Differential analysis of UV degradaed polyethylene terephthalate using JMS-S3000 “SpiralTOF™-plus2.0” and “msRepeatFinder”
MSTips No.422
Introduction
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOFMS) is a powerful tool in the analysis of polymers. Since MALDI mainly generates singly-charged ions, the m/z in the mass spectrum is the mass of the polymer ion. Using high mass resolution MALDI-TOFMS makes it easy to distinguish polymer series by the composition of repeating units and end-groups and calculate each series's molecular weight distribution. Recently, the Kendrick Mass Defect (KMD) method has made it possible to easily visualize the polymer series in complex high mass resolution mass spectra. The end groups of polymers are degraded by exposure to heat or light or by treatment with acids or alkalis. In this application note, we report an application of the differential analysis function implemented in msRepeatFinder to the end-group analysis of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which has been degraded by UV irradiation.
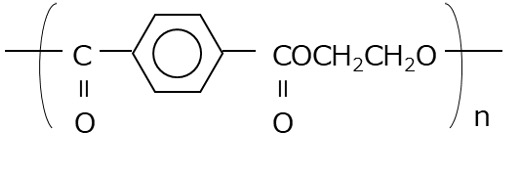
Figure 1 PET structural formula
Experiment
Commercially available PET films were used as samples. One of the films was exposed to UV irradiation for 30 minutes to degrade it. The matrix was 2',4',6'-trihydroxyacetophenone monohydrate (THAP), and the cationizing agent was sodium trifluoroacetate (NaTFA). Each film was fixed to the plate with conductive tape, and the matrix and cationizing agent mixture were dropped and air-dried on top of the film. The mass spectra of SpiralTOF mode of JMS-S3000 "SpiralTOF™-plus2.0" were acquired three times for each film, and KMD analysis was performed using msRepeatFinder V6.
Result
