Identifying structural isomers using retention index
- Qualitative analysis of mixed xylenes in lacquer paint using msFineAnalysis iQ -
MSTips No. 470
Introduction
Typically, qualitative analysis using GC-QMS involves library database (DB) searches using mass spectra obtained by electron ionization (EI) method. However, when qualitative analysis is performed based solely on the similarity to the library spectrum, depending on the compound, multiple significant candidates may be obtained, or the wrong candidate may be selected as the identification result. Therefore, it is effective to use the method in combination with soft ionization (SI) methods such as photoionization (PI) to confirm the molecular ion. In this case, two measurement data, one from the EI method and one from the PI method, are obtained for one sample, making data analysis more complicated, so an integrated qualitative analysis software capable of analyzing the two data quickly and automatically is desirable. To this end, we have developed an integrated qualitative analysis software called "msFineAnalysis iQ" that automatically combines the analysis results of the EI method and the SI method.
However, when the target compound for qualitative analysis contains structural isomers, it may be difficult to distinguish them using only mass spectra. In this case, identification using the retention index (RI) in combination is useful. The retention index is an indicator of the time a compound is retained on a GC column, and each compound has its own unique retention index. Therefore, by comparing the retention index measurement value of an unknown compound with the retention index of a known compound, the compound can be identified.
In this study, a commercially available lacquer paint was measured by pyrolysis GC/MS. Then, integrated qualitative analysis was performed using msFineAnalysis iQ. In this MSTips, we will report an identification example of mixed xylenes (xylol) using retention index.
Experimental
