Young fringe
Young fringe
When a beam exiting from a point source is passed through two slits, two waves exiting from the slits interfere with each other, resulting in formation of a fringe pattern. This fringe pattern is called "Young fringe(s)." As the distance between the two slits is smaller, the period of the Young fringes becomes larger. The Young fringe pattern is used to easily determine the resolution (information limit) of a TEM. In an actual experiment, two overlapping HREM images of an amorphous specimen are taken by shifting the electron beam within the exposure time to take one-frame CCD image, the images are acquired into a computer, and finally the diffraction pattern is obtained by FFT processing of the images. The Young fringes appear to be superposed on the diffraction pattern of the amorphous specimen. The information limit can be measured from the angular position (the radius of the Young fringe pattern) where the Young fringes disappear. The beam shift is chosen so that the Young fringes are easily seen with an appropriate separation.
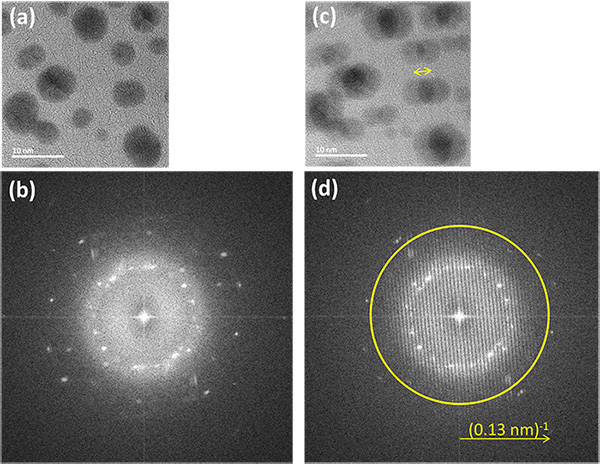
(a) High-resolution TEM image of Au particles on a carbon thin film.
(b) Fourier transform pattern of (a).
(c) High-resolution TEM image taken by shifting the field of view using the deflector system. The relative shift and shift direction of the image are indicated by a yellow arrow.
(d) Fourier transform pattern of (c). Fringes (Young fringes) corresponding to the relative shift are seen. The information limit can easily be measured from the angle at which the fringes disappear (indicated by a yellow circle).
Related Term(s)
Term(s) with "Young fringe" in the description
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.




