Analysis of Contaminants in Low Viscosity Solvents for Electrolytes in Liquid-LIB by GC-TOFMS
MSTips No. 473
Introduction
The electrolyte in a lithium-ion battery (LIB) is made by dissolving the electrolyte in a liquid mixture of ethylene carbonate (EC) and various low-viscosity solvents. Producing a high purity electrolyte requires a high purity solvent and therefore it is important to have a good understanding of the composition of impurities in the solvent.JEOL's latest analytical software, msFineAnalysis AI, is designed for rapid analysis of GC-HRMS data acquired by both EI and SI, chemical formula determination, and chemical structure prediction. This application note reports a qualitative analysis of impurity components of dimethyl carbonate (DMC), which is commonly used as a solvent in electrolytes, as a case study of msFineAnalysis AI analysis.
Experiment
Commercially available DMC (≥98%) was used as the sample. The field ionization (FI) method was used as the EI method and SI, and msFineAnalysis AI was used for analysis. Details of the measurement conditions in the measurement are shown in Table 1.

JMS-T2000GC AccuTOF™ GC-Alpha
High Performance GC-TOFMS
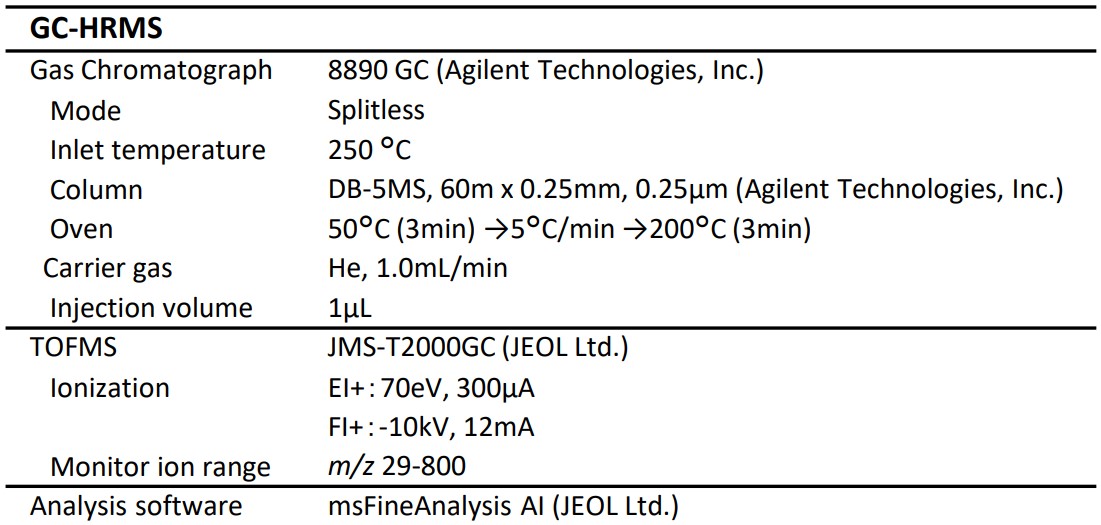
Table 1. Measurement and analysis conditions
Results and Discussion
The total ion current chromatogram (TICC) of EI is shown in Figure 1. The column bleed-derived siloxane and the main component, except DMC, were analyzed by msFineAnalysis AI as impurities. The TICC of EI and FI for the range analyzed by msFineAnalysis AI is shown in Figure 2. Impurities of 8 components were detected from the analysis range, and most of the components (ID[002]-ID[006], ID[008]) were identified with compound names and structural formulas with sufficient similarity by library search using the NIST database. For some compounds (ID[001], ID[007]) for which sufficient similarity could not be obtained by library search using the NIST database, the compound name and structural formula could be derived by structural analysis of msFineAnalysis AI. Figure 3 shows the candidate structural formula obtained from the AI structural analysis of ID[007].
