Study on higher sensitivity for analysis of pesticide residues in foods by using GC-MS/MS (1)
MSTips No. 413
Introduction
The analysis of pesticide residues in foods requires the separation and detection of trace amounts of target pesticides present in complex matrices, and therefore, analytical instruments used for such measurements must have high performance. The GC-MS/MS method is effective for simultaneous analysis of multiple components in complex matrices, and is currently used by many analytical institutions as a general analytical method. Naturally, detection sensitivity can differ depending on the analytical instrument used, but various methods exist to increase the sensitivity of conventional analytical methods. For the purpose of increasing sensitivity, it can be effective to apply a sample injection method that is different from the normal hot splitless injection method generally used in GC, and among them, a relatively large number of examples exist using large volume injection (LVI) technology. The Multi Mode Injector (MMI manufactured by Agilent) used in this study allows the selection of various modes, such as cold splitless mode and solvent vent mode, in addition to the general hot splitless mode, depending on the purpose of measurement. However, there are relatively few examples for the application of cold splitless injection methods for the analysis of pesticide residues in food products. In this study, we compare the results of various cold splitless injection methods using MMI to improve GC-MS/MS detection sensitivity by suppressing adsorption and thermal decomposition of the target pesticides in the GC inlet.
Experimental
1. Sample Conditions
| Standard Reagents : | Pesticide Mixture Standard Solution PL-1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 made by FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Co. |
|---|---|
| Sample Concentration : | Pesticide mixed standard solutions were prepared at 0.1, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, and 20 ppb |
| Sample Volume : | 2 μL (+ 0.2 μL co-injection of analyte protectants : SFA10mix made by Hayashi Pure Chemical Industry Co.) |
2. GC Conditions
| Gas chromatograph : | 8890GC (Agilent Technologies, Inc.) |
|---|---|
| Inlet mode : | Hot/cold splitless mode |
| Inlet temperature (hot splitless) : | 250°C |
| Inlet temperature (cold splitless) : | 60°C (0.01 min) → 320°C (200°C / min, 10 min) → 60°C (200°C / min, 0 min) |
| Column : | VF-5MS (length : 30 m, inner diameter : 0.25 mm, film thickness : 0.25 μm) |
| Oven temperature : | 50°C (1 min) → 125°C (25°C / min, 0 min) → 300°C (10°C / min, 10 min) |
| Flow rate : | 1.0 mL/min (constant flow) |
3. MS Conditions
| Mass spectrometer : | JMS-TQ4000GC (JEOL Ltd.) |
|---|---|
| Measurement mode : | SRM |
| SRM mode : | High-sensitivity mode |
| Ion source temperature : | 280°C |
| Interface temperature : | 300°C |
| Ionization current : | 50 μA |
| Ionization voltage : | 70 eV |

JMS-TQ4000GC
Results
Of the 292 components selected for measurement, a total of 283 components were detectable at 0.1 ppb by using hot splitless mode. The following page lists the compound names and retention times of the 283 components that were detectable. Nine components that were not detected at 0.1 ppb using the conventional hot inlet method included: procymidone, acetamiprid, halfenprox, imibenconazole, bifenox, flumiclorac pentyl, azoxystrobin, propaquizafop, and thiacloprid. On the other hand, all target components were detectable at 0.1 ppb using the MMI with cold splitless mode. Fig. 1 shows an EIC comparison of imibenconazole, bifenox, and azoxystrobin at 0.1 ppb as an example for the components that were not detected with a hot splitless injector. To confirm the effect of the application of the cold splitless mode on sensitivity, peak area ratios (cold/hot splitless) were calculated for the 283 components for which detection of 0.1 ppb was possible in both modes, and a scatter plot of the ratios sorted by compound number (retention time) is shown in Fig. 2.
