resin embedding method
resin embedding method
The resin embedding method in specimen preparation for TEM observation is to embed a specimen in a resin to make it easy to slice the specimen with an ultramicrotome.
If the specimen is soft (e.g. contains much water or lipids), it is difficult to slice the specimen thinly when making ultra-thin sections. By embedding the specimen in the resin for reinforcement, it is possible to slice the specimen to a thickness suitable for TEM observation while maintaining the morphology of the specimen. Resin embedding is also used for small specimens (e.g. powder specimens) to provide a support part during the slicing.
As an example of resin embedding, Fig. 1 shows the procedure using epoxy resin, which is widely used for biological specimens. First, a specimen is placed in the cavities on a silicon embedding plate, and a liquid mixture of the main agent (epoxy resin), a hardening agent and a cross-linking agent is poured into the cavities. The resin-embedded specimen is obtained by heating the plate for a given length of time to harden (polymerize) the resin.
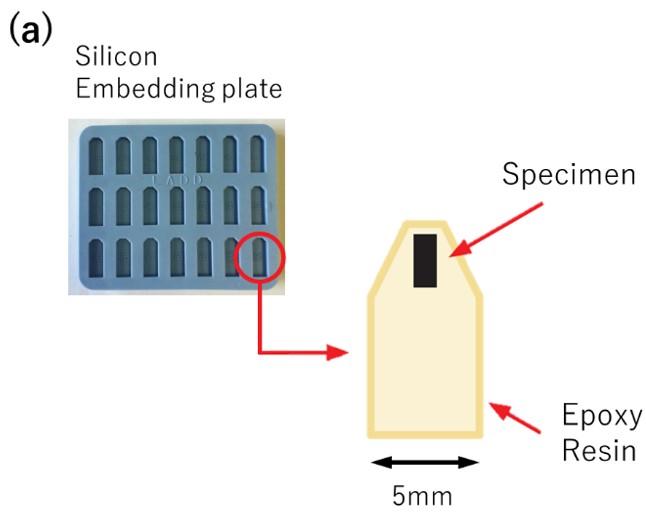
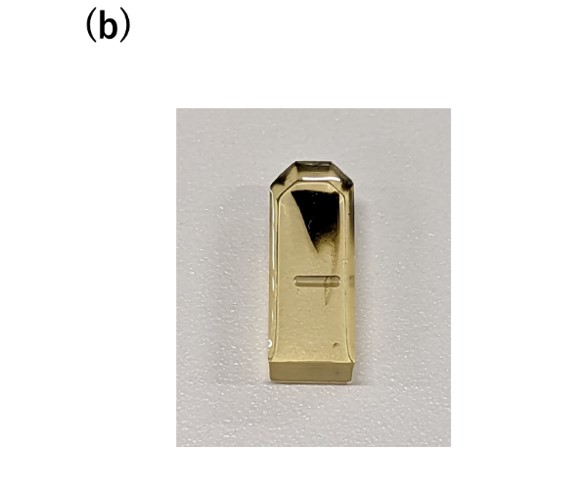
Fig. 1(a) Example of a silicon embedding plate (upper left), and schematic diagram of a specimen embedded with epoxy resin in a cavity (lower right). The specimen is placed at the upper end of the cavity. The lower part of the resin serves as a part to hold the specimen with an ultramicrotome. (b) Photo of a hardened resin containing the specimen taken out from the cavity.
Related Term(s)
Term(s) with "resin embedding method" in the description
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.




