electron staining
electron staining
Electron staining means to adsorb heavy metals of a high scattering power to biological specimens and polymer materials, which are composed of light elements with a small scattering power for electrons, in order to enhance the TEM image contrast of these specimens.
In the case of a biological specimen, uranium (uranyl acetate) and/or lead (lead citrate) are adsorbed to proteins, lipids, polysaccharides and nucleic acids in the specimen. As a result, organelles such as nuclei (chromatins), mitochondria and ribosomes in the cells, and cell membranes, which are composed of these components are stained, whereas other regions remain unstained. Consequently, the TEM images of these organelles can be observed with high contrast. Fig. 1 shows an observation example of intestinal epithelial cells.
Mitochondria and cell membranes with high protein density are well stained and appear dark.
For polymer materials, osmium (osmium tetroxide OsO4) and/or ruthenium (ruthenium tetroxide RuO4) are mainly used as staining agents. Fig. 2 shows an example of a cross-sectional polyethylene with a sheet-like structure stained with ruthenium. In this example, the amorphous regions exist outside the crystalline polyethylene. Since RuO4 penetrates and is adsorbed only into the amorphous regions of the polyethylene, these regions are preferentially emphasized as dark in the TEM image.
As described above, those heavy metals adsorbed to specific regions of the specimen strongly scatter the incident electrons, and the contrast in TEM images is enhanced.
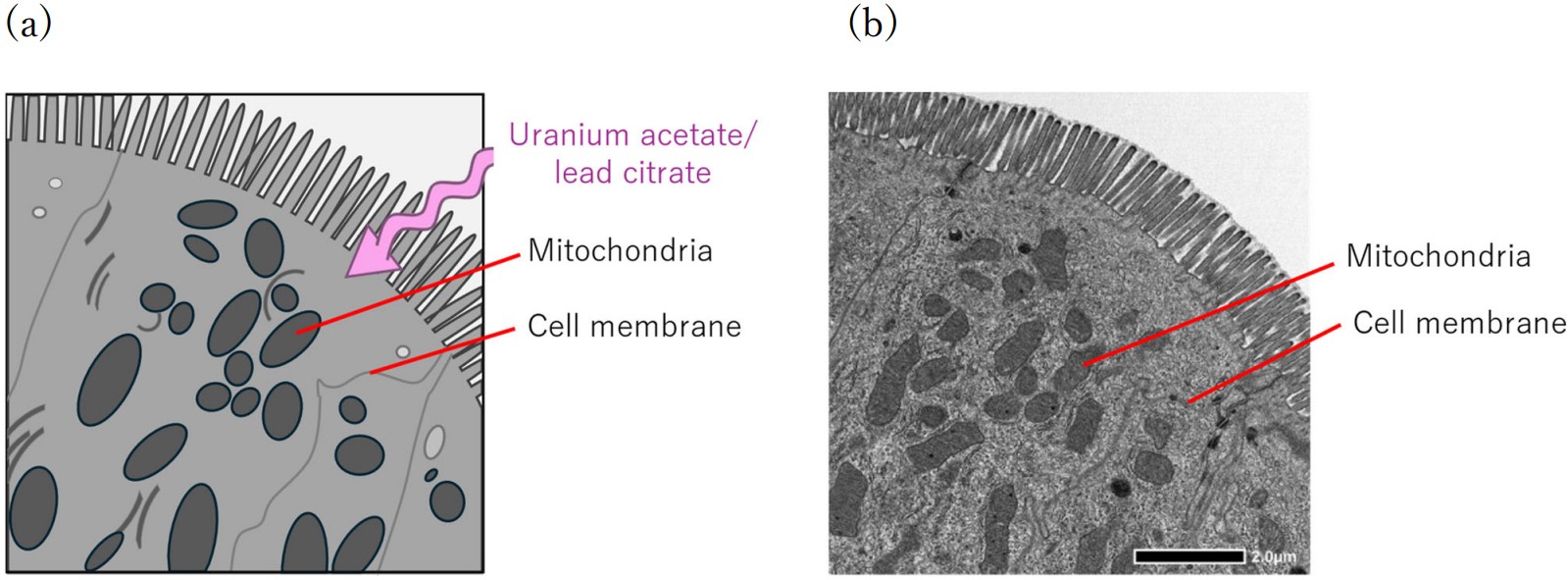
Fig. 1. (a) Schematic illustration of contrast enhancement by electron staining. Uranium and lead are adsorbed to proteins, lipids, polysaccharides and nucleic acids in the cells. Thus in this figure, mitochondria and cell membranes exhibit higher contrast against their surrounding regions. (b) TEM image of the epithelial cells of a small intestine of a rat stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate. Mitochondria and cell membranes are stained and clearly observed as dark.
