tomography
tomography
A reconstruction method of three-dimensional internal structures through computer image processing of many projection images, which are acquired from sequential tilt-series images of a specimen. "Tomography" utilizes the principle of X-ray CT (computerized tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) for a TEM image, which are broadly used in the medical field. When the analytical polepiece is used, 121 images sequentially acquired at angles from ±60° to +60° in steps of 1° are used for three-dimensional reconstruction. Various techniques for positional adjustment of each image have been devised by several TEM manufacturers. To avoid artifacts due to the missing cone, a specimen holder that allows image acquisition at tilt angles from -80° to +80°, and a specimen holder that enables image acquisition from all directions, has been developed. Furthermore, a cold stage that can cool biological, high polymer and organic substances with liquid helium is available. In tomography using STEM, focal shifts do not occur with the specimen position (occur for TEM), and also the use of the HAADF method enables us to remove diffraction contrast in a crystalline specimen. However, the disadvantages of STEM tomography are a long image-acquisition time, and unavoidable radiation damage and contamination.
Sperm
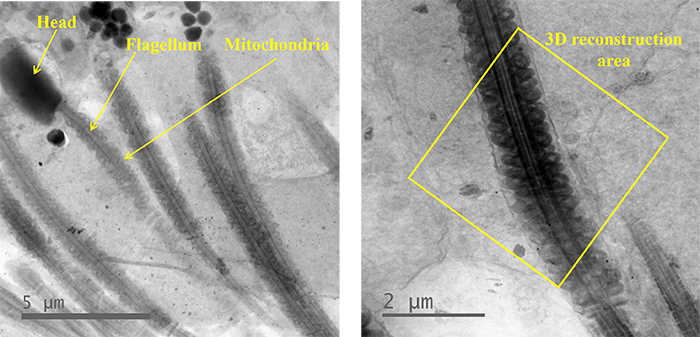
Fig. 1 TEM images of sperms.
Left) A head, a flagellum and mitochondria of a sperm are indicated by yellow lines.
Right) The mid-piece of a sperm where mitochondria stood in a line (inside a yellow frame). Tilt-series images were taken from this mid-piece, and then, 3D reconstruction was performed.
Instrument: JEM-1000EES (at Research Center for Ultra-High Voltage Electron Microscopy, Osaka University) Accelerating voltage: 1000 kV
Orthogonal views of 3D reconstruction image
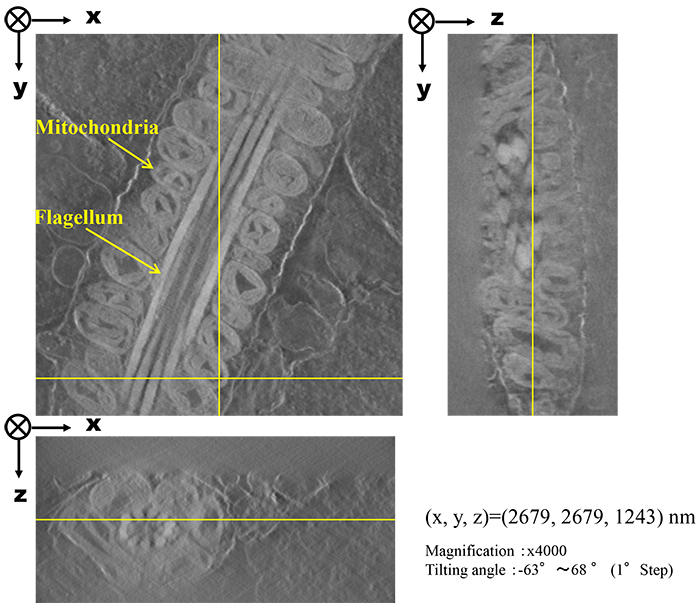
Fig. 2 3D-reconstructed cross-section image of the mid-piece of a flagellum. Mitochondria are seen to stand on the flagellum.
3D image (Volume Rendering) by Segmentation
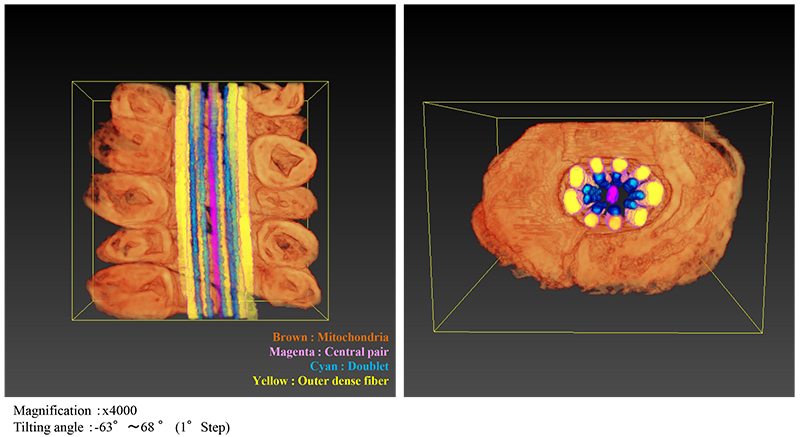
Fig. 3 3D image of the mid-piece of the flagellum, where each structural part was color-segmented (Left: Vertical cross section. Right: Lateral cross section).
MOVIE
Different colors were given for each mitochondrion. Each mitochondrion is seen to be well separated.
◆Click the "replay" button in the box above, and the movie will start (for 18 seconds)◆
Related Term(s)
Term(s) with "tomography" in the description
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.




