differential phase contrast imaging
differential phase contrast imaging
Differential phase contrast imaging is a STEM method to visualize an electromagnetic field in a specimen by measuring the deflection of an electron beam due to the field at each beam-scan point. The beam deflection is measured with a segmented detector or a pixelated detector. When a segmented detector composed of four segments is used (see Figure below), the angle and the direction of the beam deflection (beam shift on the detector plane) are measured from the difference between the signal amounts acquired with the two segments opposed to each other.
It is noted that the naming “differential phase contrast” of this imaging method is originated from that the deflection of the electron beam causes the differential or gradient of the phase of the electron wave.
Differential phase contrast imaging is utilized for observations of micrometer to nanometer scale magnetic domains. In recent years, this imaging method has been applied to analysis of electric fields, and the electric field at the atomic scale has been observed using a transmission electron microscope equipped with a Cs corrector.
Schematics of a segmented detector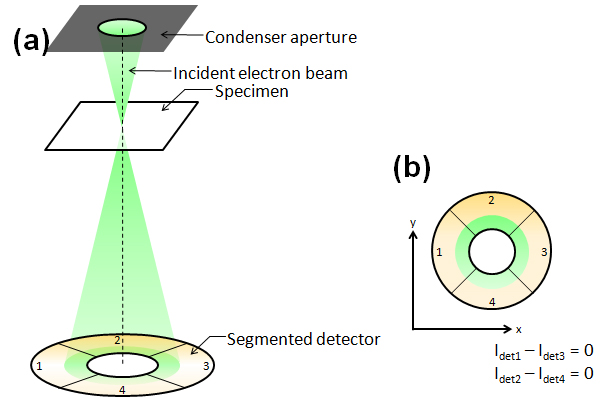
Fig.(a) Schematic of detection of the electron beam deflection in a specimen using a segmented detector (In case that the electron beam is not deflected by the specimen).
Fig.(b) A STEM detector in this case is composed of four segments. The shadow of the condenser aperture is projected onto the detector.Top view of the detector and the electron beam seen along the incident beam direction. The signal amounts are the same for the four segments. Thus, there is no difference between the signal amounts acquired from the two segments opposed to each other.
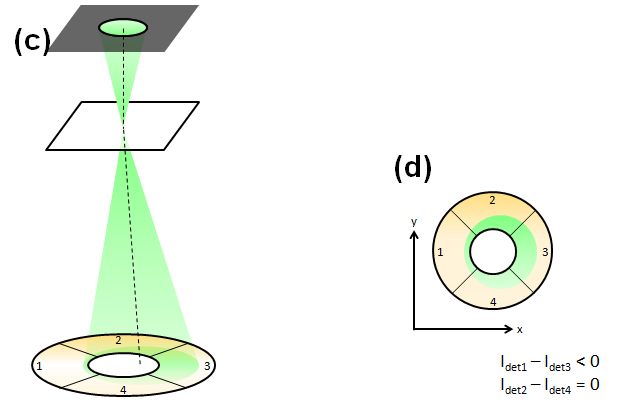
Fig.(c) Schematic of detection of the electron beam deflection in a specimen using a segmented detector (In case that the electron beam is deflected by a specimen).
Fig.(d) Top view of the detector and the electron beam seen along the incident beam direction. When the beam is deflected in the positive direction of the x axis, the signal amounts obtained by subtracting Idet3 from Idet1 becomes a negative value, whereas there is no difference between the signal amounts Ide2 and Idet4. As a result, the beam is found to be deflected in the positive direction of the x axis, and the deflection angle is measured from the absolute value of the signal difference.
It is noted that the naming “differential phase contrast” of this imaging method is originated from that the deflection of the electron beam causes the differential or gradient of the phase of the electron wave.
Differential phase contrast imaging is utilized for observations of micrometer to nanometer scale magnetic domains. In recent years, this imaging method has been applied to analysis of electric fields, and the electric field at the atomic scale has been observed using a transmission electron microscope equipped with a Cs corrector.
Schematics of a segmented detector

Fig.(a) Schematic of detection of the electron beam deflection in a specimen using a segmented detector (In case that the electron beam is not deflected by the specimen).
Fig.(b) A STEM detector in this case is composed of four segments. The shadow of the condenser aperture is projected onto the detector.Top view of the detector and the electron beam seen along the incident beam direction. The signal amounts are the same for the four segments. Thus, there is no difference between the signal amounts acquired from the two segments opposed to each other.

Fig.(c) Schematic of detection of the electron beam deflection in a specimen using a segmented detector (In case that the electron beam is deflected by a specimen).
Fig.(d) Top view of the detector and the electron beam seen along the incident beam direction. When the beam is deflected in the positive direction of the x axis, the signal amounts obtained by subtracting Idet3 from Idet1 becomes a negative value, whereas there is no difference between the signal amounts Ide2 and Idet4. As a result, the beam is found to be deflected in the positive direction of the x axis, and the deflection angle is measured from the absolute value of the signal difference.
Term(s) with "differential phase contrast imaging" in the description
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.




