high-resolution electron microscopy, HREM
high-resolution electron microscopy
A technique of transmission electron microscopy to obtain a high-resolution electron microscope (HREM) image, that is, a lattice image or a crystal structure image, from a thin specimen by utilizing wave interference between transmitted and diffracted waves.
An image which corresponds to the crystal structure is obtained by precisely adjusting the incident beam orientation to a zone axis of the crystal and by setting the focus of the objective lens to Scherzer focus. The spatial resolution of the image depends on the coefficient Cs of the objective lens and the accelerating voltage of the incident beam.
When a TEM not equipped with a Cs corrector is used, a HREM image or a crystal structure image is taken at the Scherzer focus condition (under-defocus) to optimize the effects of the spherical aberration of and the defocus of the objective lens.
When a TEM equipped with a Cs corrector is used, the original positive value of Cs can be adjusted to zero or a negative value. Thus, the focus condition for imaging is not limited by the Scherzer focus condition. The HREM image can be taken under an appropriate focus condition where the image contrast is optimal by a visual check and by prior computer simulations while changing the focus condition.
The figures below show HREM images taken with a TEM equipped with a Cs corrector, in which the focus was set to an under-focus condition and an over-focus condition.
When the specimen is thick (more than 10 nm), the image obtained does not well correspond to the crystal structure due to the dynamical diffraction effect. In HAADF-STEM images, the dynamical diffraction effect is suppressed and the reliability of the image interpretation is higher.
HREM images are used for analysis of crystal structures and lattice detects, including interface structures.
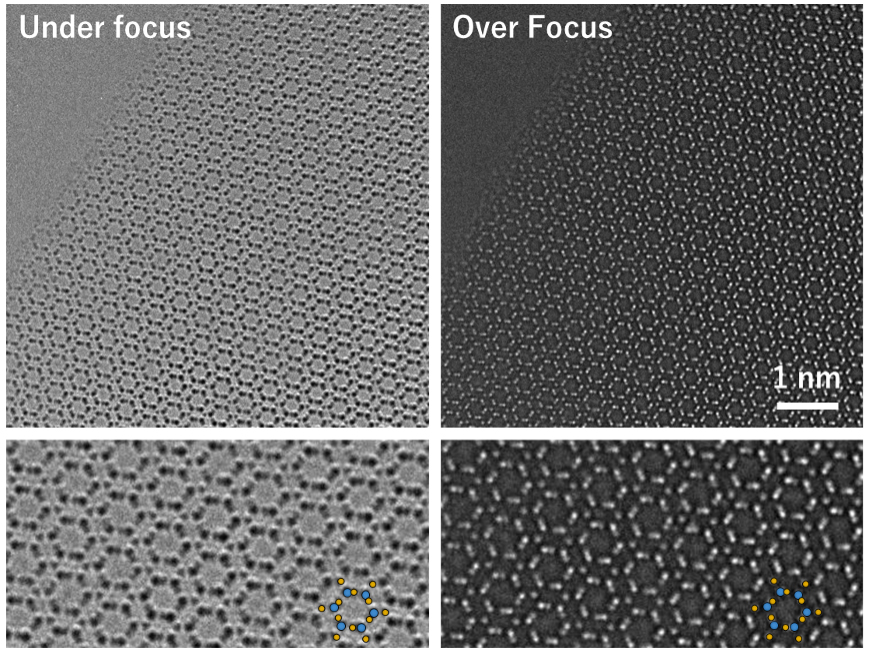
Fig. HREM images of β-Si3N4 taken at the [0001] incidence with a TEM equipped with a Cs corrector, and their partial enlarged images (lower two images). These were taken from a very thin region at the edge of the specimen. Blue circles and yellow circles in the enlarged images (lower) indicate respectively silicon atoms and nitrogen atoms. Bright or dark contrast is reversed between the images of under-focus and over-focus. The upper left part in each top image is a vacuum region without specimen.
Related Term(s)
Term(s) with "high-resolution electron microscopy" in the description
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.




