Utilizing Python® in JASON via HDF5 Files and the External Command Function
NM250005
Currently, JASON[1] provides an efficient environment for NMR spectral analysis using Python[2] through its hierarchical HDF5 file structure and integration with BeautifulJASON.
This document introduces the following two key topics:
Overview of HDF5 files and their application in JASON
Use cases of the External Command function
1. Overview of HDF5 Files and Their Application in JASON
What is HDF5?
HDF5 (Hierarchical Data Format version 5) is a file format designed for the efficient storage and management of large and complex datasets. Widely used in scientific and engineering fields, HDF5 offers the following key features:
Hierarchical Structure: Data is organized into groups and datasets in a directory-like format, making it easy to manage large volumes of information.
Support for Large Datasets: Optimized for storing and accessing massive data, HDF5 is ideal for scientific computing and image analysis.
Wide Language Support: HDF5 can be accessed from a wide range of scientific programming languages, including C, C++, Fortran, Python, MATLAB, R, Java, Julia, and many others, thanks to extensive native and community-supported libraries.
Cross-Platform Compatibility: The HDF5 format and libraries are fully cross-platform, with mature support for Windows, macOS, and Linux. HDF5 can also be built for mobile platforms such as iOS and Android for specialized applications, and browser-based access is possible through JavaScript/WebAssembly libraries.
Random Access: Enables efficient read/write operations on specific data segments, making it suitable for large-scale data processing.
Advantages of HDF5 in NMR Data Analysis
Efficient NMR Spectral Analysis: Enables fast and selective extraction of multidimensional data, facilitating smooth analysis workflows.
Hierarchical Data Access: For example, data can be retrieved from paths such as JasonDocument/NMR/NMRData/0/DataPoints or SpecInfo.
Metadata Utilization: Attributes stored in SpecInfo[3] (e.g., SW, SpectrometerFrequencies, SpectrumRef) can be easily accessed to obtain essential experimental conditions.
