magnetic field lens
magnetic field lens
The magnetic field lens generally used in SEM is a convex lens to converge an electron beam, which utilizes a magnetic field rotationally-symmetric with respect to the optical axis of the beam. This lens is used as the condenser lens and the objective lens of SEM.
Figure schematically shows the vertical cross section of a rotationally-symmetric magnetic field lens. The magnetic field, which is generated by applying a direct electric current to a magnetic excitation coil, is confined within a yoke composed of a soft iron material with a high permeability. Then, a narrow gap is created in a part of the yoke so that the magnetic field is leaked locally and focused to form a rotationally-symmetric magnetic field. The tip portion of the narrow gap or the magnetic poles is called the pole piece. It is made of a high quality material with a high accuracy processing compared to the yoke.
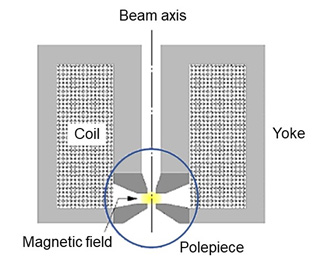
Fig. Example of the vertical cross section of a rotationally-symmetric magnetic lens.
Term(s) with "magnetic field lens" in the description
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.




