Target analysis of msFineAnalysis AI Ver.2
① Highly sensitive and rapid analysis of polymer additives
MSTips No. 478
Introduction
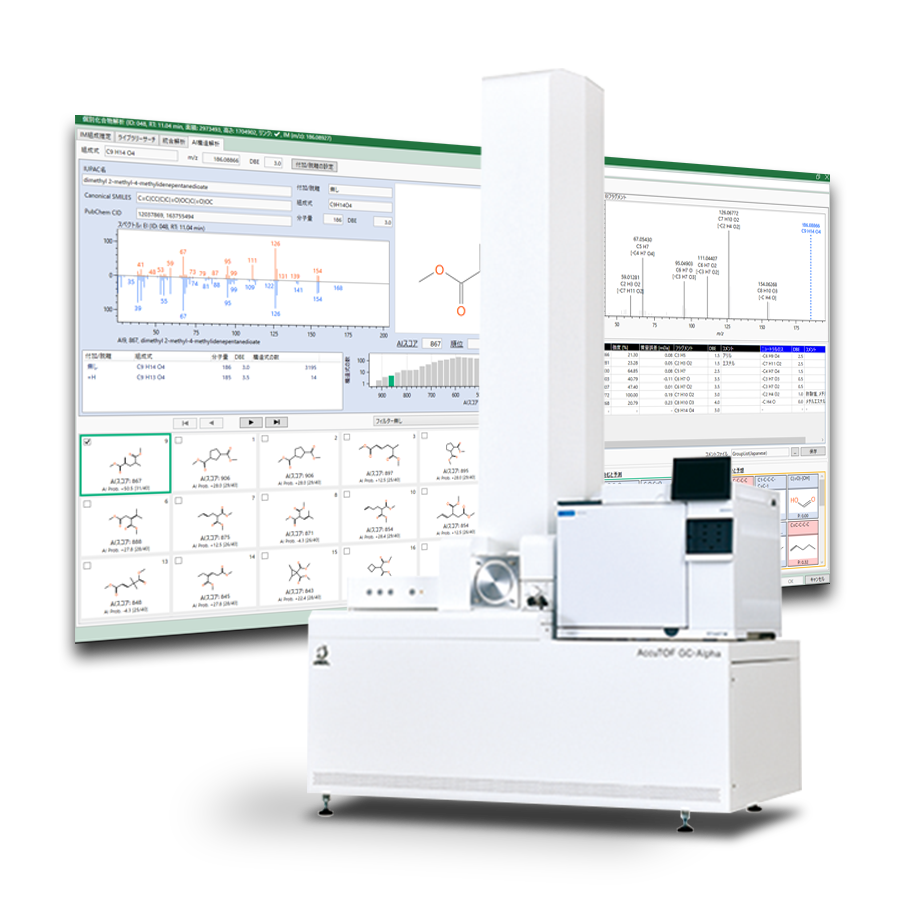
The unknown compounds structure analysis software “msFineAnalysis AI” can obtain highly accurate qualitative information by using integrated analysis that combines the EI (Electron Ionization) method with the SI (Soft Ionization) method. In addition, AI structural analysis can derive the structural formula of compounds not registered in the NIST library. Until now, it has been used for non-target analysis based on deconvolution peak detection, but Ver.2 has added a target analysis function that can determine the presence of specific compound with high sensitivity and speed.
This function detects peaks from extracted ion chromatograms (EICs) based on information such as the molecular formulas and mass spectra of pre-listed compounds. Furthermore, the detected peaks are judged using retention time (RT), retention index (RI), accurate mass analysis of molecular ions and fragment ions, isotope patterns, and mass spectrum similarity. For compounds not registered in the NIST library, the accuracy of judgment can be improved by AI structural analysis.
