Analysis of dioxins in food and feed by using New JMS-TQ4000GC and software "TQ-DioK"
MSTips No.339
MSTips No.339
Dioxins are considered as persistent organic pollutants (POPS) due to their presence in the environment and the health risks associated.
A World Health Organization (WHO) study has demonstrated the health risks (carcinogenic and immunotoxic) when population are exposed to them. In addition, dioxins have been regulated by the Stockholm convention on POPs in May 2001. In particular, 17 substances have to be monitored. The highest toxic compound is the 2378-TeCDD. Currently, dioxins analysis can be done not only using GC-HRMS but also with GC-MS/MS according to European commission regulation (EU589/2014). Recently, JEOL has developed a new GC-triple quadrupole MS (JMS-TQ4000GC) and a new dedicated dioxins analysis software called TQ-DioK.
In addition, we have already introduced dioxins analysis result by using standard sample (MSTips338). In this study, we evaluated JMS-TQ4000GC with TQ-DioK using food samples.
Experimental
Standard Sample
The standard PCDDs and PCDFs (PCDD/Fs) solutions (DF-IS-A, DF-ST-A and DF-LCS-C from WELLINGTON Laboratories (CANADA)) were used for the measurement. Then, the range of concentrations for calibration curve was prepared from 0.025 to 1 pg/µL (OCDD and OCDF: 0.05 - 2 pg/µL) (Table 1).
Table 1) Concentrations of each calibration point
| PCDD/Fs | Concentration 12C (pg/µL) | Concentration 13C (pg/µL) |
|---|---|---|
| Cal. 1 | 0.025 (OCDD and OCDF 0.05) | 1.25 (OCDD and OCDF 2.5) |
| Cal. 2 | 0.05 (OCDD and OCDF 0.1) | 1.25 (OCDD and OCDF 2.5) |
| Cal. 3 | 0.1 (OCDD and OCDF 0.2) | 1.25 (OCDD and OCDF 2.5) |
| Cal. 4 | 0.25 (OCDD and OCDF 0.5) | 1.25 (OCDD and OCDF 2.5) |
| Cal. 5 | 0.5 (OCDD and OCDF 1.0) | 1.25 (OCDD and OCDF 2.5) |
| Cal. 6 | 1.0 (OCDD and OCDF 2.0) | 1.25 (OCDD and OCDF 2.5) |
GC-MS/MS measurement conditions
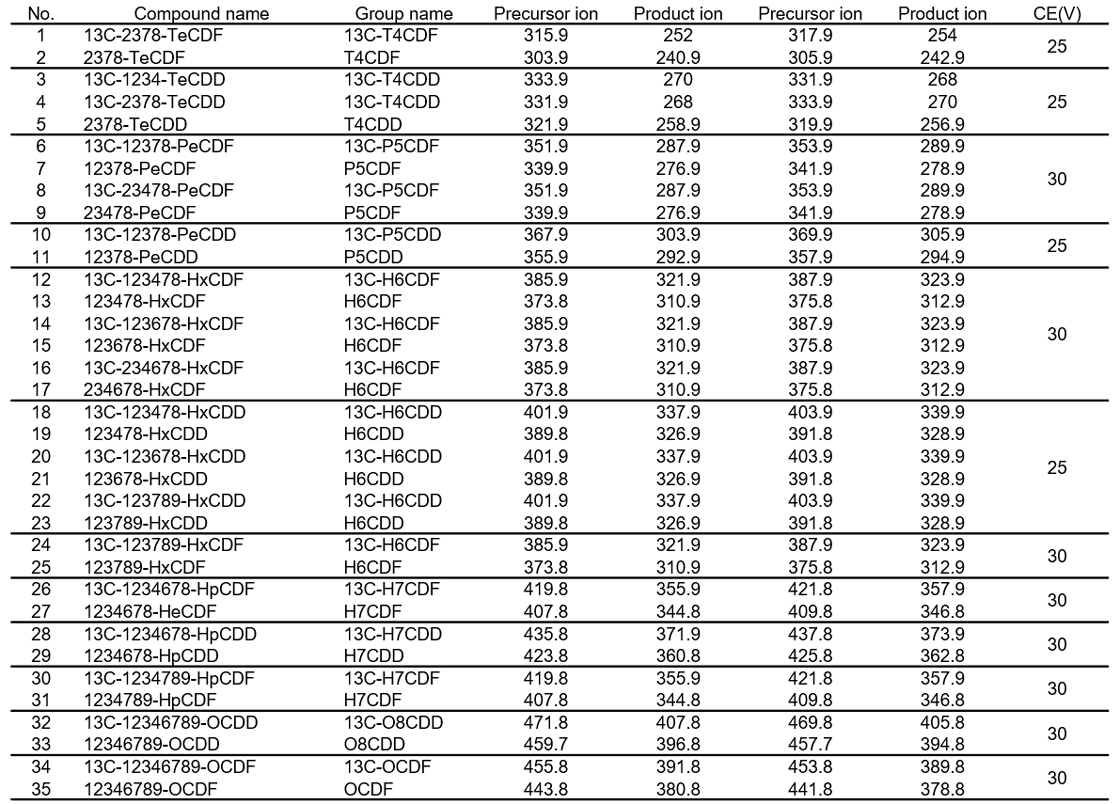
Table 2 shows the GC-MS/MS measurement conditions. A split/splitless inlet was used, and nitrogen gas was applied as collision gas. Table 3 shows the precursor ion, product ion and collision energy (CE). Two specific precursor ions from each non-labeled compound and labeled compound were set.