Target Pesticides (No.1~150)
| No. | Compound name | RT |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aldoxycarb (decomposed) | 5.73 |
| 2 | EPTC | 7.98 |
| 3 | Mevinphos 1+2 | 8.70 |
| 4 | Acephate | 8.81 |
| 5 | Nitrapyrin | 9.05 |
| 6 | Etridiazole | 9.06 |
| 7 | Methacrifos | 9.50 |
| 8 | Chloroneb | 9.66 |
| 9 | Isoprocarb | 9.98 |
| 10 | XMC | 10.26 |
| 11 | Omethoate | 10.63 |
| 12 | Tecnazene | 10.68 |
| 13 | Fenobucarb | 10.74 |
| 14 | Propoxur | 10.77 |
| 15 | Propachlor | 10.80 |
| 16 | Chlorethoxyphos | 10.86 |
| 17 | Diphenylamine | 11.05 |
| 18 | Ethoprophos | 11.07 |
| 19 | Ethalfluralin | 11.14 |
| 20 | Trifluralin | 11.30 |
| 21 | Chlorpropham | 11.31 |
| 22 | Benfluralin | 11.36 |
| 23 | Dicrotophos | 11.36 |
| 24 | Bendiocarb | 11.45 |
| 25 | Monocrotophos | 11.53 |
| 26 | Cadusafos | 11.60 |
| 27 | Phorate | 11.71 |
| 28 | Hexachlorobenzene | 11.98 |
| 29 | Dimethoate | 12.11 |
| 30 | Dicloran | 12.15 |
| 31 | Carbofuran | 12.19 |
| 32 | Simazine | 12.23 |
| 33 | Atrazine | 12.33 |
| 34 | Propazine | 12.41 |
| 35 | Clomazone | 12.41 |
| 36 | Quintozene | 12.48 |
| 37 | Propetamphos | 12.51 |
| 38 | Terbufos | 12.58 |
| 39 | Cyanophos | 12.61 |
| 40 | Propyzamide | 12.66 |
| 41 | Diazinone | 12.67 |
| 42 | Phosphamidon 1 | 12.72 |
| 43 | Pyroquilon | 12.83 |
| 44 | Pyrimethanil | 12.85 |
| 45 | Tefluthrine | 12.90 |
| 46 | Prohydrojasmon 1 | 12.90 |
| 47 | Disulfoton | 12.94 |
| 48 | Isazophos | 12.94 |
| 49 | Terbacil | 12.98 |
| 50 | Triallate | 13.10 |
| No. | Compound name | RT |
|---|---|---|
| 51 | δ-BHC | 13.16 |
| 52 | Pirimicarb | 13.20 |
| 53 | Prohydrojasmon 2 | 13.22 |
| 54 | Iprobenfos | 13.23 |
| 55 | Oxabetrinil | 13.26 |
| 56 | Benoxacor | 13.38 |
| 57 | Formothion | 13.40 |
| 58 | Phosphamidon 2 | 13.48 |
| 59 | Benfuresate | 13.54 |
| 60 | Dichlofenthion | 13.55 |
| 61 | Dimethenamid | 13.59 |
| 62 | Propanil | 13.62 |
| 63 | Acetochlor | 13.64 |
| 64 | Bromobutide | 13.68 |
| 65 | Chloropyriphos-methyl | 13.70 |
| 66 | Metribuzin | 13.71 |
| 67 | Spiroxamine 1 | 13.76 |
| 68 | Vinclozoline | 13.77 |
| 69 | Alachlor | 13.84 |
| 70 | Parathion methyl | 13.84 |
| 71 | Tolclofos-methyl | 13.85 |
