ray Emission Spectrometer(SXES)
The Soft X-Ray Emission Spectrometer (SXES) is an ultra-high resolution spectrometer consisting of a
newly-developed diffraction grating and a high-sensitivity X-ray CCD camera.
In the same way as EDS, parallel detection is possible, and 0.3 eV (Fermi-edge, Al-L standard)
ultra-high energy resolution analysis can be performed, surpassing the energy resolution of WDS.
Moreover, AES and XPS makes it possible to obtain signals from the very shallow surface layer of about several nanometers deep. They are optimal for evaluating chemical state of the surface layer such as surface processing, contamination, and oxidization state.
Thus, to investigate the extreme surface at the nanometer scale, AES or XPS is suitable. For local analysis at the micrometer level, SEM combined with EDS or EPMA is appropriate. If the target is a wide area on the millimeter scale, XRF is the best choice. The appropriate instrument varies depending on the required analysis depth and the field of view size.
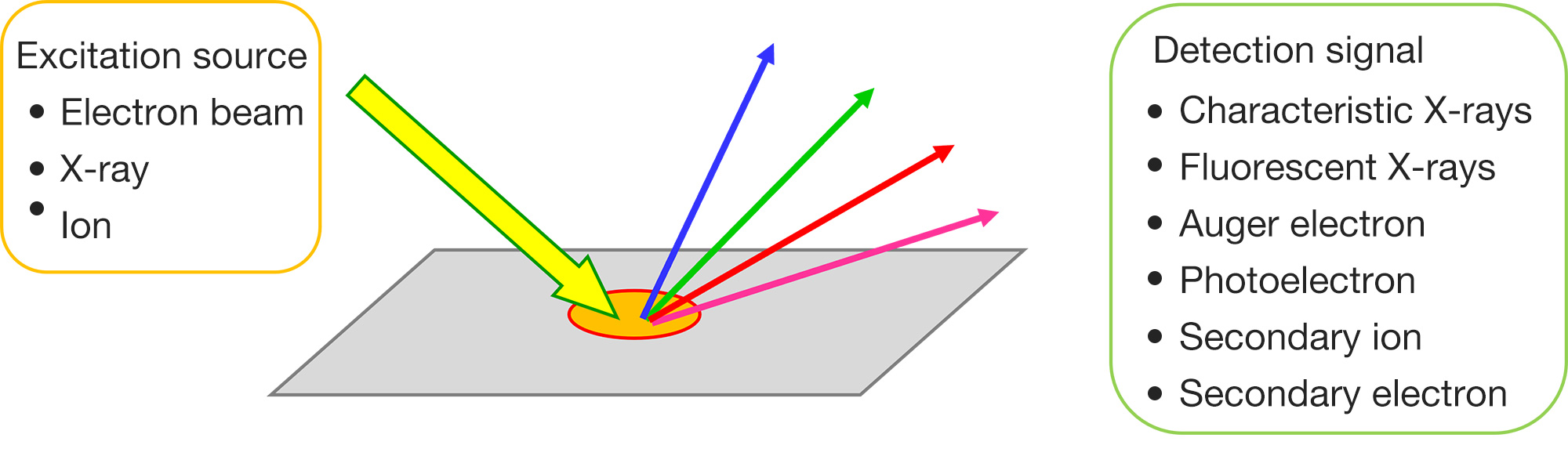
Difference in principles and detection signals of surface analysis instruments
As shown below, each instrument has a different excitation source (incident probe) and detection signal, and the information obtainable is different according to their features.
