spherical aberration
spherical aberration
The spherical aberration causes a spread of electron beams on the focal plane of the objective lens due to the difference in the focal positions between the electron beams passing near the optical axis and the electron beams passing away from the optical axis.
As shown in Fig. 1, the electron beams parallel to the optical axis and passing near the center (near the optical axis) of the objective lens intersect with the optical axis on the focal plane of the lens. However, the electron beams tracking away from the optical axis intersect with the optical axis at positions closer to the lens than the focal plane. This feature results in a spread of the electron beams on the focal plane. The diameter of the spread is given by 2Csα3, where Cs is the spherical aberration coefficient of the objective lens and α is the convergence semi-angle of the electron beam. Cs is a function of the distance between the objective lens and specimen (working distance, WD). As shown in Fig. 2, Cs monotonically increases with increasing WD. The electron probe becomes smallest at a point a little near the lens from the focal plane. The diameter of the electron probe at this point is called "minimum confusion circle" (ds), expressed as ds = Csα3/2.
The SEM instrument equipped with an out-lens objective lens is normally used with a WD of about 10 mm and at an accelerating voltage of 15 kV. In such a case, ds is calculated to be 3.1 nm, when Cs and α are assumed respectively as 50 mm and 5.0 mrad.
※1 L. Reimer, Scanning Electron Microscopy, Springer, Berlin, Germany, p. 24 (1998).
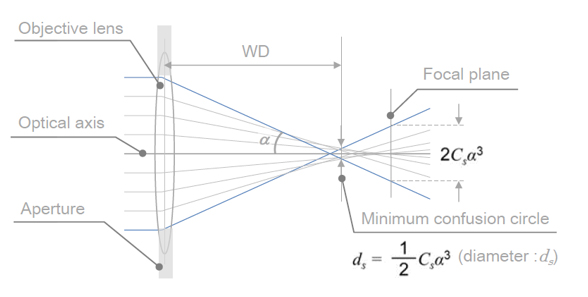
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the spread of electron beams due to the spherical aberration of the objective lens.
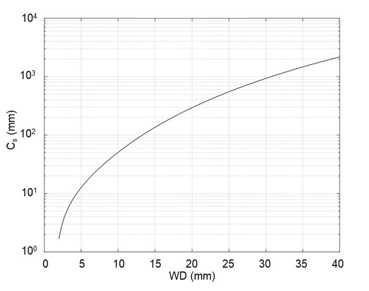
Fig. 2 Relationship between the working distance (WD) and spherical aberration coefficient Cs for an objective lens.
Related Term(s)
Term(s) with "spherical aberration" in the description
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.