Figure 2 shows the mass spectra before (a) and 30 minutes after UV irradiation (b). Although groups of peaks with 192u intervals are observed in both mass spectra, the change in m/z observed before and after degradation indicates that the end groups have changed. The KMD plot of the peak lists of the two mass spectra (Base unit C10H8O4 , divisor 191)(c) is superimposed below. The polymer series parallel to the abscissa on the KMD plot has different end groups.
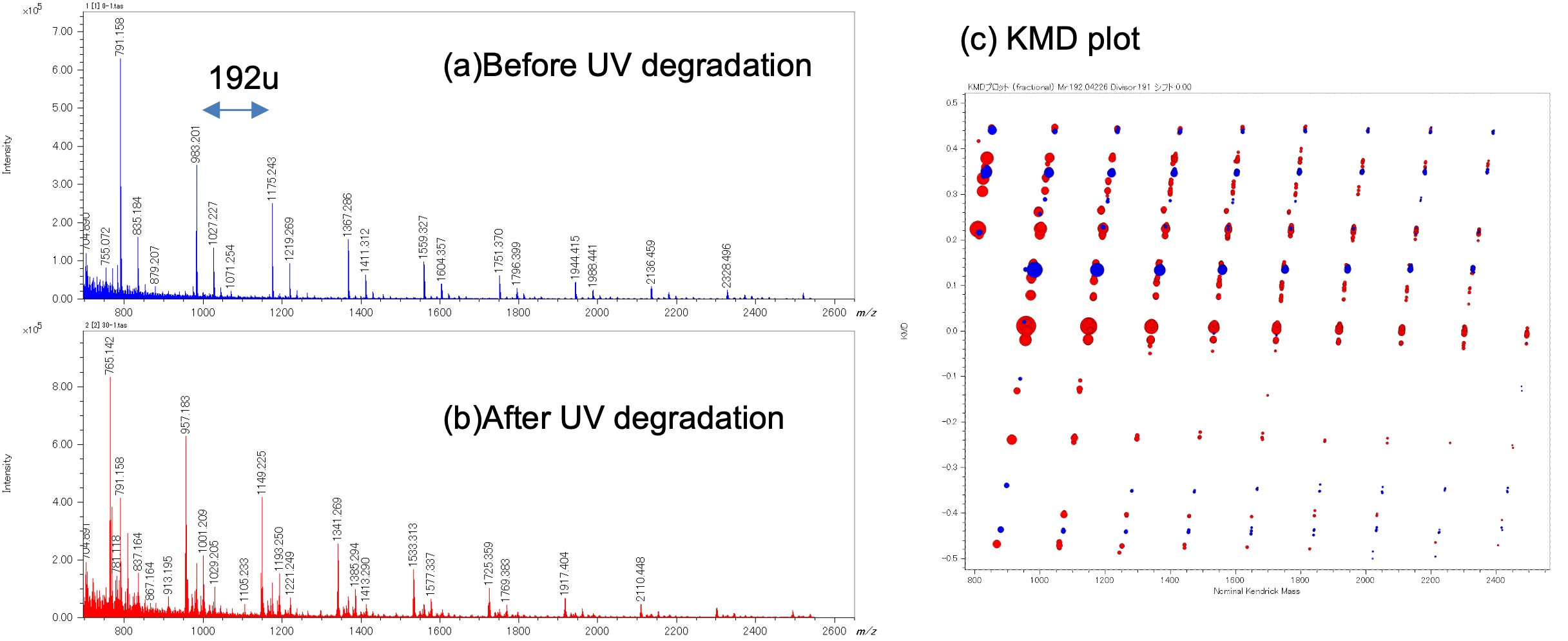
Figure 2 Mass spectra of PET before(a) and after(b) UV degradation. The overlaid KMD plot is also shown (c)
In the differential analysis, the peaks in the mass spectra of the samples before and after UV degradation (three peaks each) were considered identical if their mass errors were within 10 mDa. Figure 3 shows the averaged mass spectra before and after UV irradiation. Here, the ion intensities are normalized so that the ion intensities of the entire mass spectrum were identical. Figure 4a shows a volcano plot of the results of differential analysis. The horizontal axis is Log2 (average ion intensity before UV degradation/average ion intensity after UV degradation), The vertical axis is -Log10 (p-value). In Figure 4b, KMD plots (Base unit C10H8O4, divisor 191) are shown as KMD plots. Blue and light blue plots are the characteristic peaks before UV degradation, and red is the characteristic peaks after UV degradation. Thus, the differential analysis enables us to extract a group of peaks characteristic before and after UV degradation. As a result of the composition estimation of the end groups, it is estimated that the main component before UV irradiation is a cyclic oligomer, and the main component after UV degradation is a series of carboxylic acids at both ends (all [M+Na]+ ).
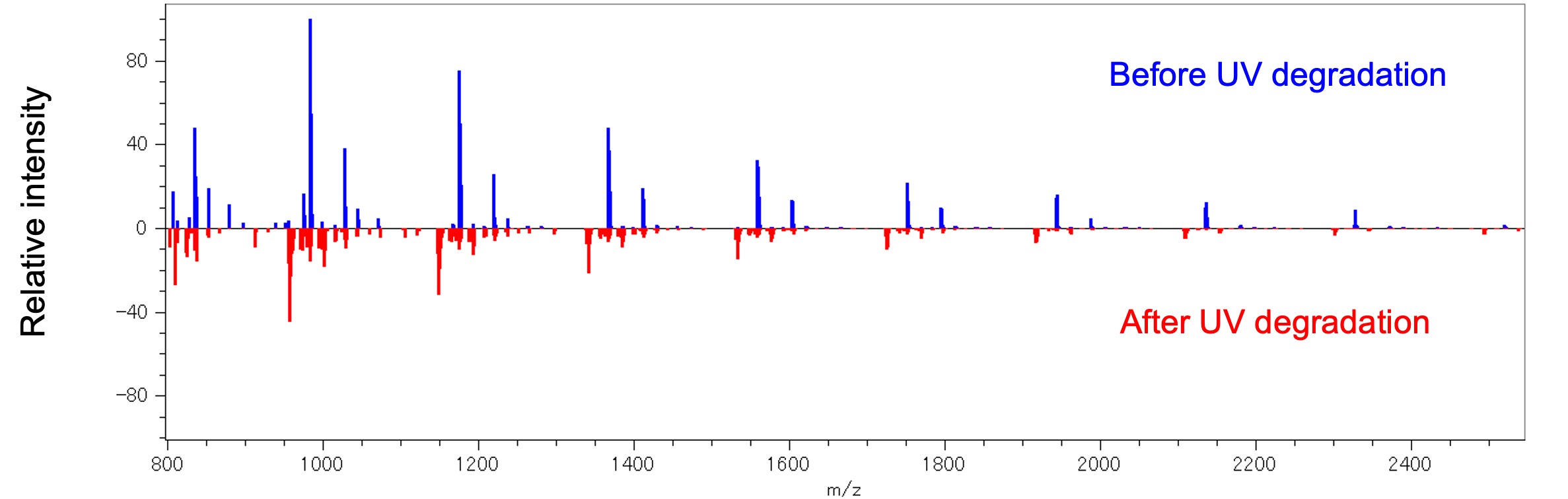
Figure 3 Averaged Mass spectra of PET before(blue) and after(red) UV degradation.