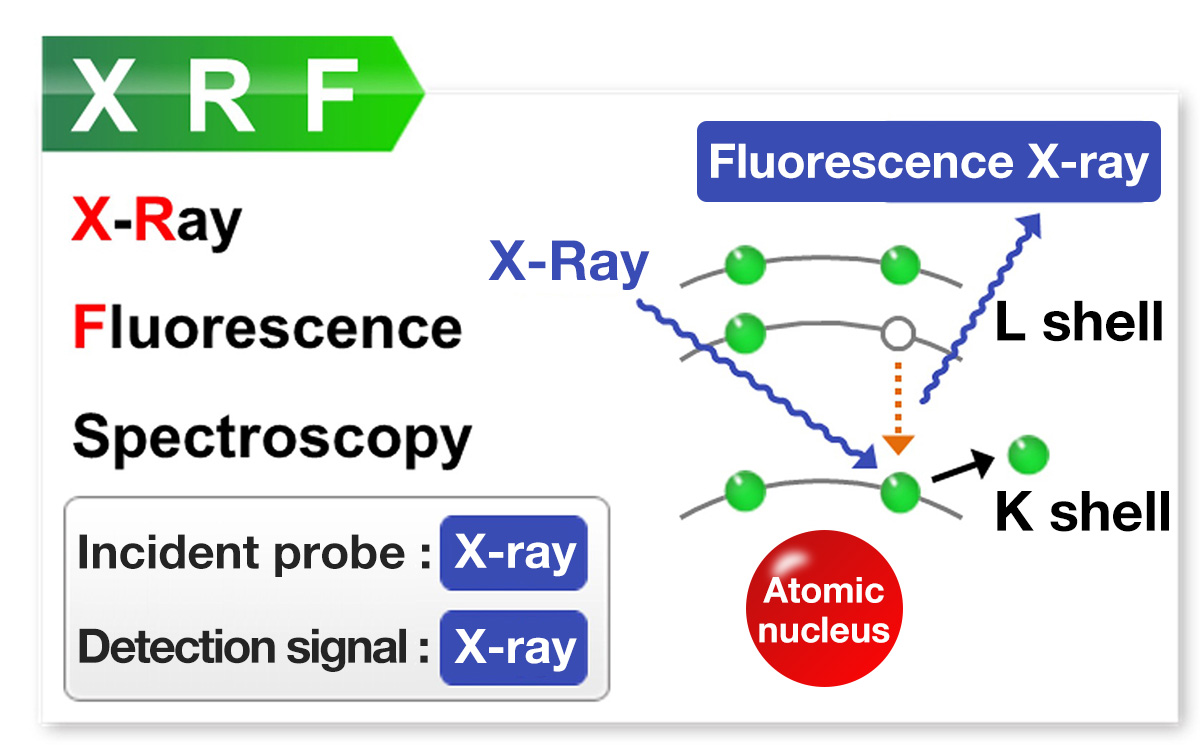
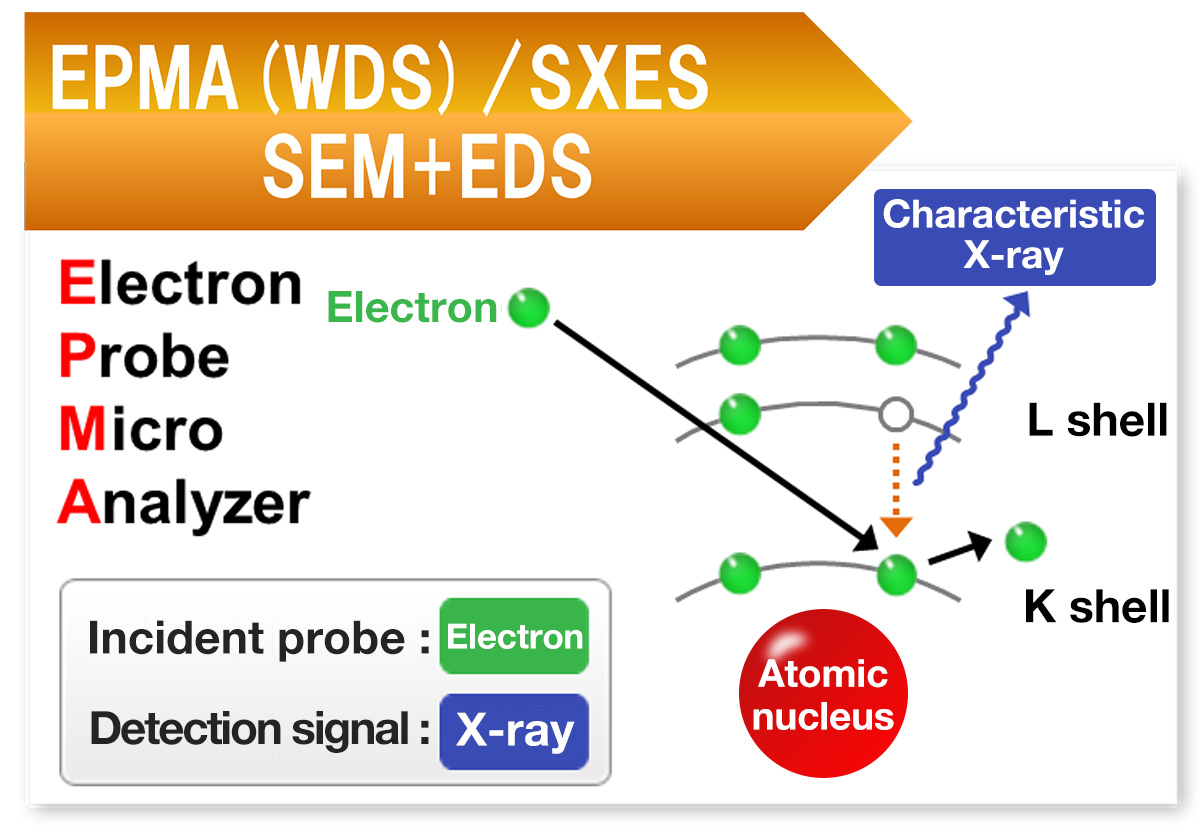
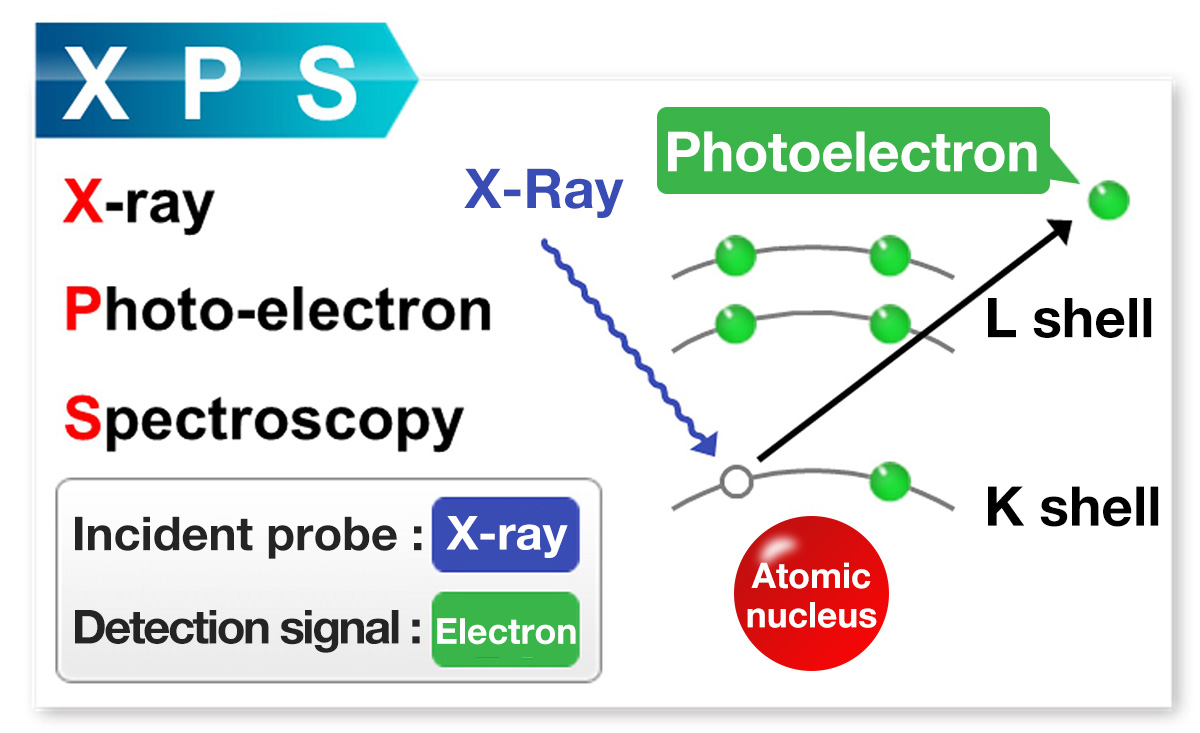
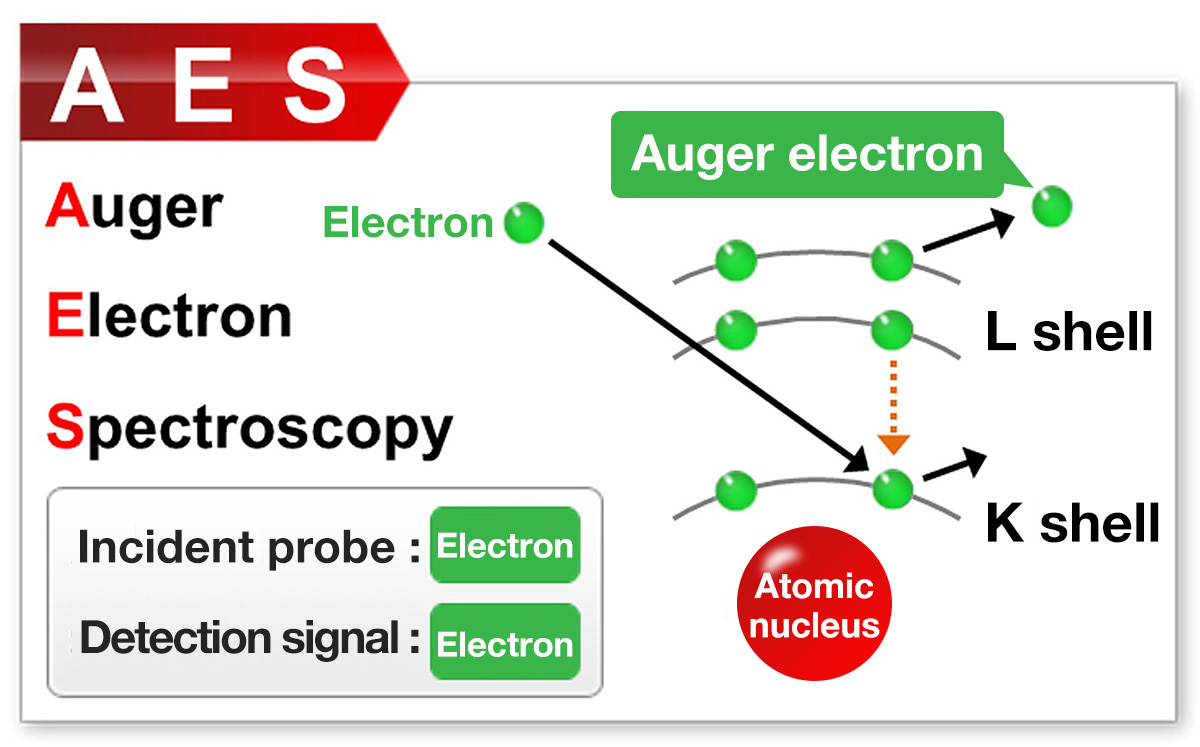
Please check the following for principles of each instrument.
Points for selecting surface analysis method
In surface analysis, it is important to select the appropriate technique based on
the properties of the specimen and the purpose of the analysis. For specimens that are susceptible to
vacuum, such as biological or liquid specimens, methods like XRF, which can be performed under atmospheric
pressure, or SEM equipped with a low-vacuum mode are effective. If the specimen can withstand a vacuum
environment, more sensitive and higher-resolution techniques such as XPS, AES, or EPMA can also be
considered.
This section introduces the optimal analytical method for each purpose, along with the figures.