| 72 | Simetryn | 13.92 |
| 73 | Mefenoxam | 13.95 |
| 74 | Ametryn | 13.98 |
| 75 | Carbaril | 13.98 |
| 76 | Prometryn | 14.02 |
| 77 | Fenchlorphos | 14.04 |
| 78 | Heptachlor | 14.06 |
| 79 | Pirimiphos methyl | 14.21 |
| 80 | Spiroxamine 2 | 14.28 |
| 81 | Terbutryn | 14.28 |
| 82 | Fenitrothion | 14.31 |
| 83 | Ethofumesate | 14.32 |
| 84 | 1-Naphthylacetamide | 14.34 |
| 85 | Bromacil | 14.38 |
| 86 | Malathion | 14.43 |
| 87 | Esprocarb | 14.47 |
| 88 | Metolachlor | 14.59 |
| 89 | Diethofencarb | 14.59 |
| 90 | Chlorpyrifos | 14.61 |
| 91 | Quinoclamine | 14.62 |
| 92 | (Z)-Dimethylvinphos | 14.66 |
| 93 | Benthiocarb | 14.67 |
| 94 | Cyanazine | 14.69 |
| 95 | Fenpropimorph | 14.70 |
| 96 | Fenthion | 14.70 |
| 97 | Flufenacet | 14.71 |
| 98 | Chlorthal dimethyl | 14.72 |
| 99 | Isofenphos oxon | 14.75 |
| 100 | Parathion | 14.78 |
| No. | Compound name | RT |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | Aldrin | 14.79 |
| 102 | Tetraconazole | 14.80 |
| 103 | Triadimefon | 14.83 |
| 104 | Nitrothal isopropyl | 14.85 |
| 105 | Dicofol (decomposed) | 14.97 |
| 106 | Fthalide | 15.07 |
| 107 | Bromophos | 15.08 |
| 108 | Diphenamid | 15.08 |
| 109 | Fosthiazate 1 | 15.11 |
| 110 | Fosthiazate 2 | 15.15 |
| 111 | trans-Chlorfenvinphos | 15.23 |
| 112 | Pendimethalin | 15.26 |
| 113 | Fipronil | 15.28 |
| 114 | Dimethametryn | 15.36 |
| 115 | Isophenphos | 15.39 |
| 116 | Penconazole | 15.43 |
| 117 | cis-Chlorfenvinphos | 15.45 |
| 118 | Allethrin 3+4 | 15.46 |
| 119 | Mecarbam | 15.47 |
| 120 | Pyrifenox 2 | 15.53 |
| 121 | Heptachlor Epoxide (isomer A) | 15.53 |
| 122 | Oxychlordane | 15.55 |
| 123 | Phenthoate | 15.56 |
| 124 | Diclocymet 1 | 15.57 |
| 125 | Quinalphos | 15.59 |
| 126 | Heptachlor Epoxide (isomer B) | 15.63 |
| 127 | Methoprene | 15.65 |
| 128 | Triadimenol 1 | 15.67 |
| 129 | Dimepiperate | 15.70 |
| 130 | Triflumizole | 15.70 |
| 131 | Thiabendazole | 15.72 |
| 132 | Zoxamide (decomposed) | 15.76 |
| 133 | Triadimenol 2 | 15.81 |
| 134 | Bromophos ethyl | 15.86 |
| 135 | Propaphos | 15.88 |
| 136 | Diclocymet 2 | 15.89 |
| 137 | Methidathion | 15.90 |
| 138 | Tetrachlorvinphos | 15.97 |