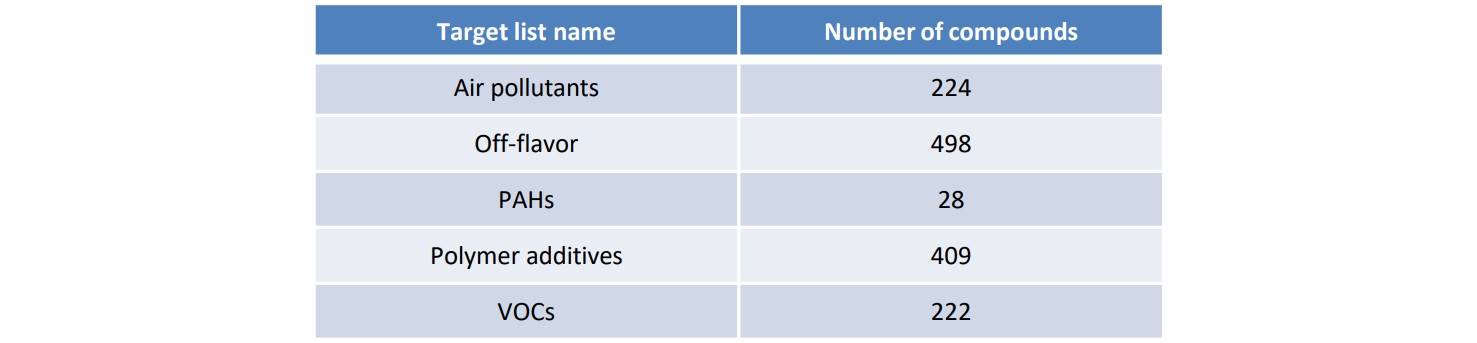
Table 1 shows the software preset target list and the number of compounds. In this MSTips, we will introduce an application using "Polymer additives".
Table 1 Preset target list
Experiment
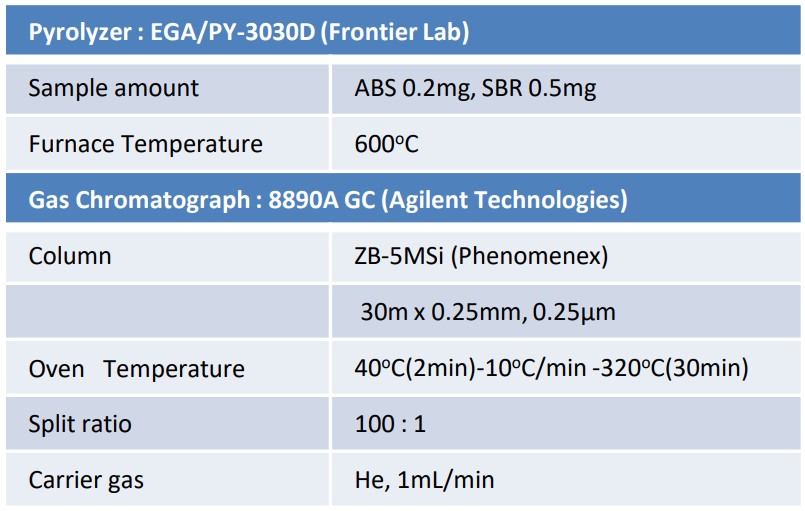
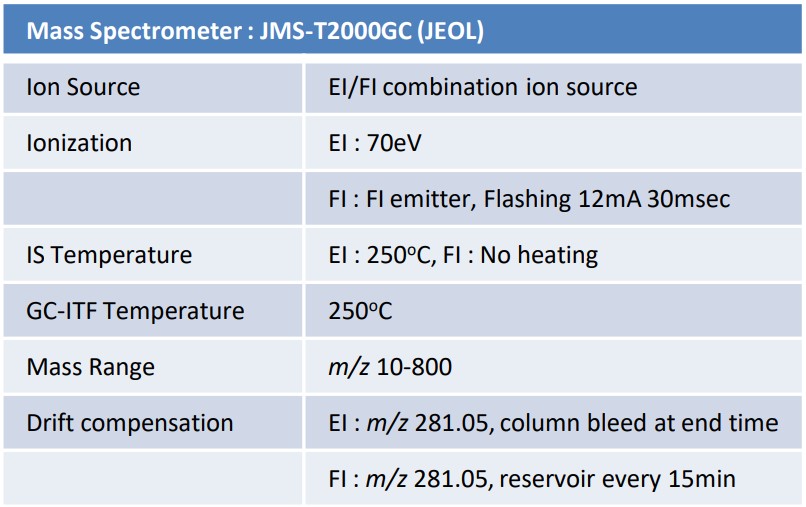
As the sample, commercially available acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) copolymer and styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) products were used. 0.2 mg of ABS and 0.5 mg of SBR were weighed and measured using Pyrolysis-GC-MS. EI and FI (field ionization) methods were used for ionization. The obtained data were analyzed using msFineAnalysis AI. Table 2 shows details of the measurement conditions.