Table 2) GC-MS/MS measurement conditions
| [GC] | |
|---|---|
| Inj. volume: | 2µL |
| Inlet type: | Split/Splitless |
| Inj. mode: | Splitless (Purge time 1 min, Purge flow 20 mL/min) |
| Inlet temp.: | 280 °C |
| Column flow: | 1 mL/min (Constant flow) |
| GC column: | DB- 5MS (60 m x 0.25 mm, 0.25 µm) |
| Oven temp.: | 120 °C (3 min) → 50 °C/min → 200 °C (0 min) → 4 °C/min → 300 °C (5 min) → 40 °C/min → 325 °C (5 min) |
| [MS] | |
|---|---|
| MS: | JMS-TQ4000GC |
| Ionization: | EI+ |
| Acquisition mode: | High sensitivity mode |
| IS temp.: | 280 °C |
| ITF temp: | 280 °C |
Table 3) Precursor ion, product ion and CE
Result
Dioxins in “Grass”, “Egg” and “Pork fat” samples were extracted and purified using the Büchi “SpeedExtractor E-914” and the MIURA "GO-4 HT”. After then, samples were measured by both GC-HRMS and GC-MS/MS, and the obtained results were compared. Also, ratio of the selected two transition product ions was confirmed before calculation of quantitative value.
Ratio of selected two transition product ion