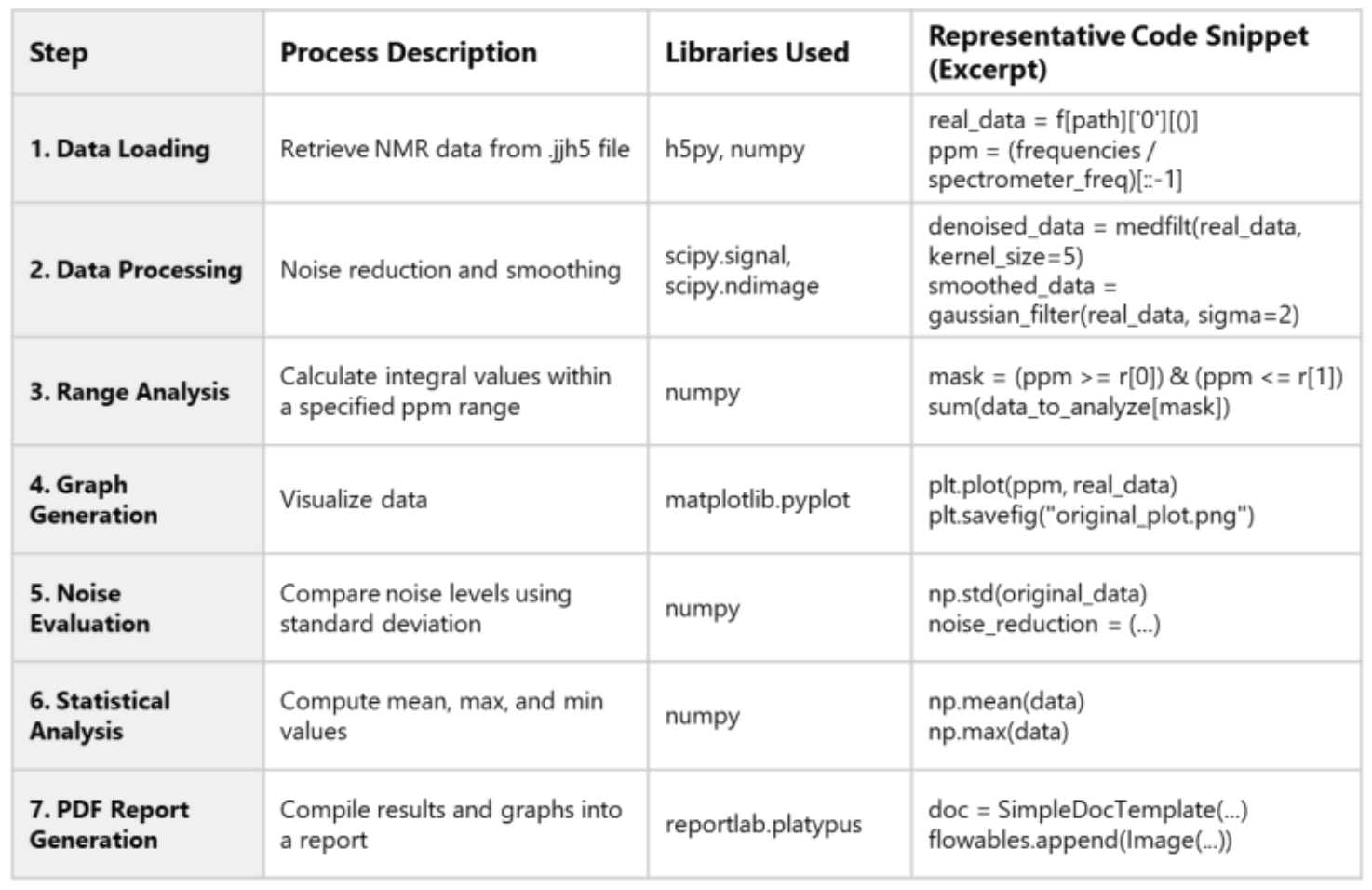
Table 1. Example Workflow for NMR Spectral Analysis
Example: Python-Based Data Analysis Using JASON and HDF5
This section presents a simple workflow for NMR data analysis and report generation using Python, leveraging the structure of HDF5 files:
Load NMR data
Process and analyze the data
Automatically generate graphs and reports
Details of each step and the Python libraries used are summarized in Table 1.
This example serves as a practical reference for understanding HDF5 file structures and performing spectral analysis.
Reading NMR Data and Calculating the ppm Axis
The function shown in Figure 1 demonstrates how to extract real signal data and compute the chemical shift (ppm axis) from NMR measurement files in .jjh5[4] format.
This approach is applicable to various spectra, including 13C NMR, and can be adapted as a general-purpose data loading function by accounting for differences in file structure and metadata attributes.