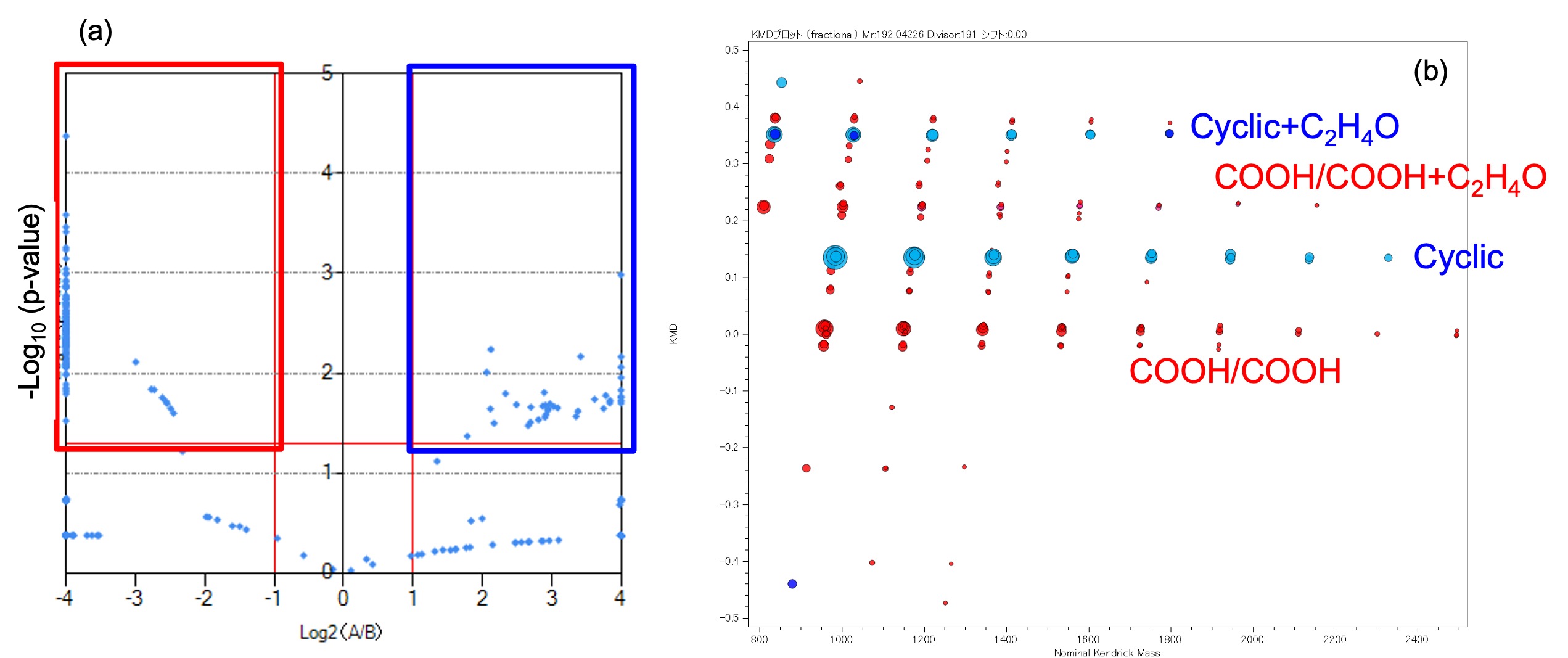
Figure 4 Volcano plot of the differential analysis (a) and KMD plot of the characteristic peaks in the mass spectra before and after UV irradiation.
Summary
In this application note, we showed that the difference analysis function of msRepeatFinder can be used to visualize the differences in the end groups of PET before and after UV degradation. The high mass resolution of JMS-S3000 enables us to visualize the difference of separated end-group, which is useful for polymer analysis.
Solutions by field
Related products
Product category
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.