The sample used was a commercially available lacquer paint (gold). A GC-QMS (JMS-Q1600GC UltraQuad™ SQ-Zeta, JEOL) was used for the measurements. A pyrolysis device (PY-3030D, Frontier Labs) was used for the sample pretreatment, and the sample was heated to 550°C. The ionization methods used were the EI method and the PI method. The detailed conditions for the pyrolysis GC/MS measurements are shown in Table 1. Both GC/EI and PI data were analyzed using the GC-QMS dedicated integrated qualitative analysis software msFineAnalysis iQ (JEOL).

JMS-Q1600GC UltraQuad™ SQ-Zeta
Table 1 Measurement condition

Results and Discussion
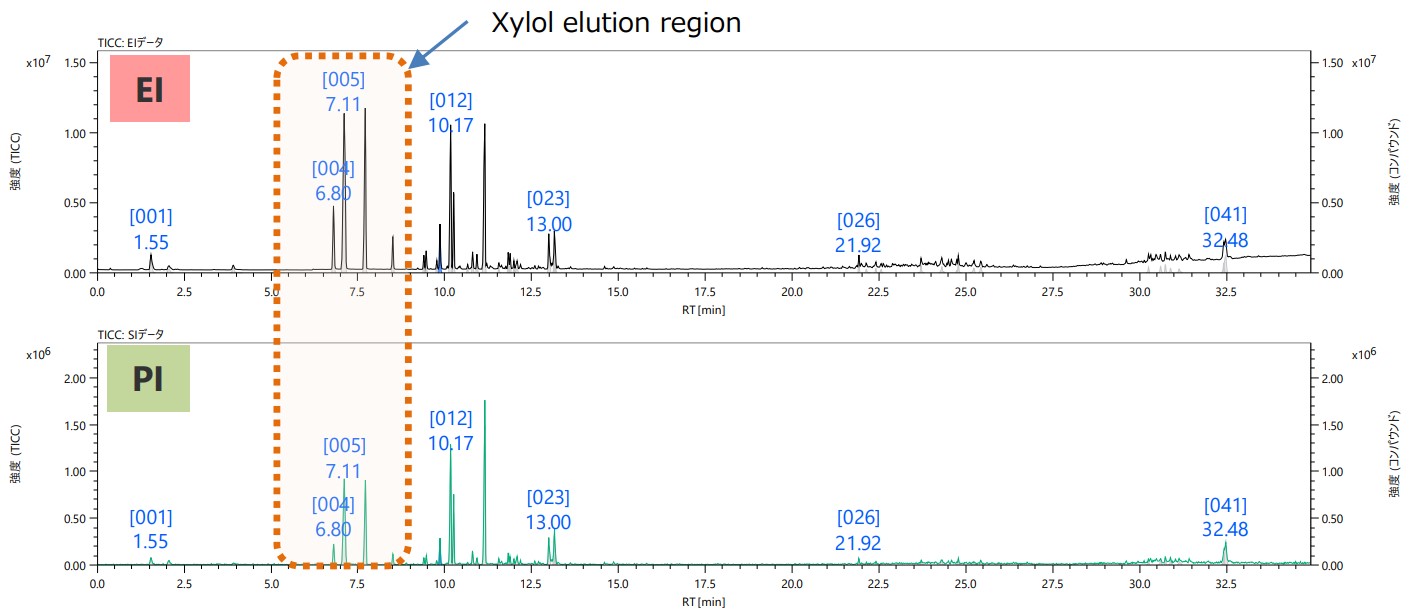
Figure 1 Total ion current chromatograms
Figure 1 shows the measurement results of lacquer paint (gold) using the pyrolysis GC/MS method. The upper row is the total ion current chromatogram (TICC) obtained by the EI method and the lower row is the PI method. In addition, Figure 2 shows an enlarged TICC image (RT5.5-9 minutes) where mixed xylene elutes and the EI/PI mass spectrum of the three peaks ID004-006. All three mass spectra in Figure 2 are similar, and are presumed to be structural isomers with the same molecular composition.
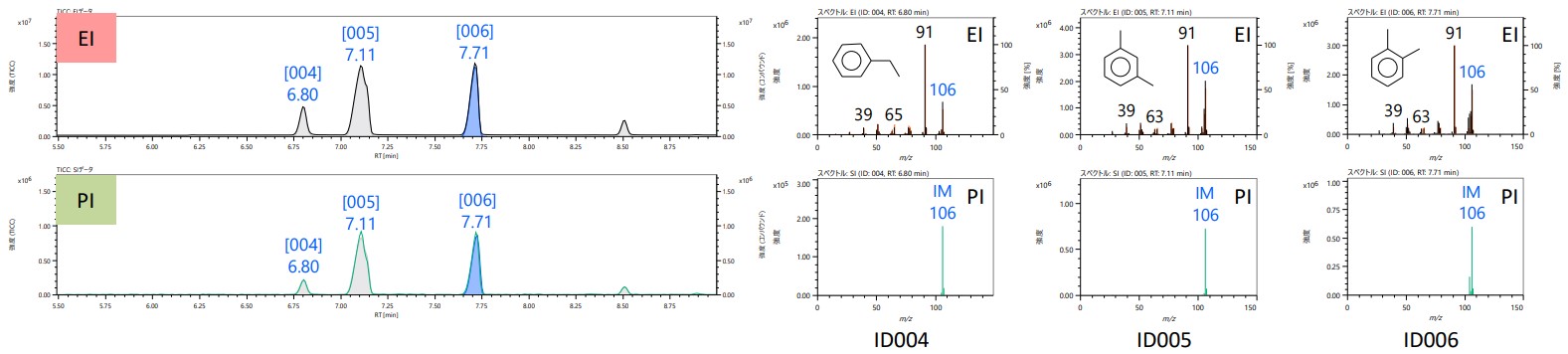
Figure 2 Expanded TICC and mass spectra of peak [ID004~ID006]
Table 2 Integrated qualitative analysis result of peak [ID004~006]

Table 3 shows the molecular formulas, structural formulas, boiling points, and retention index (RI) registered in the library for the four mixed xylene components. The GC column used for this measurement is a low-polar type, so it is thought that the structural isomers elute in roughly order of boiling point. Therefore, based on the boiling point information in Table 3, it is estimated that the four components of the mixed xylenes are eluted in the following order: Ethylbenzene, p-Xylene, m-Xylene, and o-Xylene. In addition, in the TICC in Figure 2, there are only three elution peaks. This is presumably because the boiling points of p-xylene and m-xylene differ by only 1°C, and so they cannot be separated on the chromatogram and are detected as a single peak.