Table 2 Measurement conditions
Results
Figure 1 shows the TIC chromatograms of the EI measurement results. The major pyrolysis products, such as styrene, acrylonitrile, and butadiene, were detected.
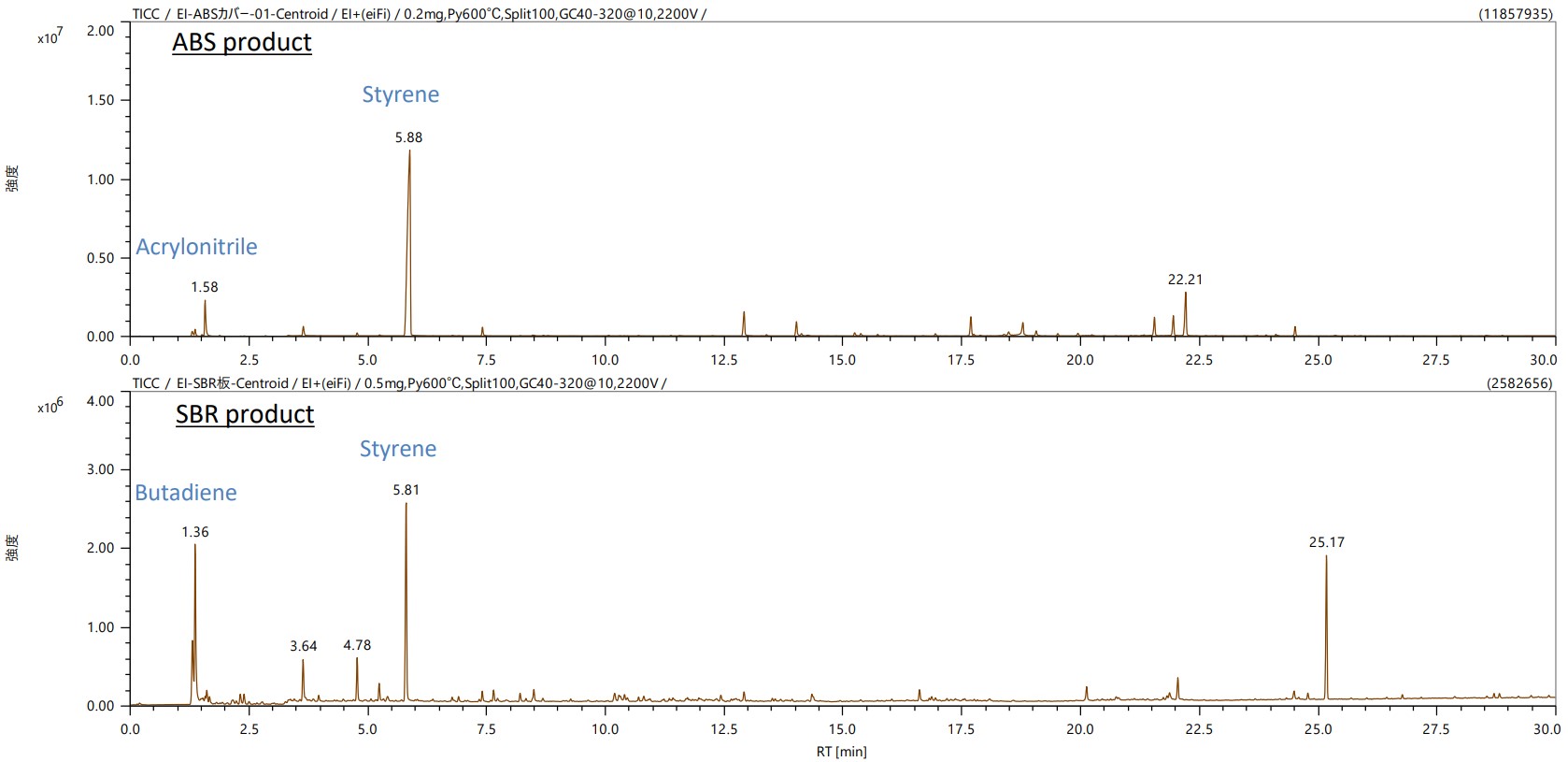
Figure 1 TIC chromatograms
Target analysis results ① - ABS product
Figure 2 shows the result window of the target analysis of msFineAnalysis AI. The left side shows the chromatograms (TICCs and EICs) for each ionization method. The right side shows qualitative information such as the mass spectrum of the detected peaks and their judgment results.
