Debye-Waller factor
Debye-Waller factor
The Debye-Waller factor expresses the magnitude of thermal vibrations (lattice vibrations) of atoms, called B factor. B is given by 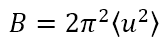 and expressed in units of Å2, where
and expressed in units of Å2, where 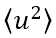 is the mean square amplitude of an atom due to thermal vibration. The angular dependence of scattering amplitude (θ or k dependence) of an atom for X-rays, neutrons and electrons, is given by the following equation.
is the mean square amplitude of an atom due to thermal vibration. The angular dependence of scattering amplitude (θ or k dependence) of an atom for X-rays, neutrons and electrons, is given by the following equation.
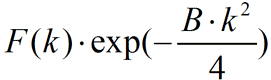
Here, F is the atomic scattering amplitude without thermal vibration, and 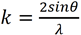 (λ: the wavelength of a quantum wave, θ : half angle of the scattering angle). Due to the B factor, the amplitude of the scattering (Bragg reflection) is attenuated at high scattering angles (at θ or large k). As the temperature of a specimen is lowered, thermal vibrations are reduced and the value of B becomes small. As a result, the decrease in the amplitude of high order reflections is suppressed and the intensities of those reflections are increased, making them easier to observe.
(λ: the wavelength of a quantum wave, θ : half angle of the scattering angle). Due to the B factor, the amplitude of the scattering (Bragg reflection) is attenuated at high scattering angles (at θ or large k). As the temperature of a specimen is lowered, thermal vibrations are reduced and the value of B becomes small. As a result, the decrease in the amplitude of high order reflections is suppressed and the intensities of those reflections are increased, making them easier to observe.
Related Term(s)
Term(s) with "Debye-Waller factor" in the description
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.




