grid
grid
A "grid" is a plate of a metal, etc. with a diameter of 3 mm and a thickness of 20 to 50 μm, which supports a specimen for TEM observation. Various grids such as a square-, a circular-, and a slit-grid, are available. They are selectable depending on observation requirements. The material of the grid is copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), gold (Au) or titanium (Ti), etc. In elemental analysis, a grid which does not contain the elements to be analyzed, is used.
- Reticular grid
The grid is most commonly used. Fragmented specimens are placed or pasted on the grid. For viruses or small particles, a supporting film is pasted on the grid and then, the specimen is placed on it. - Single hole grid
The grid is used to observe a wide area of specimen without disturbance of the mesh of a reticular grid. Thus, it is suitable for observation at ultra-low magnifications. - Reference grid
The grid is conveniently used at repeated observation of the same field because the marks (letters) to memorize the observation position are prepared on the grid. - FIB grid
The grid is used to attach a thin film specimen prepared by FIB, to the heads of the grid.
Examples of grid
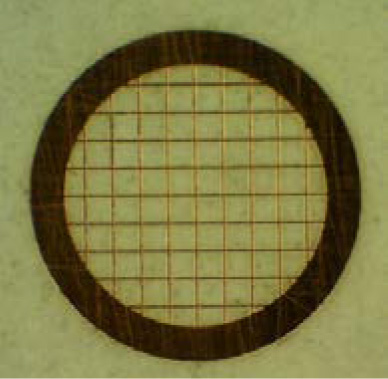
1. Square grid

2. Single hole grid
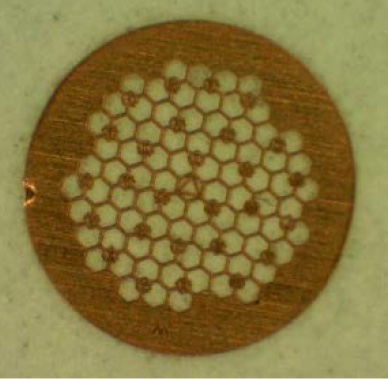
3. Reference grid

4. FIB grid
Related Term(s)
Term(s) with "grid" in the description
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.