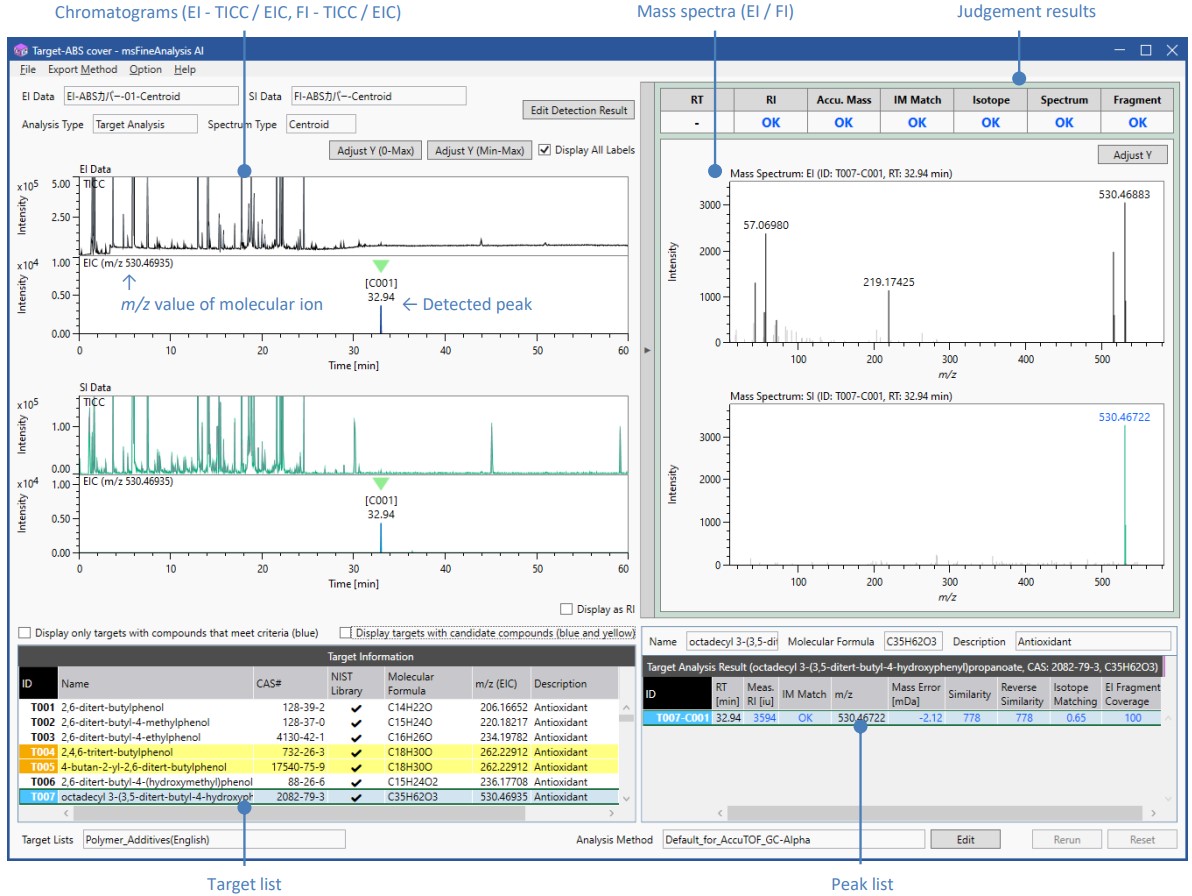
Figure 2 Result window of target analysis
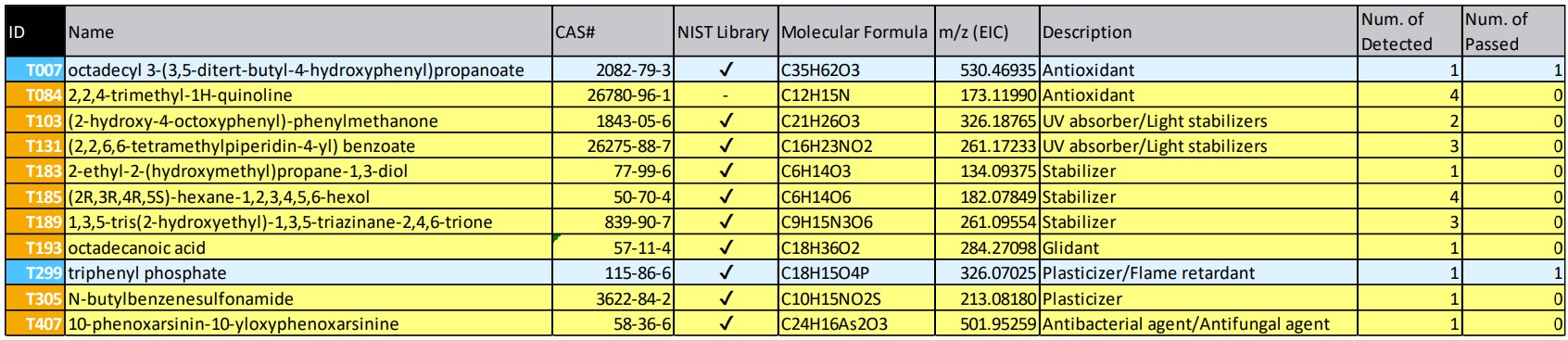
Table 3 shows the target list of the analysis results. The background color reflects the analysis results. Yellow indicates compounds with peaks detected on the EIC, and blue indicates compounds that also passed qualitative analysis such as mass spectrum similarity (=compound identified to be targets). In this result, two compounds were identified : octadecyl 3-(3,5-ditert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate, an antioxidant, and triphenyl phosphate, a plasticizer / a flame retardant. These peaks were weak, with an intensity ratio of less than 1%, so they were difficult to identify in non-target analysis. But they were easily identified in targeted analysis.
Table 3 Target list *selected blue and yellow
Target analysis results ② - SBR product
Figure 3 shows the results window of the target analysis.