Example of Path Specification
HDF5 files are structured like hierarchical databases, consisting of folders and datasets organized in layers. Below is an example of how to specify a path: path = "JasonDocument/NMR/NMRData/0/DataPoints" real_data = f[path]['0'][()] # Real component of the signal
Note:
The string "JasonDocument/NMR/NMRData/0/DataPoints" represents the hierarchical structure within the file. The expression f[path]['0'][()] accesses the data associated with the key '0' under the specified path. Metadata such as SpecInfo can also be accessed using similar path specifications.
Example of Generated Report
Figure 2 shows a sample report generated from the workflow described in Table 1.
For more details on libraries such as NumPy, SciPy, and ReportLab, please refer to their respective user guides.
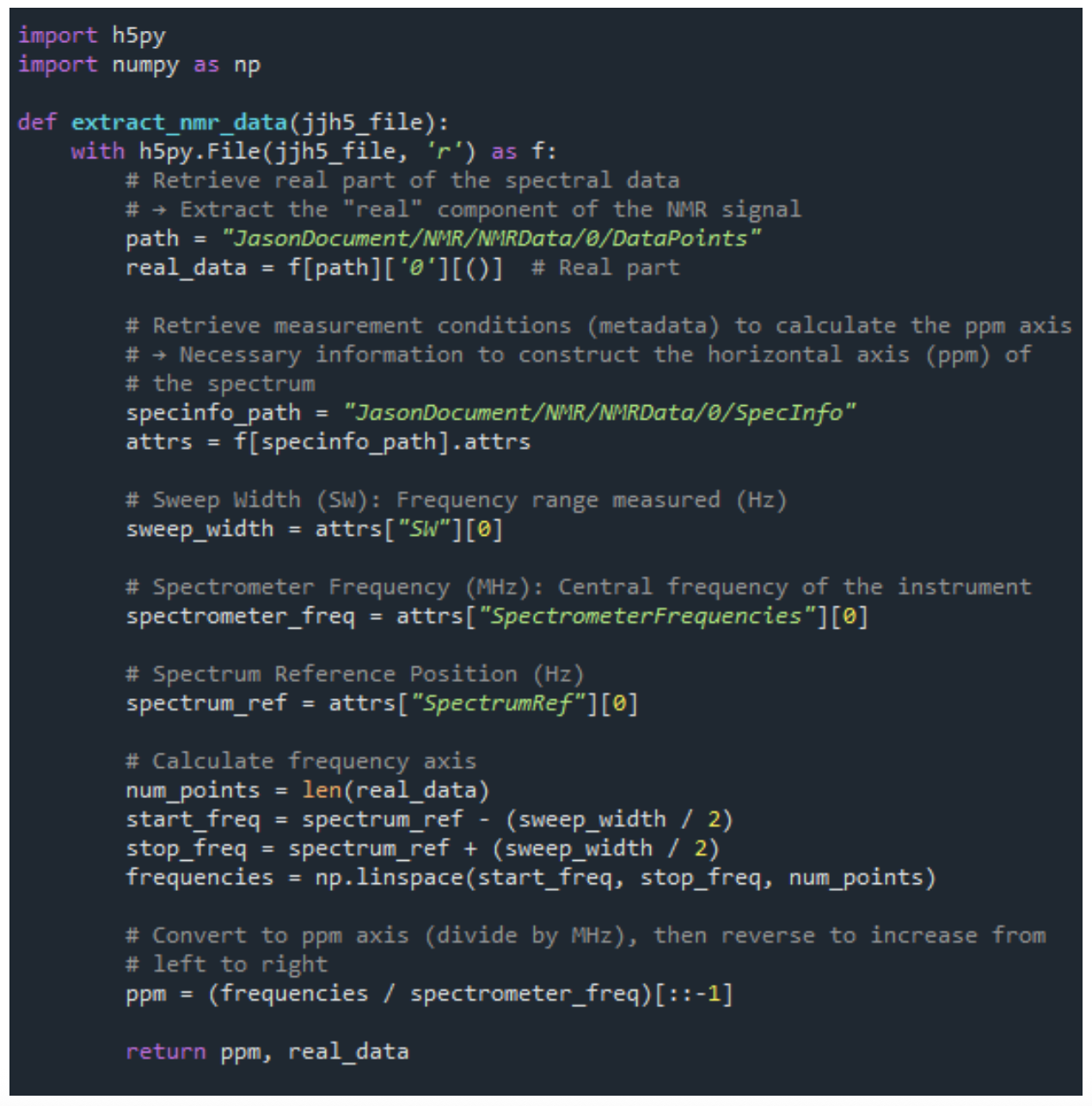
Figure 1. Excerpt from the NMR Data Extraction Script
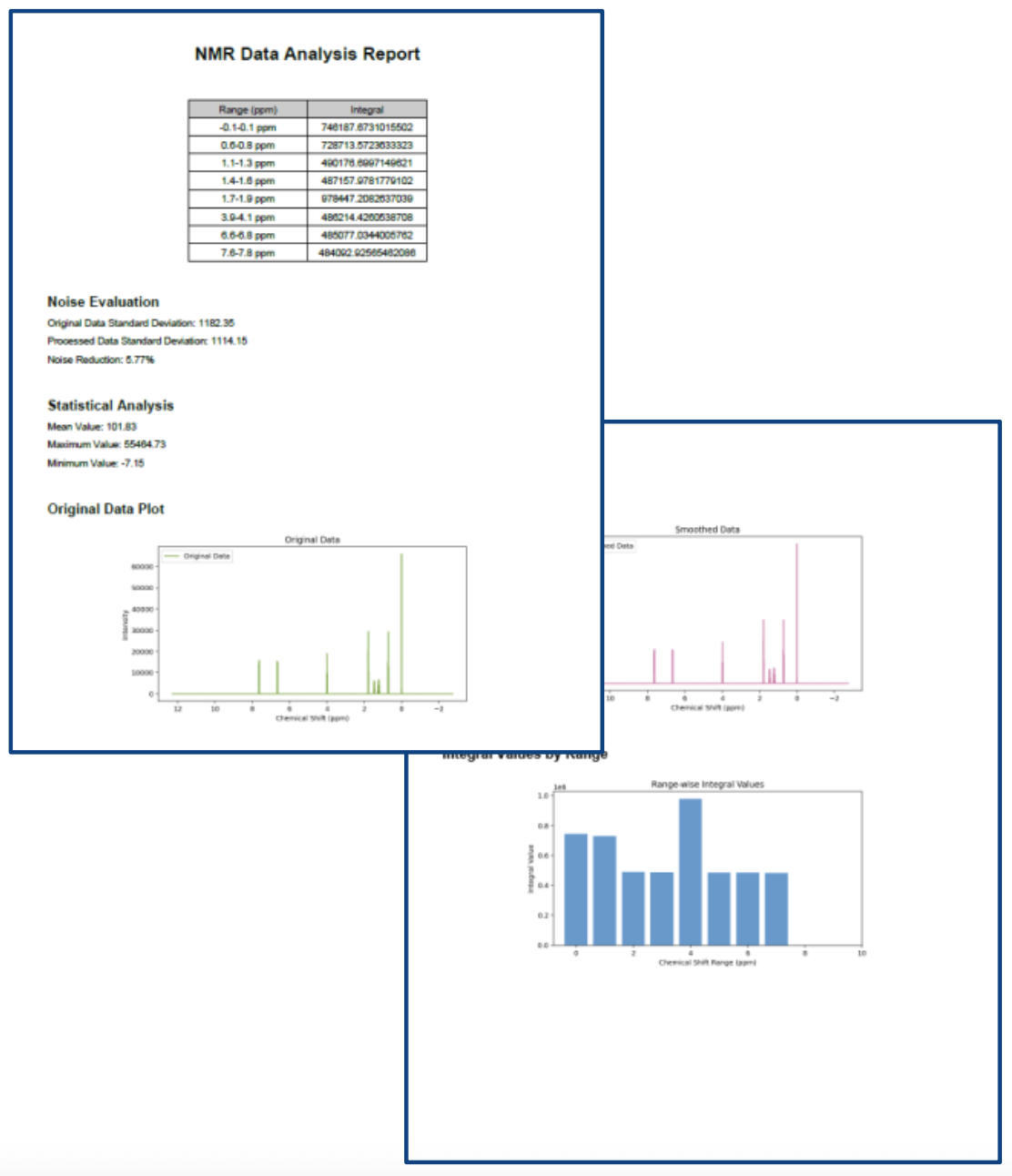
Figure 2. Example of Report Output
2. Use Case of the External Command Function