| 139 | Chlorbenside | 15.97 |
| 140 | trans-Chlordane | 15.99 |
| 141 | Butachlor | 16.00 |
| 142 | Pyrifenox 1 | 16.02 |
| 143 | Paclobutrazol | 16.05 |
| 144 | Fenothiocarb | 16.06 |
| 145 | Butamifos | 16.17 |
| 146 | Fenamiphos | 16.23 |
| 147 | Imazamethabenz methyl 1 | 16.24 |
| 148 | cis-Chlordane | 16.24 |
| 149 | Imazamethabenz methyl 2 | 16.26 |
| 150 | Flutriafol | 16.28 |
Target Pesticides (No.151~283)
| No. | Compound name | RT |
|---|---|---|
| 151 | Flutolanil | 16.29 |
| 152 | Napropamide | 16.31 |
| 153 | Pretilachlor | 16.42 |
| 154 | Prothiofos | 16.42 |
| 155 | Hexaconazole | 16.42 |
| 156 | Chlorofenson | 16.42 |
| 157 | Isoprothiolane | 16.44 |
| 158 | Profenofos | 16.50 |
| 159 | Oxadiazon | 16.52 |
| 160 | Tribufos | 16.59 |
| 161 | Flamprop methyl | 16.59 |
| 162 | p,p'-DDE | 16.60 |
| 163 | Uniconazole P | 16.61 |
| 164 | Oxyfluorfen | 16.62 |
| 165 | Myclobutanil | 16.65 |
| 166 | Tricyclazole | 16.65 |
| 167 | Bupirimate | 16.66 |
| 168 | Kresoxim-methyl | 16.67 |
| 169 | Flusilazole | 16.68 |
| 170 | Buprofezin | 16.70 |
| 171 | Dieldrin | 16.78 |
| 172 | Imibenconazole debenzyl | 16.80 |
| 173 | Carboxin | 16.80 |
| 174 | Azaconazole | 16.84 |
| 175 | Chlorfenapyr | 16.85 |
| 176 | Isoxathion | 16.92 |
| 177 | Fenoxanil | 17.01 |
| 178 | Cyproconazole 1+2 | 17.05 |
| 179 | 1,1-Dichloro-2,2-bis (4-ethylphenyl) ethane | 17.05 |
| 180 | Flufenpyr ethyl | 17.07 |
| 181 | Pyriminobac methyl 1 | 17.12 |
| 182 | Chlorobenzilate | 17.20 |
| 183 | Endrin | 17.21 |
| 184 | Fensulfothion | 17.24 |
| 185 | Ethion | 17.33 |
| 186 | Fluacrypyrim | 17.37 |
| 187 | Oxadixyl | 17.37 |
| 188 | p,p'-DDD | 17.41 |
| 189 | o,p'-DDT | 17.46 |
| 190 | Mepronil | 17.61 |
| 191 | Triazophos | 17.64 |
| 192 | Carfentrazone ethyl | 17.73 |
| 193 | Trifloxystrobin | 17.79 |
| 194 | Famphur | 17.79 |
| 195 | Azamethiphos | 17.79 |
| 196 | Benalaxyl | 17.82 |
| 197 | Norflurazon | 17.91 |
| 198 | Pyriminobac methyl 2 | 17.93 |
| 199 | Pyraflufen-ethyl | 17.95 |
| 200 | Propiconazole 1 | 17.97 |
| No. | Compound name | RT |
|---|---|---|
| 201 | Edifenphos | 17.97 |
| 202 | Quinoxyfen | 18.01 |
| 203 | Lenacil | 18.06 |