The tolerance of ratio of the selected two transitions product ions for average value or calculated value should be < ±15% according EU regulation(EU2017/644). Average value of each compound was calculated using all calibration points. Those ratios for each compound were within ±15% of average value(Fig. 1).
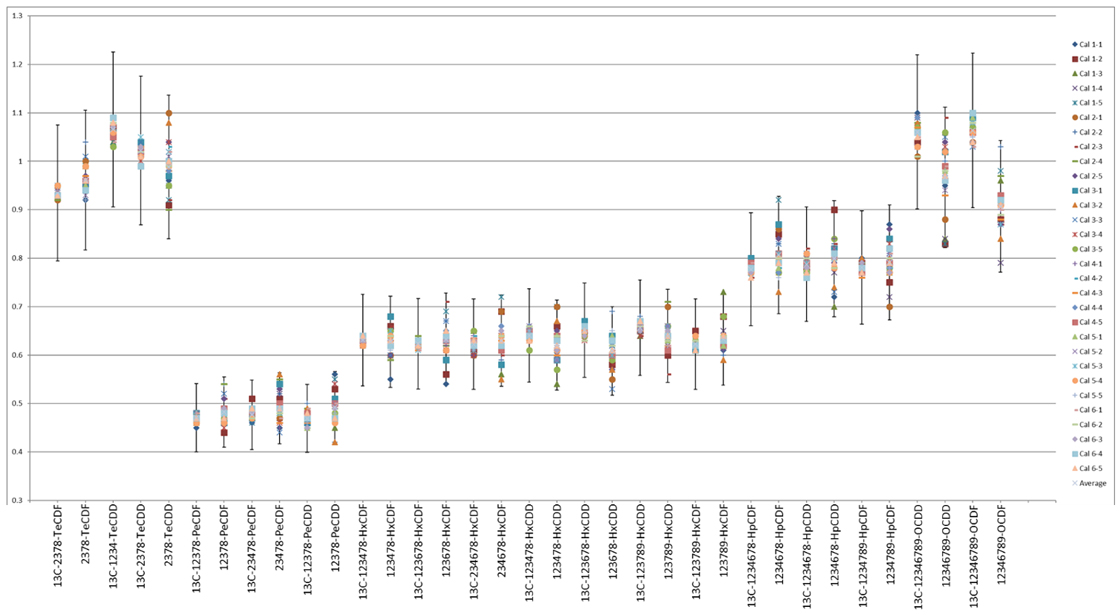
Fig. 1 Ratios of selected two transition product ions
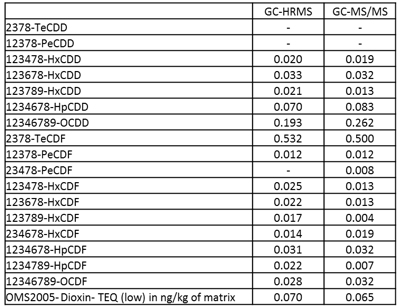
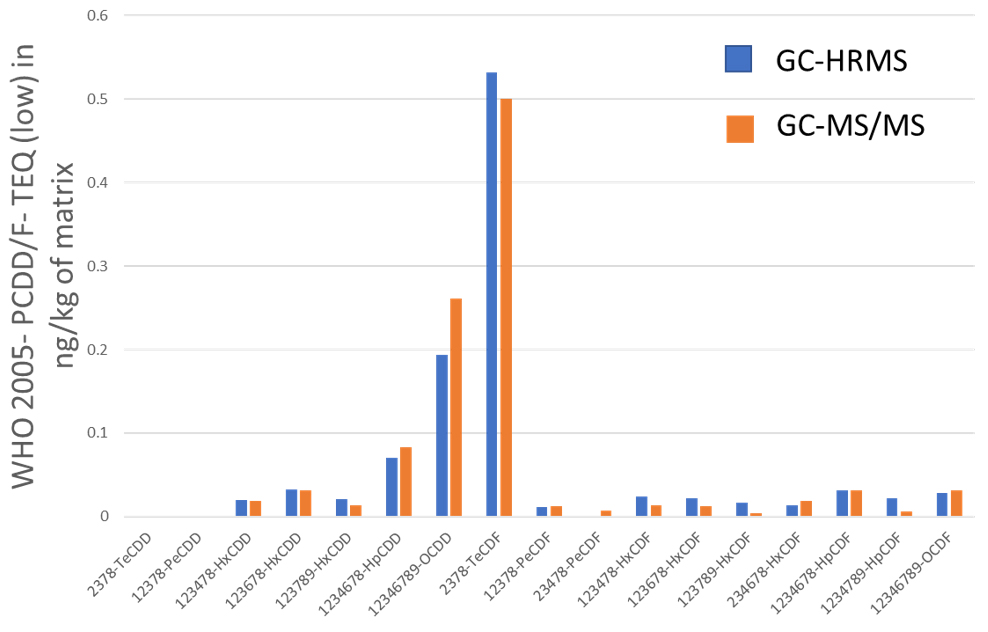
Comparison of GC-HRMS and GC-MS/MS systems
Grass, Egg and Pork fat were measured by both GC-HRMS and GC-MS/MS systems. Toxic Equivalent Quantity (TEQ) was calculated using Toxic Equivalency Factors (TEF) based on WHO 2005. Fig. 2 shows the comparison data of Grass, Egg and Pork fat. The TEQ calculated for each compound by GC-MS/MS was similar to GC-HRMS result. By consequence the difference between the Dioxin OMS-TEQ in ng/kg of matrix calculated by GC-HRMS and the GC-MS/MS TEQ(dioxins) was within 20%.