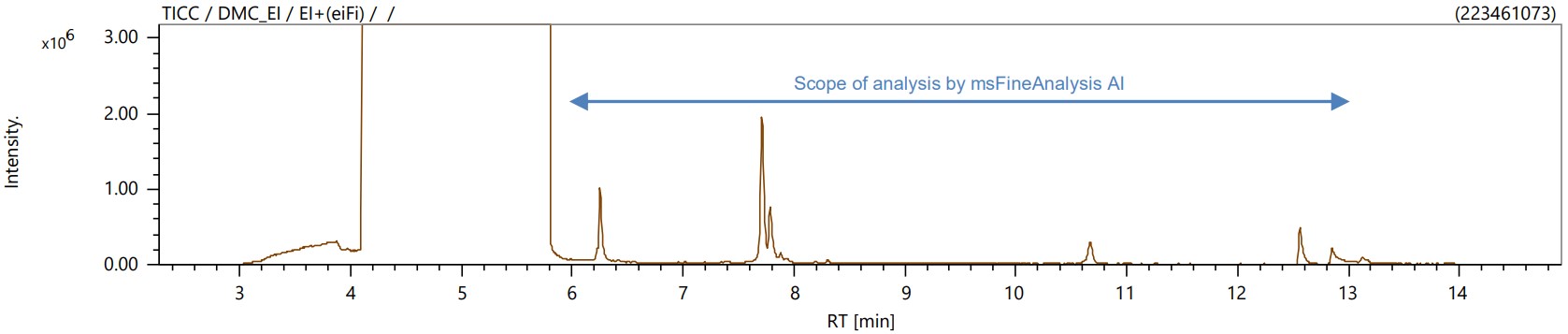
Figure 1. TICCs for ionization techniques EI.
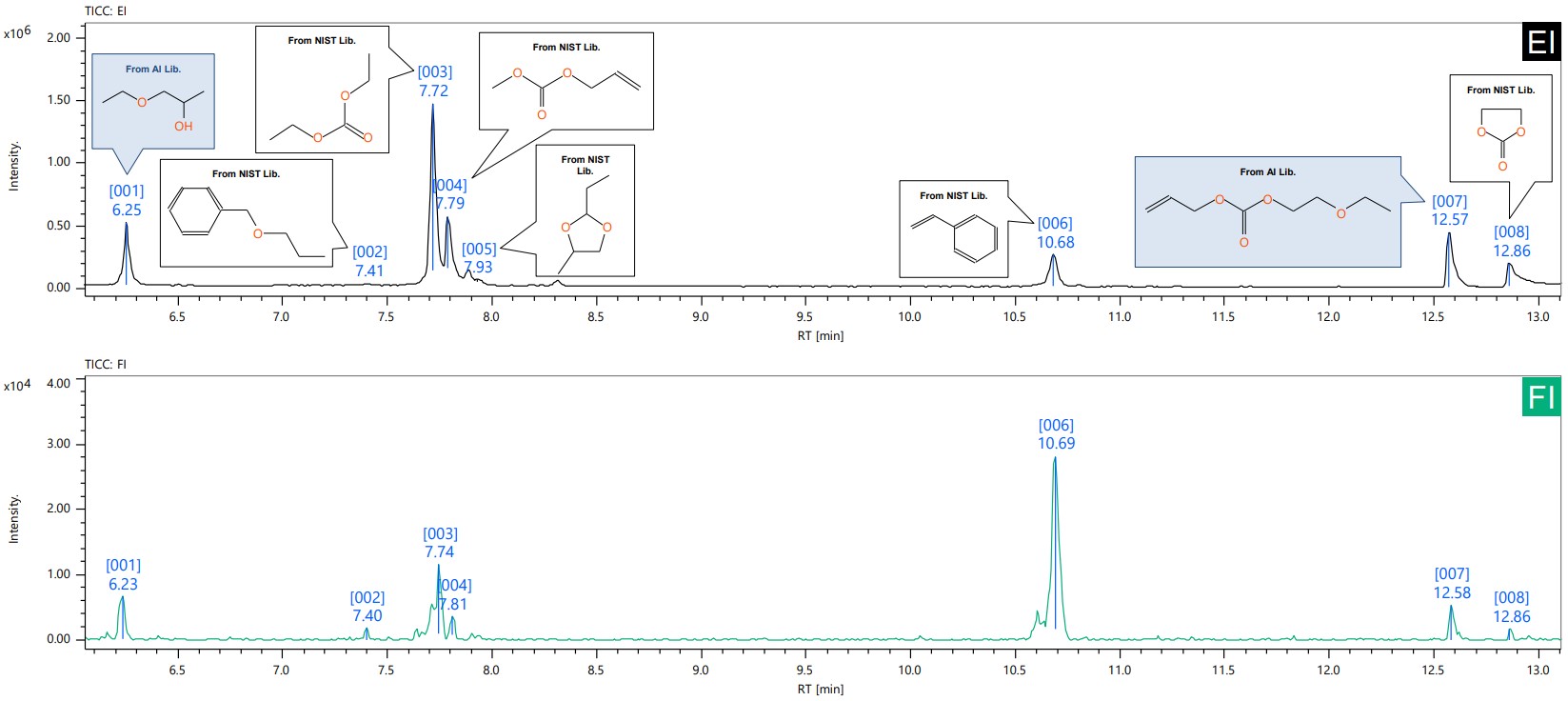
Figure 2. TICC for EI and FI methods with extended scope of msFineAnalysis AI analysis (Upper: EI, Lower: FI).