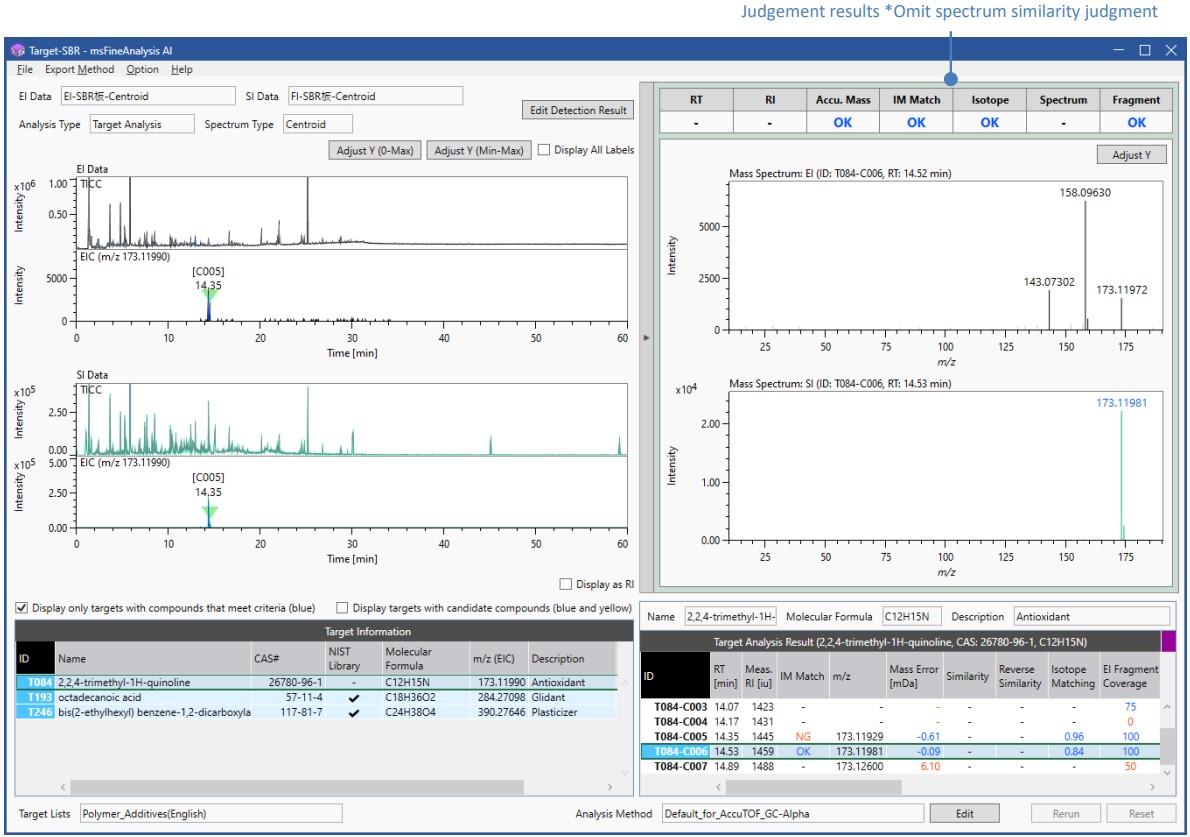
Figure 3 Result window of target analysis
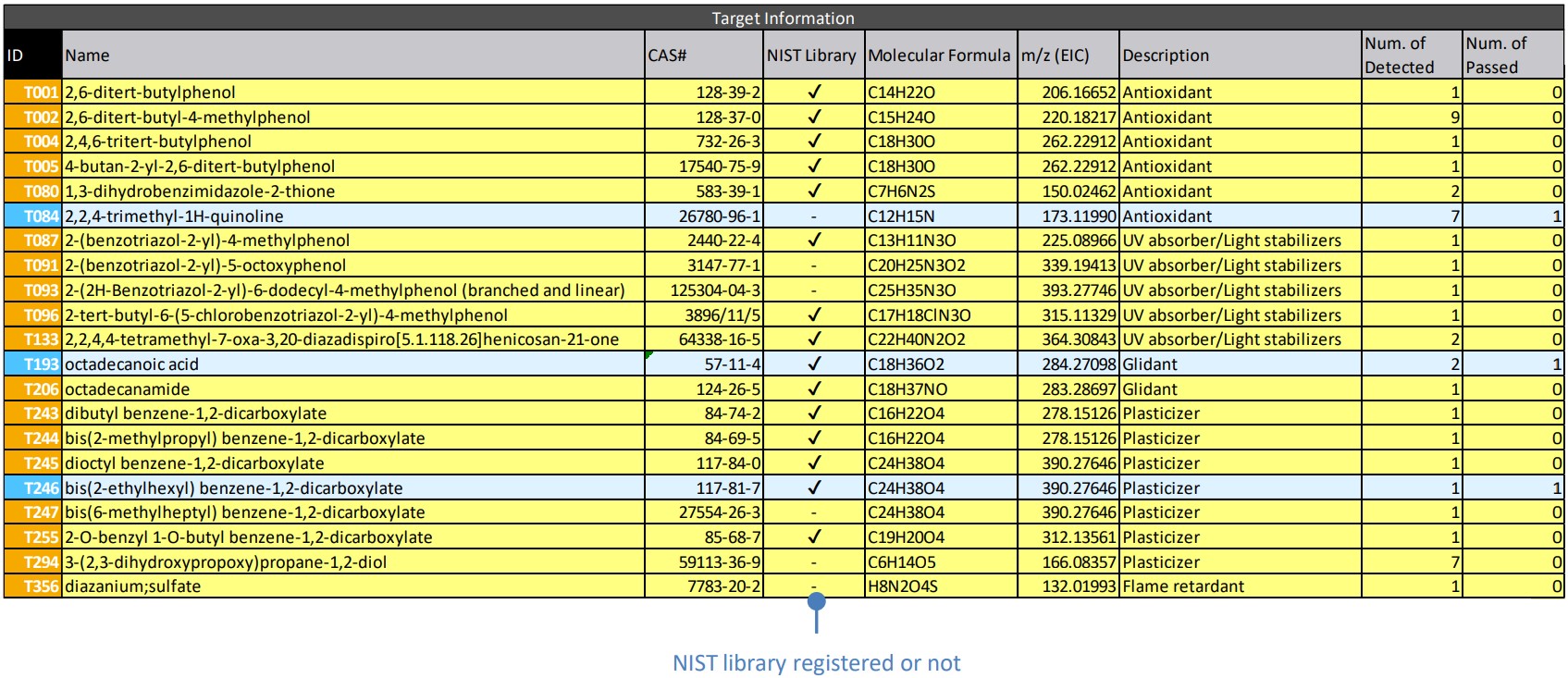
Table 4 shows the target list. Three compounds were identified : 2,2,4-trimethyl-1H-quinoline, an antioxidant, octadecanoic acid, a glidant, and bis(2-ethylhexyl) benzene-1,2-dicarboxylate (DEHP), a plasticizer. 2,2,4-trimethyl-1H-quinoline was not registered in the NIST library, so the spectrum similarity judgement was omitted.
Table 4 Target list *selected blue and yellow
However, mass spectrum evaluation is necessary to prevent misidentification. msFineAnalysis AI can compensate this information with AI structural analysis. Figure 4 shows the AI structural analysis result window. The similarity between the measured spectrum and the spectrum predicted from the structural formula of 2,2,4-trimethyl-1H-quinolinen was high, with an AI score of 791, suggesting that it may be the target compound.
