low-vacuum SEM, Natural SEM, Wet SEM, variable pressure SEM, VP-SEM, Environmental SEM, ESEM
low-vacuum SEM, Natural SEM, Wet SEM, variable pressure SEM, VP-SEM, Environmental SEM, ESEM
The Low vacuum SEM (LV-SEM) is designed to increase the pressure in the specimen chamber between a few Pa and a few 100 Pa (low vacuum range). Some LVSEM instruments can switch the pressure from 2000 Pa to 3000 Pa. LV-SEM is also called Environmental SEM (ESEM), Natural SEM, or VP-SEM (product name).
In an LV-SEM, using the cations which are produced from the residual gas molecules in the specimen chamber by collision with the incident electrons or the electrons emitted from the specimen, electrically negative charging of the specimen surface can be neutralized. This phenomenon allows a non-conductive specimen to be observed without conductive coating while avoiding the influence of charging. In an ordinary SEM, the accelerating voltage has to be lowered to about 1 kV to observe non-conductive specimens without coating. However in the LV-SEM, it is not necessary to lower the acceleration voltage to observe non-conductive specimens. In addition, the LV-SEM is also effective to observe a specimen with a lot of out-gasses.
There is a small hole (orifice) between the bottom of the objective lens and the specimen chamber, but due to the differential pumping system in the LV-SEM the part above the objective lens is safely kept at a high vacuum without the influence of the low vacuum of the specimen chamber.
The ordinary secondary electron detector attached to the specimen chamber cannot be used because it can cause discharge due to a high voltage applied to a scintillator. Thus, a backscattered electron detector or a specialized secondary electron detector adopting a gas amplification system (ESED; environmental secondary electron detector or GSED; gaseous secondary electron detector) is used.
Fig. (a) illustrates the vacuum evacuation system of the LV-SEM. Fig. (b) shows the feature of electric charge neutralization in the LV-SEM.
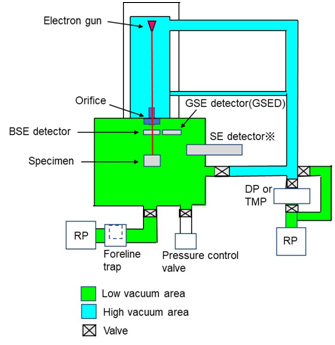
Fig. (a) Schematic of the vacuum evacuation system of an LVSEM.
(The secondary electron detector* cannot be used under a low-vacuum condition.)
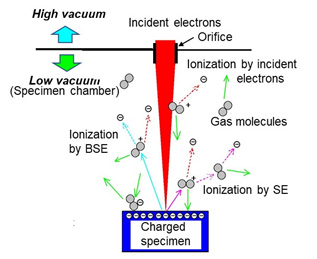
Fig. (b) Feature of charge neutralization.
The residual gas molecules in the specimen chamber become cations by colliding with the incident electrons and the electrons emitted from the specimen. Then, these cations are attracted with the negative charge on the specimen surface. As a result, charging over the specimen surface is neutralized.
Related Term(s)
Term(s) with "low-vacuum SEM, Natural SEM, Wet SEM, variable pressure SEM, VP-SEM, Environmental SEM, ESEM" in the description
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.




