negative staining
negative staining
Negative staining is one of electron staining techniques. This technique leaves heavy metals at the gaps in a specimen and on the supporting film at the surrounding regions of the specimen. Negative staining enables enhancement of the TEM image contrast.
An aqueous solution of viruses or purified proteins, etc. is dropped onto a supporting film, and then excessive water is removed from the specimen with a filter paper. Immediately after the removal of excessive water, a staining solution containing heavy metals (uranium acetate, phosphotungstic acid, etc.) is dropped onto the specimen. Then, water is removed from the specimen with a filter paper to dry the specimen, leaving the heavy materials at the gaps and on the supporting film at the surrounding regions of the specimen. As a result, these regions appear dark due to strong scattering of incident electrons, and the morphology of the specimen is elucidated. Since the specimen itself is not stained, this technique is termed "negative" staining.
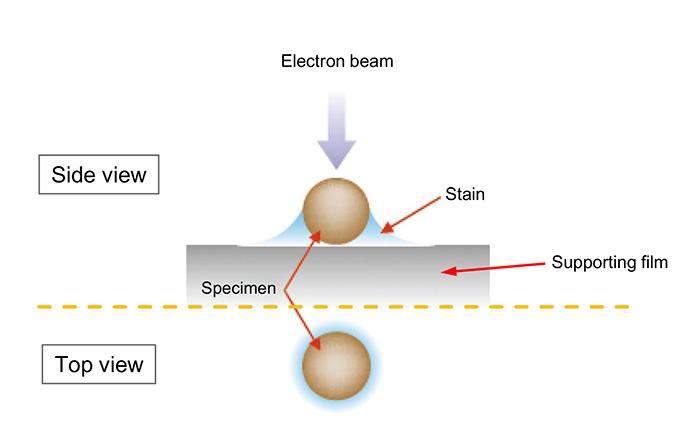
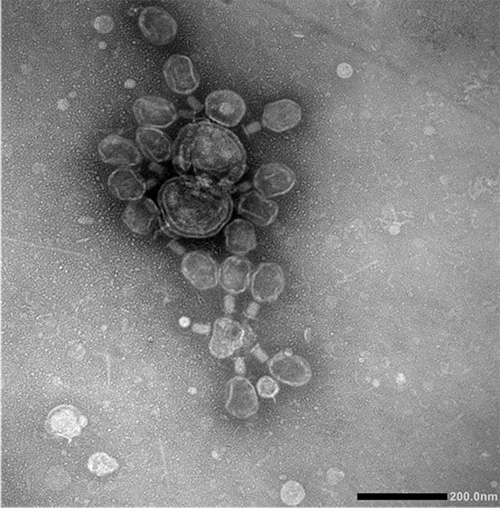
TEM image of negatively stained bacteriophage T4
Related Term(s)
Term(s) with "negative staining" in the description
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.