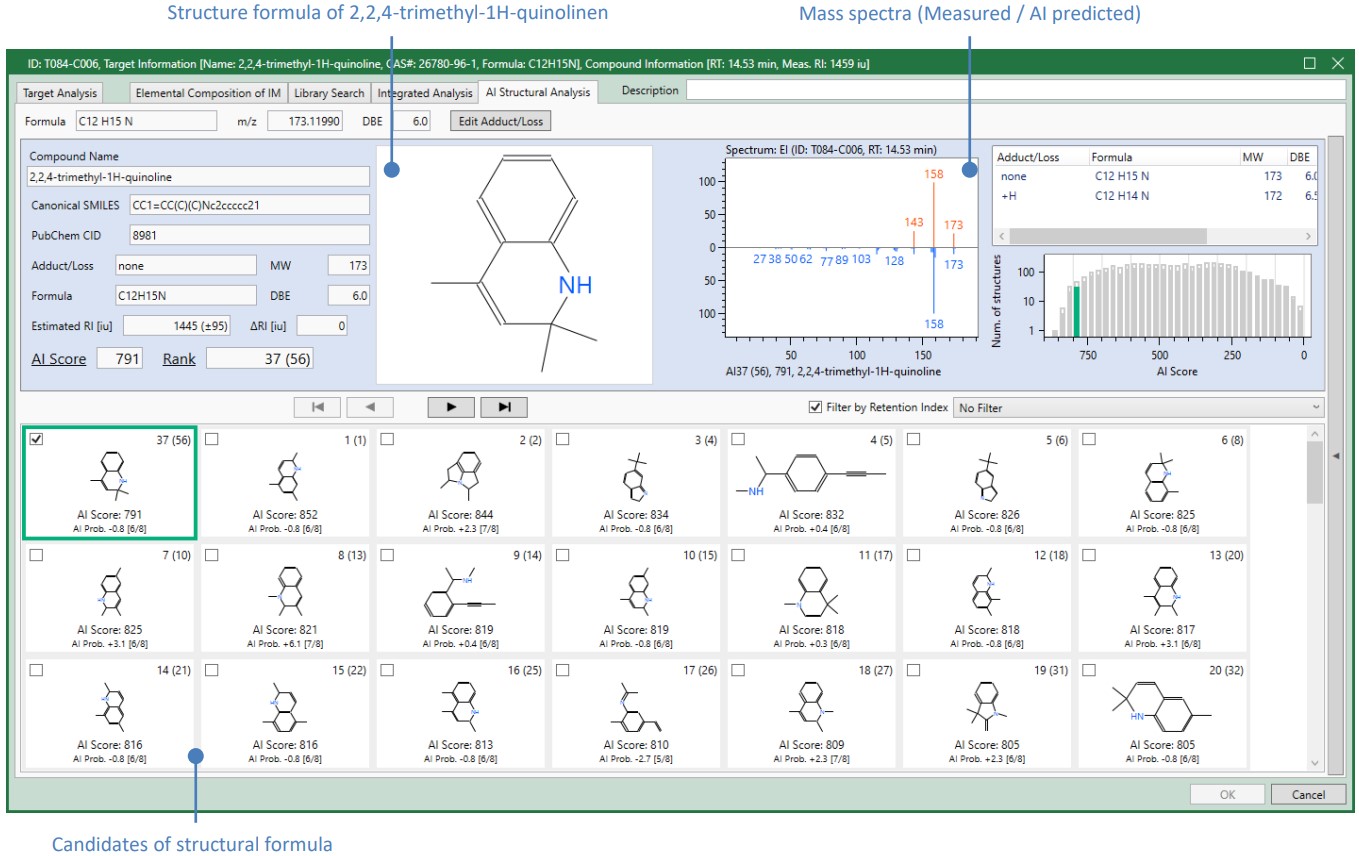
Figure 4 Result window of AI structural analysis
Conclusion
Additive analysis of polymer products was performed using target analysis of msFineAnalysis AI Ver.2. As a result, minor compounds could be quickly identified. Also, unregistered compound in the NIST library was identified using AI structural analysis with high accuracy.
Solutions by field
Related products
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.