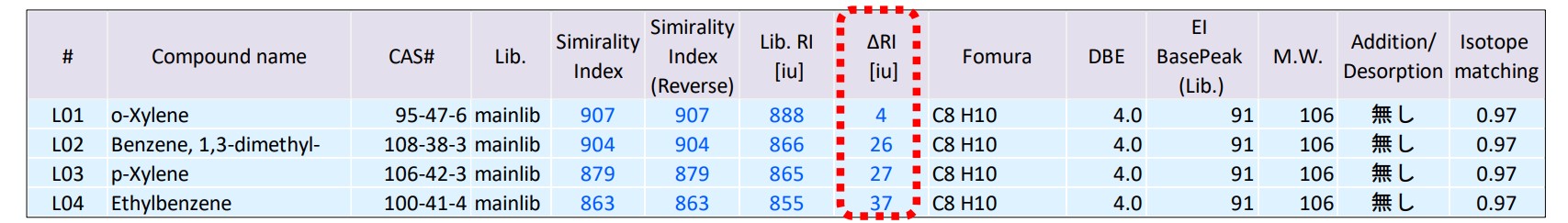
As an example, Table 4 shows a list of individual mass spectrum analysis results (top four candidates) for ID006 using msFineAnalysis iQ. Since the similarity obtained by library search was around 900 for all four candidates (mixed xylene components), indicating good agreement, it was difficult to distinguish between the isomers using mass spectra alone. However, the ΔRI value made it possible to narrow down the candidates to o-xylene, which has smallest error of ΔRI=4. Furthermore, for the two peaks ID004 and 005 in Table 2, it was possible to narrow down the identification of ID004 as ethylbenzene with a ΔRI of 7, and ID005 as 1,3-dimethylbenzene (= m-xylene) with a ΔRI of 6.
From the above, it was possible to narrow down the structural isomers for the three peaks ID004 to 006 using RI information.
Table 3 Information on the 4 components of mixed xylene
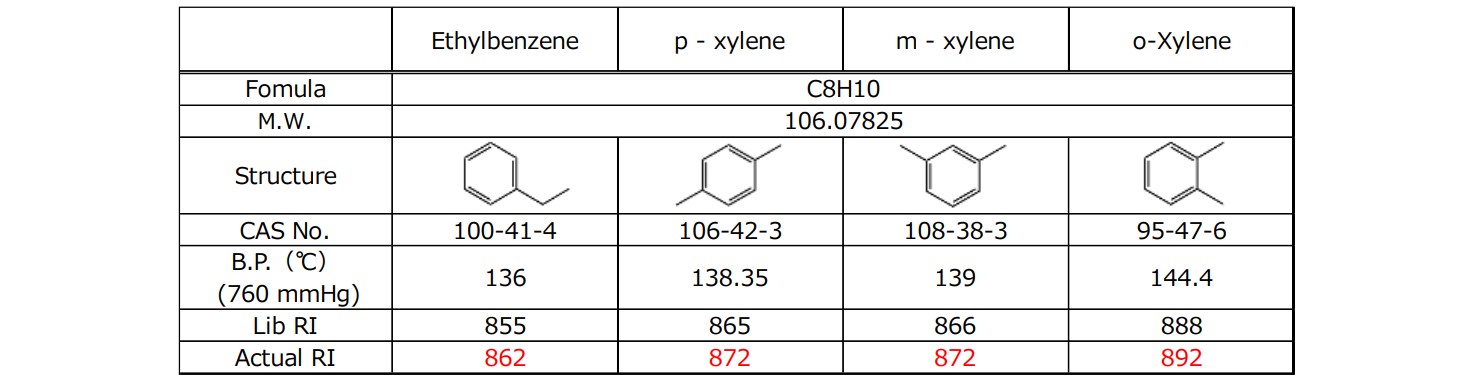
Table 4 Individual integrated qualitative analysis result of peak [ID006]
Conclusion
In this report, we showed an example of identification structural isomers using the retention index function of msFineAnalysis iQ. Although it is difficult to distinguish between structural isomers in mass spectrum analysis , by using this software and utilizing the retention index, which is the original qualitative analysis method of GC, it is expected that the qualitative accuracy of qualitative analysis using GC-QMS will be improved and analysis work will be more efficient.
Solutions by field
Related products
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.