Overview of the External Command Function
The External Command function in JASON allows users to execute external Python scripts directly from the Processing tab in the JASON GUI.
This feature is particularly useful for automation and custom data processing.
Here, we introduce an example of using Python scripts from the downloadable package External NMR Processing Scripts, available on the official JASON website.
Sample Code Access
Sample scripts can be downloaded from the following JASON official resource page:
https://www.jeoljason.com/resources-external-nmr-processing-scripts/
Figure 3 shows a list of Python scripts included in the External NMR Processing Scripts directory.
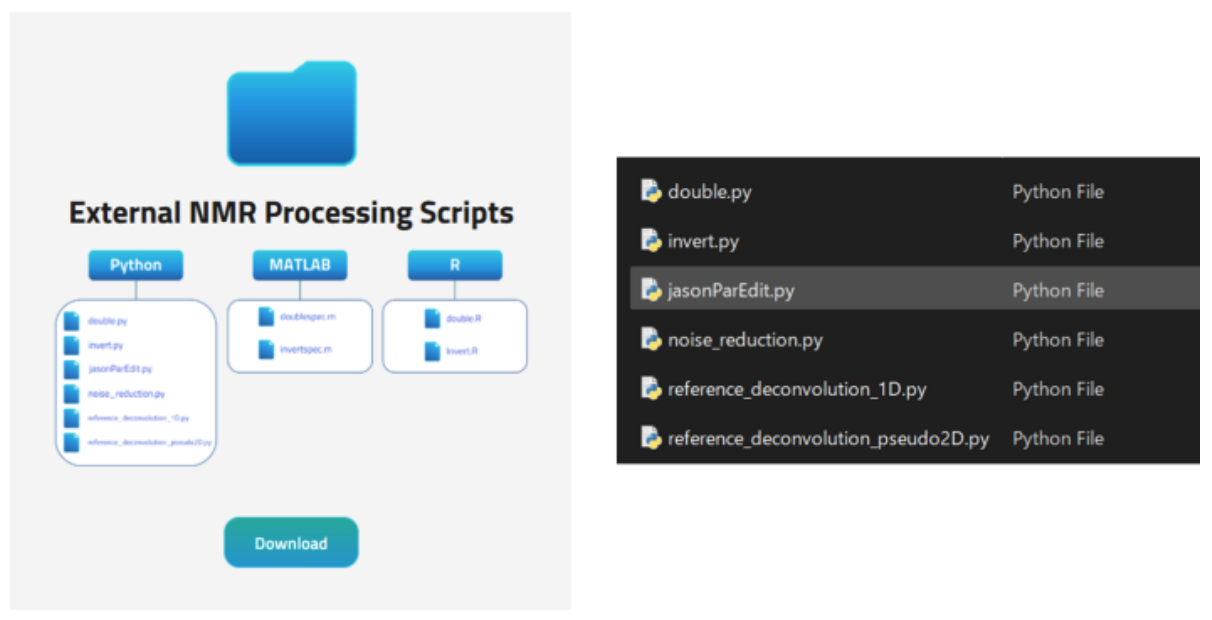
Figure 3. External NMR Processing Scripts
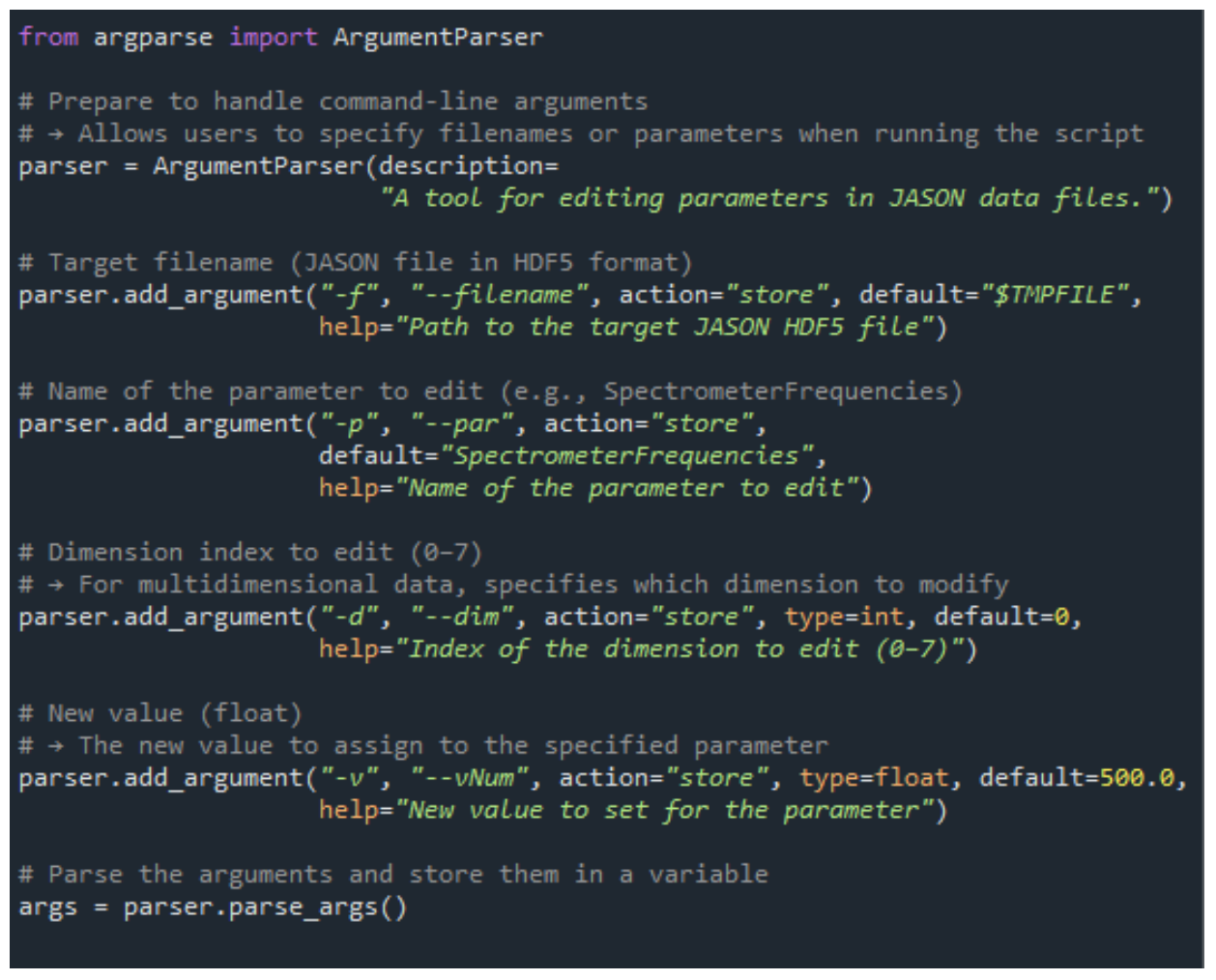
Figure 4. Excerpt from the jasonParEdit.py Script
About the jasonParEdit.py Script
jasonParEdit.py is a Python script designed to edit parameters within JASON data files, such as SW, SpectrumRef, and SpectrometerFrequencies.
