dry scroll vacuum pump
dry scroll vacuum pump
The dry scroll vacuum pump is an oil-free vacuum pump that compresses and exhausts gases by rotating the orbiting scroll, and evacuates the target device from atmospheric pressure to a vacuum of a few Pa. In a SEM, the dry scroll vacuum pump is used as a backing pump for the turbo-molecular pump (TMP).
The pump is equipped with a fixed scroll and an orbiting scroll. The centers of the fixed scroll and orbiting scroll are slightly off-center, creating a spiral gap (groove) between the two scrolls. The tip seals are attached to the fixed and orbiting scrolls to keep the spiral gap airtight. When rotating the orbiting scroll against the fixed scroll, the tip seals move to rub against the opposing scroll. The gas is drawn in from the inlet port and trapped in the gap between the scrolls. Then, it is carried to the center while being compressed and is pushed to the exhaust port located at the center.
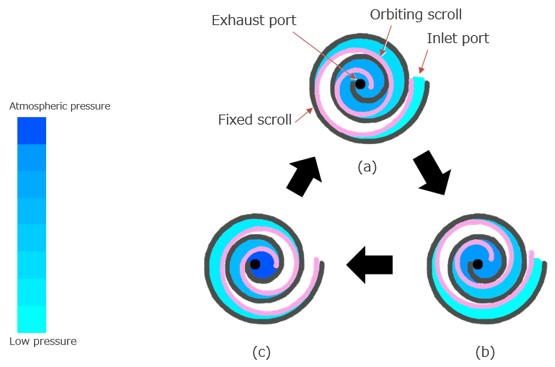
Fig. 1. Schematic of the movement of the orbiting scroll
The orbiting scroll and the fixed scroll are displayed by pink lines and black lines, respectively. Gas drawn in and trapped in the gap created between the two scrolls is displayed by light blue. When the orbiting scroll rotates against the fixed scroll, the gas is carried to the center while being compressed, and then the gas is pushed to the exhaust port located at the center. As the pressure of the gas near the center is higher, it is displayed by dark blue.
As the orbiting scroll rotates, the inlet port opens, and gas is introduced into the gap between the orbiting and fixed scrolls (Fig. 1a, b). As the rotation continues, the orbiting scroll comes close to the fixed scroll and closes the inlet port, and the gap between the two scrolls moves toward the center, carrying the gas to the center (shown in dark blue). Then, the gas is pushed out to the exhaust port located at the center (Fig. 1c). The inlet port then opens, and the next gas is drawn into the pump (Fig. 1a). This sequence of rotations is repeated to continue pumping of gas of the device at the inlet port side.
Fig. 2 illustrates a schematic of the cross section of the orbiting scroll and the fixed scroll. Pink color indicates the orbiting scroll, black does the fixed scroll, and light-green colors indicate the tip seals made of resin. The tip seals are attached to both the fixed scroll and orbiting scroll, which keep the space (gap) created by both the scrolls airtight. Tip seals are consumable and should be regularly replaced with new ones to maintain the performance of the pump.
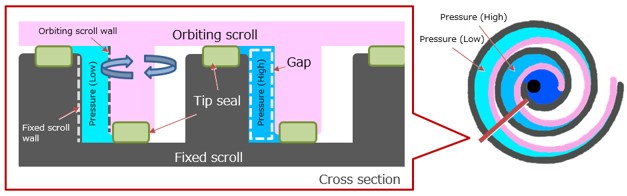
Fig. 2. Scrolls and tip seals
Tip seals attached to the two scrolls contact the opposing scroll to trap gas between the orbiting and fixed scrolls. The pressure of the gas increases toward the center. Gas with higher pressure is shown in dark blue and gas with lower pressure is shown in light blue.
The dry scroll vacuum pump is effectively used in clean rooms of semiconductor manufacturing sites, where air pollution causes a direct problem, and in nuclear facilities and radiation facilities, where waste disposal is difficult. In addition, as oil used in oil-sealed rotary vacuum pumps is flammable, the oil-free scroll pump is highly recommended from the point of safety management.
Term(s) with "dry scroll vacuum pump" in the description
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.