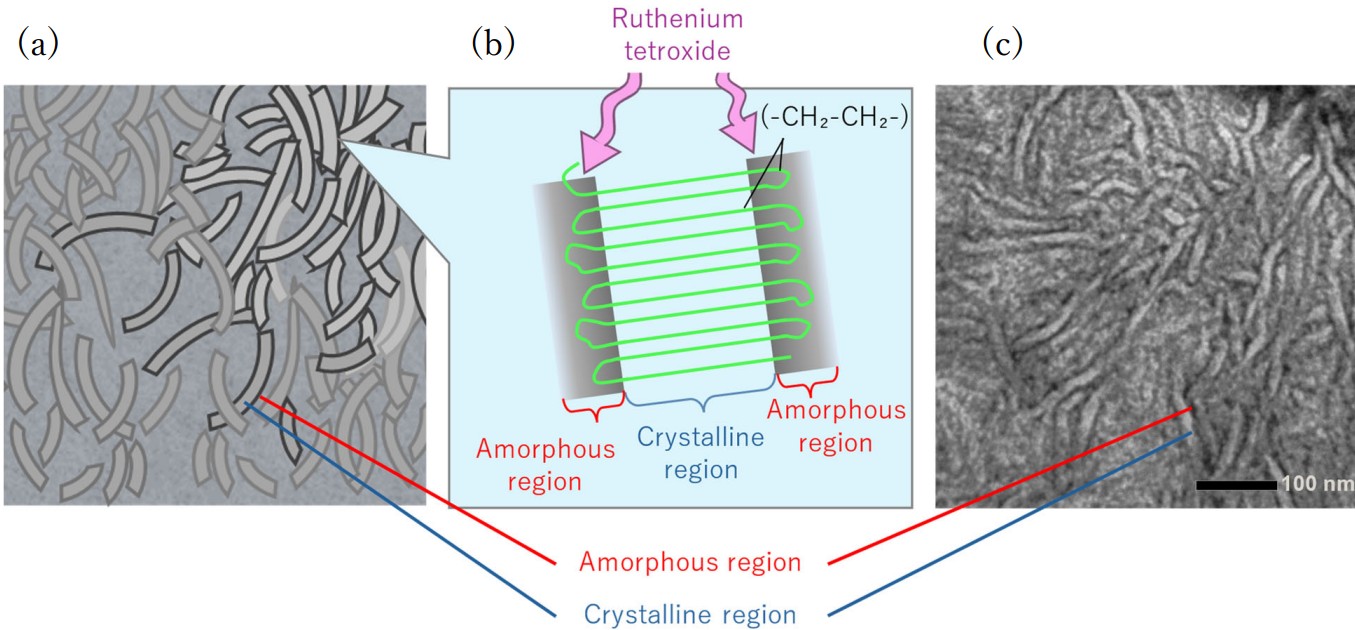
Fig. 2. (a) Schematic illustration of electron staining for the amorphous regions of polyethylene using RuO4. The amorphous regions on the surface of polyethylene are stained with ruthenium and observed dark, whereas the crystalline regions remain unstained and are observed light. (b) Schematic illustration of the crystalline regions inside the polyethylene and the amorphous regions on its surface. (c) TEM image of the polyethylene stained with RuO4. The amorphous regions on the surface are stained and clearly seen dark.
Related Term(s)
Term(s) with "electron staining" in the description
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.