| 204 | Propiconazole 2 | 18.07 |
| 205 | Endosulfan sulfate | 18.11 |
| 206 | p,p'-DDT | 18.12 |
| 207 | Hexazinone | 18.21 |
| 208 | Thenylchlor | 18.29 |
| 209 | Diflufenican | 18.32 |
| 210 | Diclofop methyl | 18.33 |
| 211 | Propargite 1+2 | 18.34 |
| 212 | Resmethrin 1 | 18.34 |
| 213 | Tebuconazole | 18.36 |
| 214 | Piperonyl butoxide | 18.41 |
| 215 | Resmethrin 2 | 18.45 |
| 216 | Mefenpyr diethyl | 18.58 |
| 217 | Zoxamide | 18.61 |
| 218 | Epoxiconazole | 18.62 |
| 219 | Pyributicarb | 18.65 |
| 220 | Pyridafenthion | 18.79 |
| 221 | Iprodione | 18.79 |
| 222 | Bifenthrin | 18.88 |
| 223 | Phosmet | 19.00 |
| 224 | EPN | 19.00 |
| 225 | Picolinafen | 19.00 |
| 226 | Piperophos | 19.01 |
| 227 | Bromopropylate | 19.02 |
| 228 | Etoxazole | 19.06 |
| 229 | Fenpropathrin | 19.10 |
| 230 | Methoxychlor | 19.12 |
| 231 | Fenamidone | 19.18 |
| 232 | Tebufenpyrad | 19.19 |
| 233 | Anilofos | 19.28 |
| 234 | Furathiocarb | 19.35 |
| 235 | Phenothrin 1 | 19.36 |
| 236 | Phenothrin 2 | 19.47 |
| 237 | Tetradifon | 19.56 |
| 238 | Phosalone | 19.63 |
| 239 | Triticonazole | 19.65 |
| 240 | Cyhalothrin 1 | 19.67 |
| 241 | Azinphos-methyl | 19.75 |
| 242 | Cyhalofop butyl | 19.76 |
| 243 | Pyriproxyfen | 19.77 |
| 244 | Cyhalothrin 2 | 19.84 |
| 245 | Mefenacet | 19.90 |
| 246 | Acrinathrin | 19.95 |
| 247 | Pyrazophos | 20.08 |
| 248 | Fenarimol | 20.22 |
| 249 | Pyraclofos | 20.41 |
| 250 | Fenoxaprop ethyl | 20.45 |
| No. | Compound name | RT |
|---|---|---|
| 251 | Spirodiclofen | 20.63 |
| 252 | Bitertanol 1 | 20.69 |
| 253 | trans-Permethrin | 20.71 |
| 254 | Bitertanol 2 | 20.80 |
| 255 | cis-Permethrin | 20.83 |
| 256 | Fluquinconazole | 20.91 |
| 257 | Pyridaben | 20.91 |
| 258 | Prochloraz | 20.97 |
| 259 | Cafenstrole | 21.20 |
| 260 | Cyfluthrin 1 | 21.23 |
| 261 | Fenbuconazole | 21.30 |
| 262 | Cyfluthrin 2 | 21.32 |
| 263 | Cyfluthrin 3+4 | 21.42 |
| 264 | Cypermethrin 1 | 21.56 |
| 265 | Cypermethrin 2 | 21.66 |
| 266 | Flucythrinate 1 | 21.70 |
| 267 | Boscalid | 21.73 |
| 268 | Cypermethrin 3+4 | 21.76 |
| 269 | Flucythrinate 2 | 21.90 |
| 270 | Etofenprox | 21.90 |
| 271 | Fluridone | 22.19 |
| 272 | Fenvalerate 1 | 22.56 |