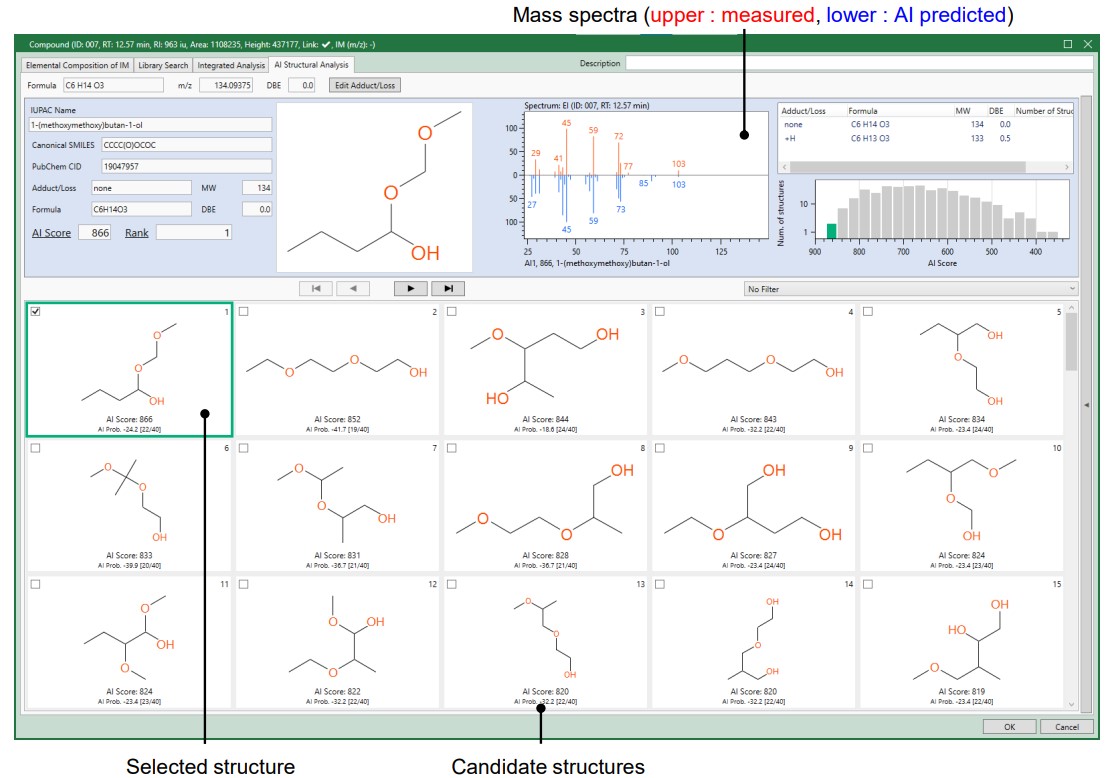
Figure 3. AI Structural analysis results of Peak ID [007].
Conclusion.
Impurities of DMC, which is commonly used as a solvent in electrolytic solutions, were measured by JMS-T2000GC and analyzed by msFineAnalysis AI, and as a result, DMC-like compounds such as Diethyl carbonate[003], Isobutylene carbonate[004], Ethylene carbonate[008] were detected as impurities. carbonate[004], and ethylene carbonate[008], which are compounds similar to DMC, were detected as impurities.
Solutions by field
Related products
Product category
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.


