topographic image, BSE topographic image
topographic image, BSE topographic image
"BSE topographic image" means a backscattered electron image which exhibits the topography of a specimen.
This image is obtained by the difference of the output signals from two detectors placed symmetrically against the incident (primary) electron beam. The commonly-used backscattered electron (BE) detector is a semiconductor pair detector that divides an annular semiconductor device into a pair of two segments or into a pair of four segments. For a two-segmented pair detector, when the specimen is inclined with respect to the direction parallel to the detector placement, the contrast due to the specimen inclination is produced. But when the specimen is inclined with respect to the direction perpendicular to the detector placement, no topographic contrast is produced. This principle is shown in Fig. 1(a) and (b). The use of a four-segmented pair detector (Fig. 1(c)) solves this problem. The four-segmented pair detector enables to make a pair detector which combines detector devices A and B, and C and D, and also to create a pair detector which combines A and D, and B and C. By combining these two pair detectors, the images taken with these two detectors are compared, enabling the observation of the topographic contrast of the specimen being inclined in any directions. However it should be noted that, even with the use of only the two-segmented pair detector, the same image taken with the four-segmented pair detector is obtained by mechanically rotating the specimen about 90 degrees to take a topographic image after one topographic image is acquired and then, by comparing these two images.
Adding the output signals from all segments results in the disappearance of the topographic contrast and instead, the compositional image due to the compositional difference in the specimen is obtained.
Fig. 2 shows a set of a BSE topographic image (right) and a BSE compositional image (left) of a diamond grindstone. In the right topographic image, the topographic details (very small difference in topography) of the specimen are observed. In the left compositional image, the topographic contrast disappears; but diamond particles appear dark (black) and the image formed by the compositional contrast is obtained.
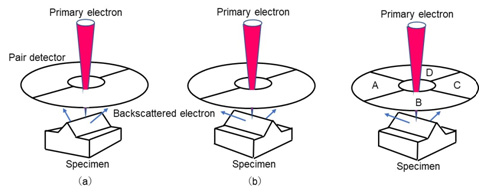
Fig.1 Relations between the directions of placement of pair detectors and the inclination of a specimen
(a) Since the specimen is inclined with respect to the direction parallel to the placement of the two-segmented pair detector, the topographic contrast is produced.
(b) Since the specimen is inclined with respect to the direction perpendicular to the placement of the two-segmented pair detector, no topographic contrast is produced.
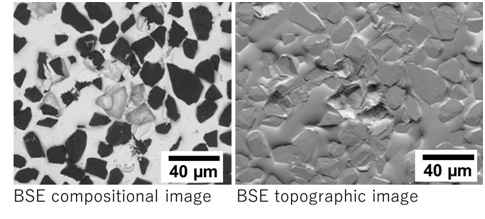
Fig.2 Comparison of BSE compositional image and BSE topographic image of a diamond grindstone, taken at an accelerating voltage of 10 kV.
In the right topographic image, the topographic details (very small difference in topography) are clearly observed. In the left compositional image, diamond particles are seen to be dark (black) because of a small backscattered electron emission coefficient of diamond.
Term(s) with "topographic image, BSE topographic image" in the description
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.