| 273 | Flumioxazin | 22.60 |
| 274 | Fluvalinate 1 | 22.63 |
| 275 | Fluvalinate 2 | 22.72 |
| 276 | Fenvalerate 2 | 22.81 |
| 277 | Difenoconazole 1 | 23.19 |
| 278 | Difenoconazole 2 | 23.26 |
| 279 | Deltamethrin | 23.53 |
| 280 | Famoxadone | 24.11 |
| 281 | Tolfenpyrad | 24.18 |
| 282 | Cinidon ethyl | 25.14 |
| 283 | Fluthiacet methyl | 25.60 |
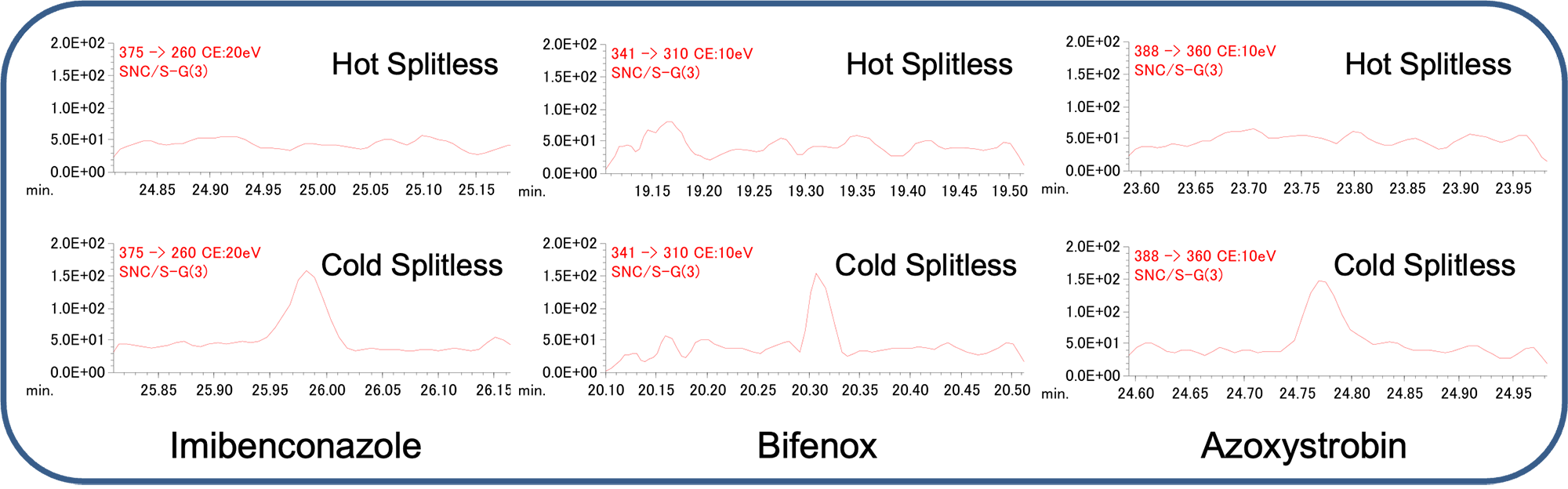
Fig.1 Comparison of EICs at 0.1 ppb (Hot / Cold Splitless)
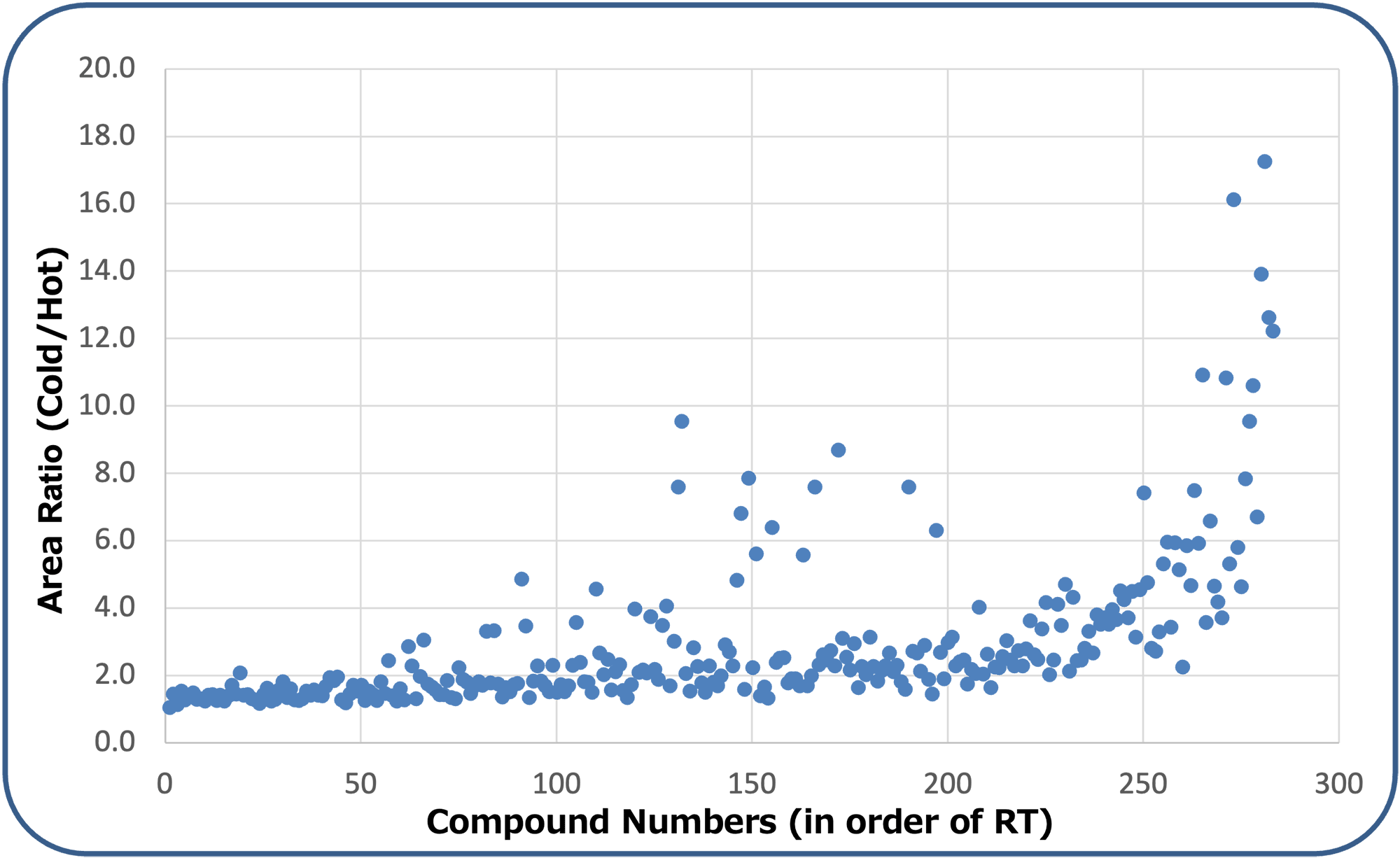
Fig.2 Scatter diagram of area ratios of measured pesticides (Cold / Hot)
By using the cold splitless method, the peak area ratio for the components in the first half of the retention time range increased by 1.5 to 2 times. Additionally, several components near the middle of the retention time range had area ratios that increased by approximately 5 to 10 times. These compounds are presumed to be components that experience a large suppression effect caused by compound decomposition in the GC injection port. Similarly, the higher the boiling point component (higher retention time range), the larger the area ratio increases (up to 17 times). These results are likely due to the combination of suppressing decomposition and suppressing adsorption inside the inlet while using cold splitless mode. In this study, there were no components whose sensitivity decreased (area ratio < 1) due to the application of cold splitless mode when compared to the conventional hot splitless mode.
Conclusion
This study showed that cold splitless injections using MMI improved the sensitivity of pesticides analysis by GC-MS/MS when compared to the more traditional hot splitless injection method. Furthermore, a number of components showed very large improvements in sensitivity in the middle to late retention times that were likely due to both suppression of thermal decomposition and minimization of adsorption in the inlet when using cold splitless methods. These results show that cold splitless injection methods using MMI can be effective for improving overall GC-MS/MS pesticide sensitivity.
Solutions by field
Related products
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.