Qualitative/Quantitative Analysis
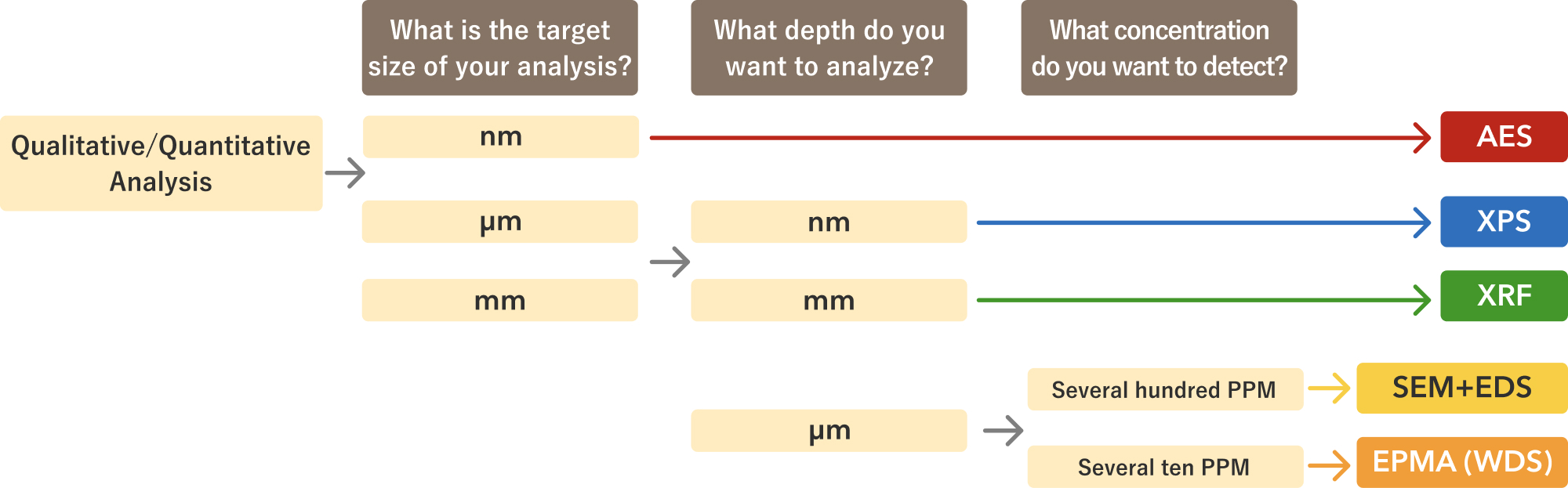
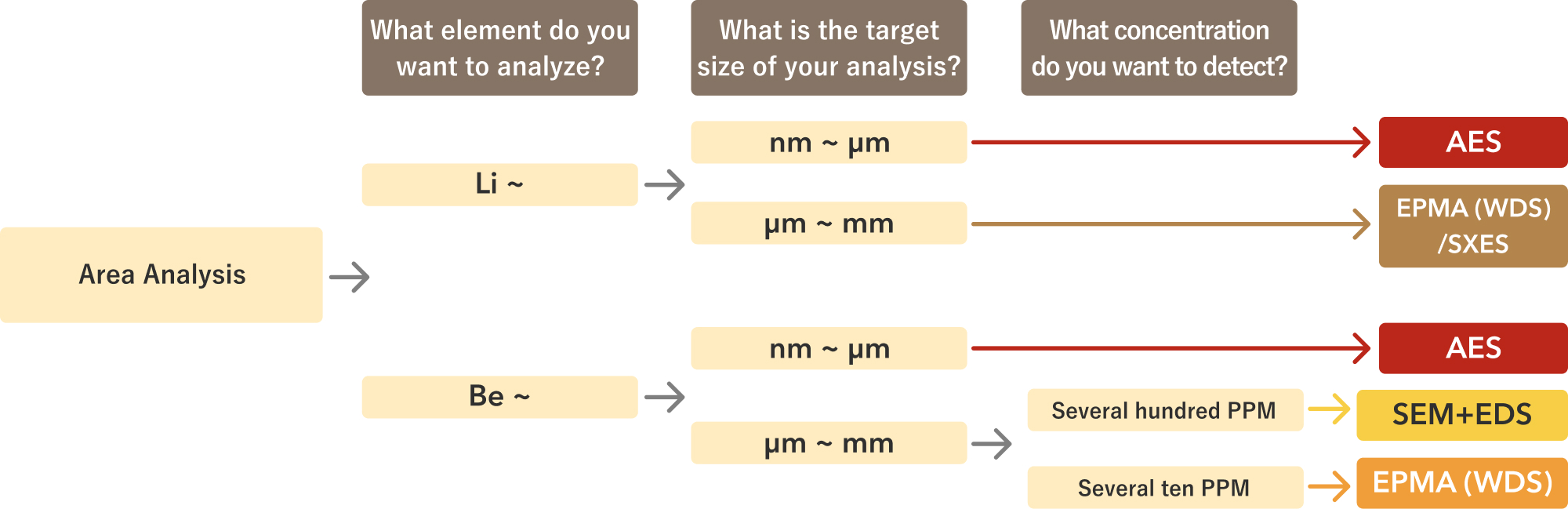
Area Analysis
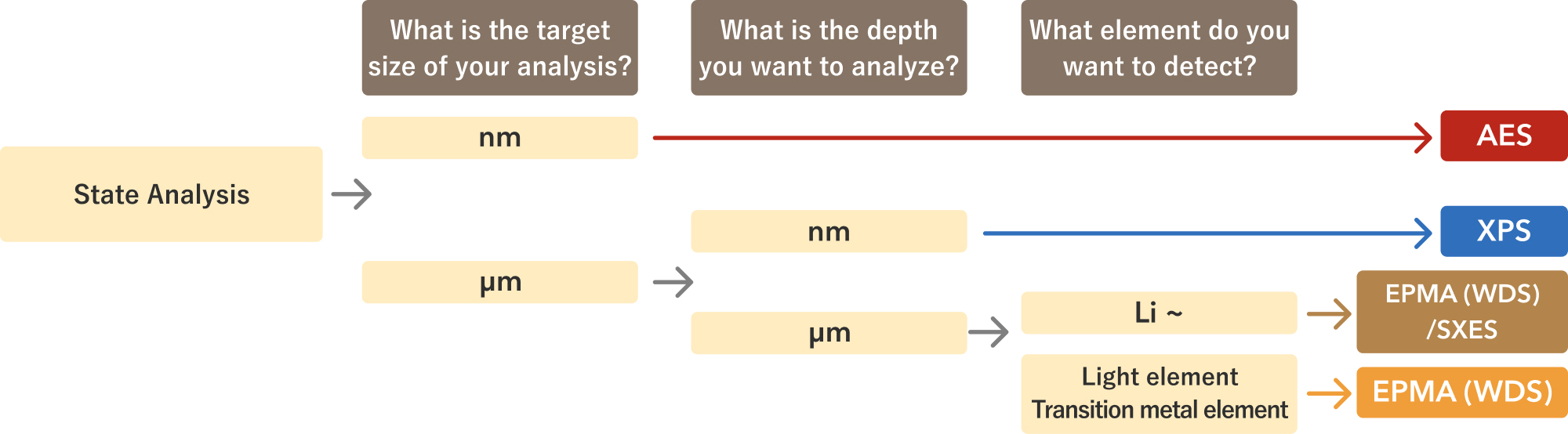
State Analysis
Examples of surface analysis
This section introduces specific application examples using surface analysis instruments such as XPS, AES, and EPMA.
XPS
A New Specimen Treatment Chamber for XPS and Its Applications
Simple and Easy Chemical Bond Analysis in XPS
Analysis of organic thin films
AES
【JEOL NEWS Vol.45 No.1, 2010】Analysis of Insulator Samples with AES
Chemical Status Analysis using AES
Auger Analysis of CP Cross Section
AES / XPS
【JEOL NEWS Vol.49 No.1, 2014】Advanced Analysis of Active Materials in Li-Ion Battery by XPS and AES
SEM / AES
EPMA
Electron Microprobe Study of the Yinxu (Anyang) Bronze of Academia Sinica Collection
A New WDS Spectrometer for Valence Electron Spectroscopy Based on Electron Microscopy
Analyzing conditions for high spatial resolution X-ray images
EPMA (WDS) /SXES
Summary
Surface analysis is a technique to obtain key information that directs to performance and reliability of the instrument. This article explains the tips of instrument selection through the features of typical analysis methods and points of selection, strength by instrument, and concrete application examples.
JEOL Ltd. has product line-ups that can satisfy a wide range of needs from beginners
to researchers, and that can be utilized with support from introduction to operation.
For questions on surface analysis and inquiries about selection of an instrument, please do not hesitate to
contact us.
Catalogue download

JEOL Ltd.
Since its foundation in 1949, JEOL has been committed to the development
of cutting-edge scientific and metrology instruments, industrial and medical equipment.
Today,
many of our products are used throughout the world and we are highly regarded as a truly global
company.
Aiming to be a 'top niche company that supports science and technology around the
world', we will continue to respond precisely to the increasingly sophisticated and diverse needs
of our customers.
Contacts
JEOL provides a variety of support services to ensure that our customers can use our products with peace of mind.
Please feel free to contact us.