It can be executed from the GUI to modify values interactively.
Figure 4 shows a portion of the jasonParEdit.py source code.
This script allows users to freely modify the parameters mentioned above.
Usage instructions are included at the top of the script and should be reviewed before execution.
How to Use
The operation procedure is summarized in Table 2.
An example of the GUI settings and input format is shown in Figure 5.
Table 2. Operation Steps for Using External Command in JASON GUI
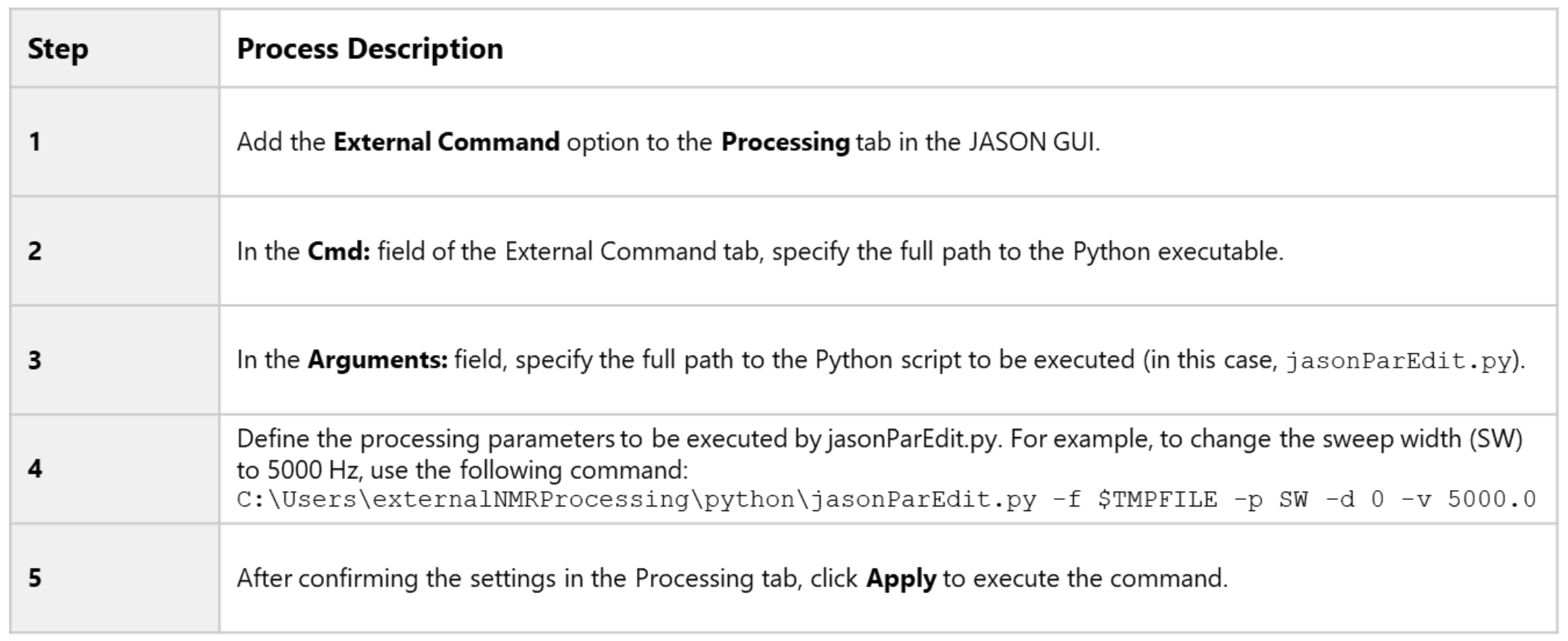
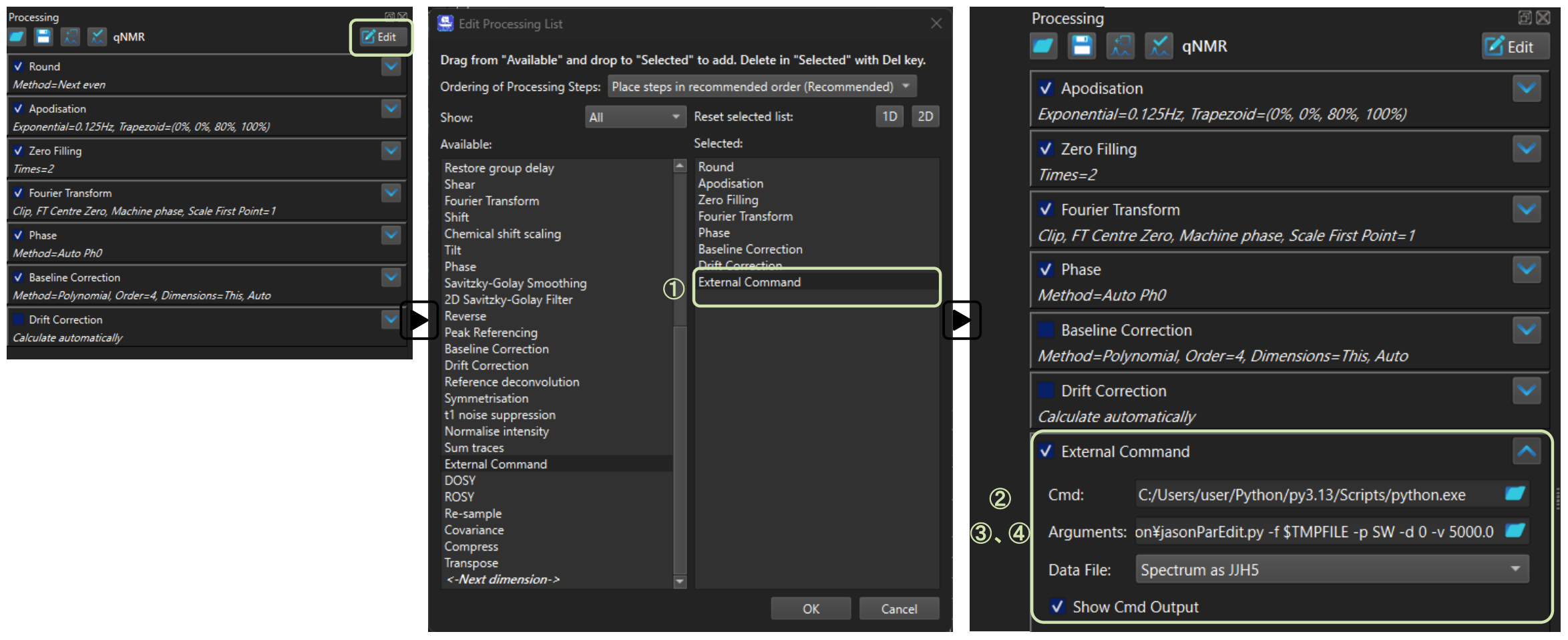
Figure 5. Example Configuration for jasonParEdit.py
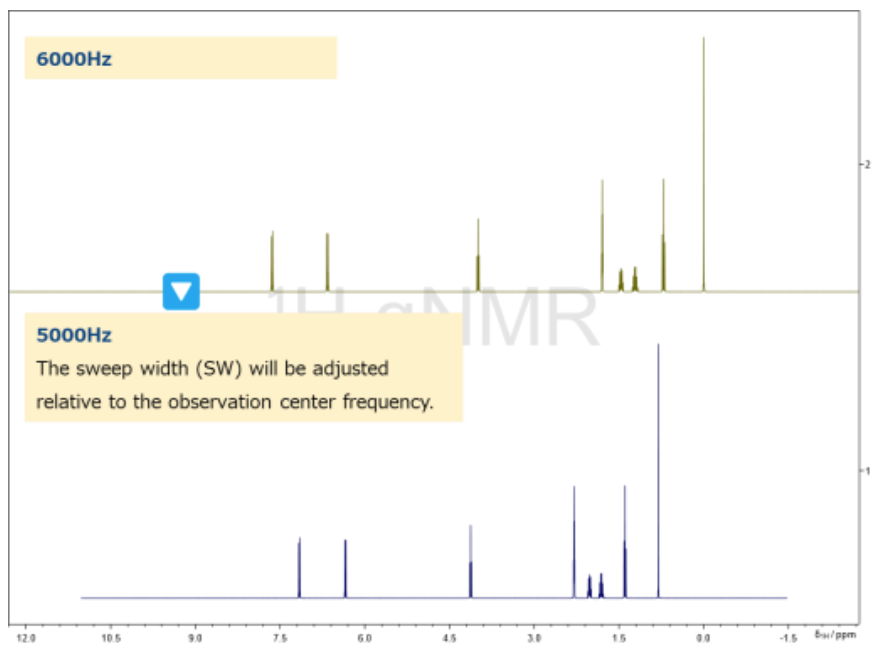
Figure 6. Example of SW Output from jasonParEdit.py
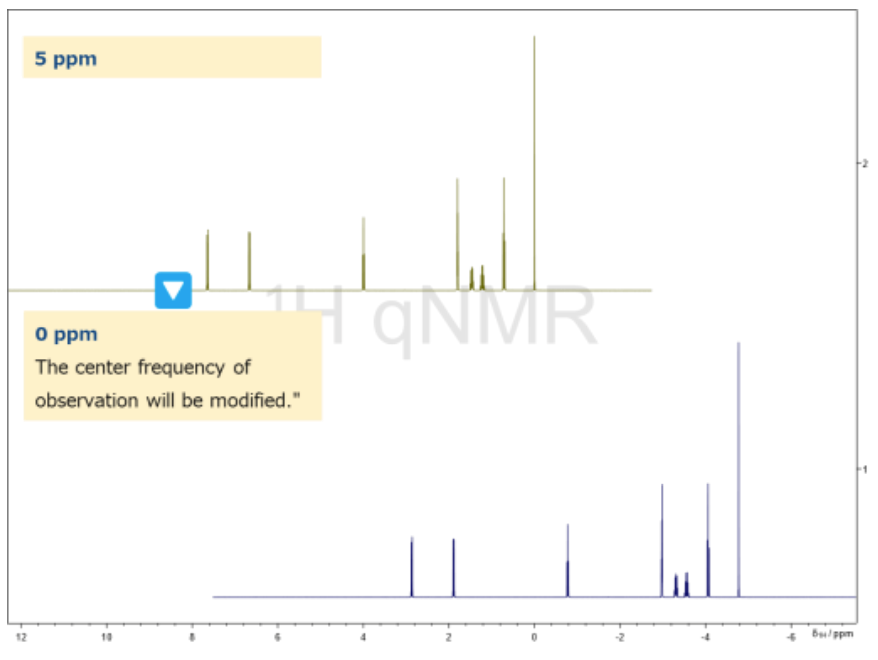
Figure 7. Example of SpectrumRef Output from jasonParEdit.py
Output Example
Figure 6 presents an example of the spectral output after processing.
The updated spectrum is reflected in the JASON GUI and can be compared with the original data.
Error Messages
If incorrect settings are provided during script execution, clear error messages are displayed to help identify the issue:
Unsupported parameter name: Error: parameter: XXX is not supported by this script.