(A) Grass
(B) Egg
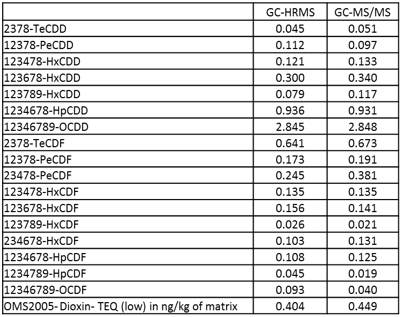
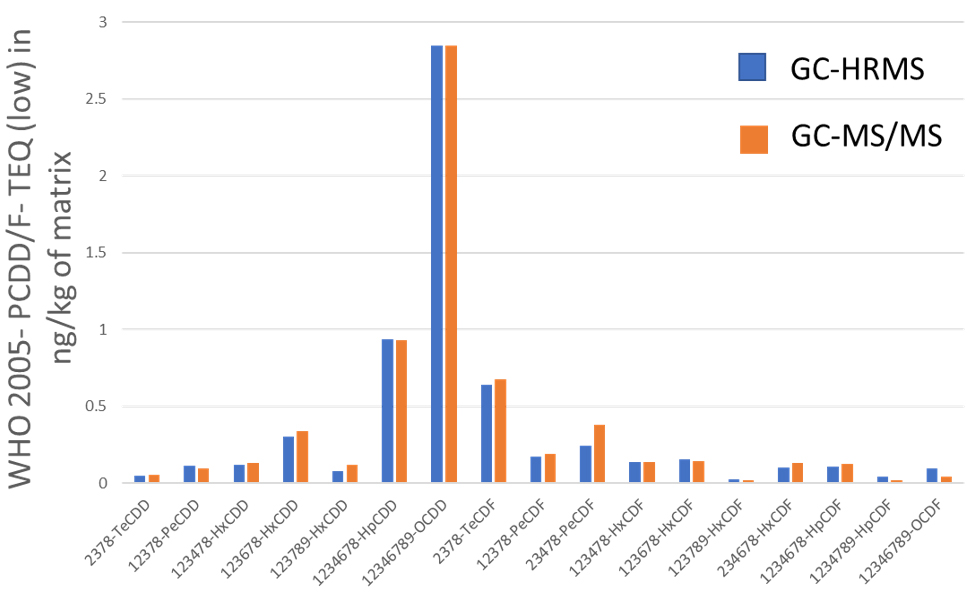
(C) Pork fat
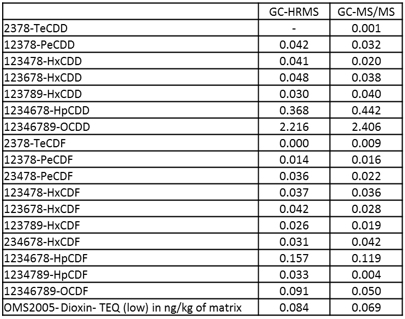
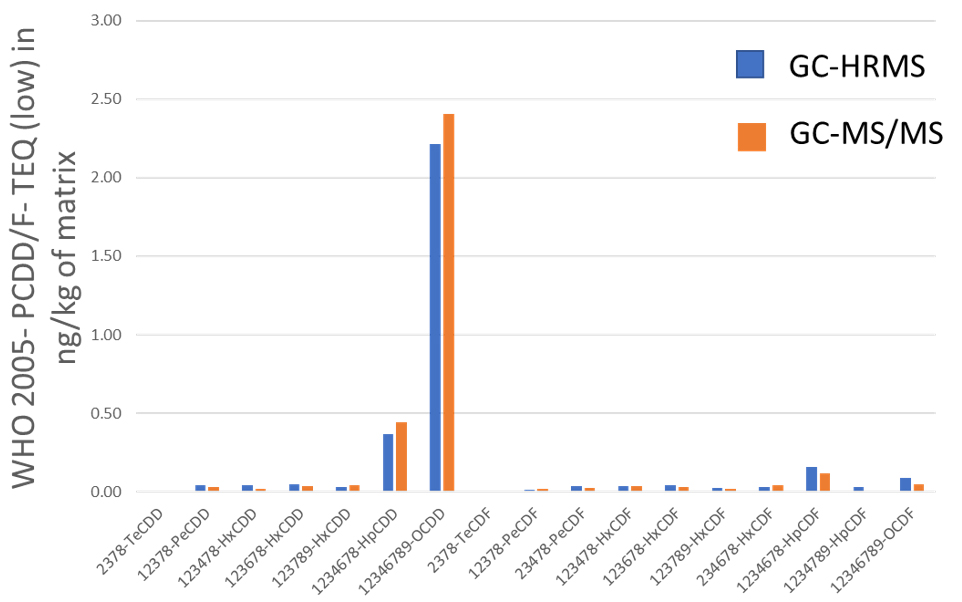
Fig. 2 Comparison data by GC-HRMS and GC-MS/MS of Grass(A), Egg(B) and Pork fat(C).
Conclusion
The JMS-TQ4000GC was evaluated for analysis of dioxins in food and feed. The results have shown that the obtained TEQ(dioxins) of JMS-TQ4000GC was similar to GC-HRMS. This result shows that the JMS-TQ4000GC is a powerful tool for analyzing dioxins.
Acknowledgement
All measurements and evaluation about the basic performances of JMS-TQ4000GC were organized and tested by the ‘LABoratoire d’Etude des Résidus et Contaminants dans les Aliments (LABERCA), Nantes, France.
Related products
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.