Nonexistent attribute: Error: parameter: XXX does not exist.
Invalid dimension index: Error: dimension index must be in range of 0-7.
These messages ensure that any issues encountered after clicking the Apply button can be quickly diagnosed, making the script safe and user-friendly.
Example: Adjusting SpectrumRef with jasonParEdit.py
Figure 7 illustrates an example of adjusting the SpectrumRef parameter using jasonParEdit.py.
The operation method follows the same steps as described in Table 2.
Below is an example of a full path argument used to set the observation center to 0.0 ppm:
C:\Users\externalNMRProcessing\python\jasonParEdit.py -f $TMPFILE -p SpectrumRef -d 0 -v -0.0
Supplement: Exploring HDF5 File Structure
If the structure of an HDF5 file is unclear, the following types of exploration scripts can be used to inspect the types and locations of stored data:
Structure Exploration Script Example: Allows listing of all datasets within the file.
Metadata Inspection: Enables retrieval of measurement conditions and other metadata (e.g., frequency, sweep width).
Tips
For interactive exploration and inspection of HDF5 file contents, users can use HDFView, a free graphical browser provided by The HDF Group.
HDFView allows users to navigate the hierarchical structure of HDF5 files, view datasets, and examine metadata without any programming.
Summary
By combining JASON, HDF5, and Python, efficient processing and analysis of NMR data becomes possible.
The hierarchical structure of HDF5 enables flexible data extraction.
The External Command function facilitates seamless integration with external programs such as Python.
Custom processing and report generation enhance analytical flexibility.
Understanding HDF5 structure and utilizing exploration scripts are key to advanced applications.
References
External NMR Processing Scripts
[1] JEOL Analytical Software Network
[2] Python is a trademark or registered trademark of the Python Software Foundation.
[3] SpecInfo is a structure that stores metadata related to NMR measurements, such as experimental conditions. SW refers to the sweep width (measurement range), SpectrumRef indicates the center frequency, and SpectrometerFrequencies represents the observation frequency.
[4] .jjh5 is a file format used in JASON, based on the HDF5 structure.
Solutions by field
Related products
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.


