Confirmation of the chemical formula of heat/light sensitive compounds using field desorption coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry
MSTips No. 403
Introduction
Field desorption (FD) is a soft ionization technique useful for producing molecular ions in an MS ion source. The combination of high-resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometry (HRTOFMS) and FD is useful for direct MS measurement of a sample, and provides information for identifying the chemical formula of synthetic compounds and confirming the molecular weight. Since FD-HRMS vaporizes and ionizes a sample rapidly in a vacuum, and does not use a gas chromatograph, it has advantages for measuring unstable compounds, such as those sensitive to heat and light.
The FD emitter consists of carbon whiskers on a tungsten wire, and is inserted into the ion source using a probe. After coating the emitter with a sample solution and installing the probe to MS, FD measurement is performed by turning on the high voltage in the mass spectrometer. The most common method for coating the FD emitter is using a micro-syringe. This application note reports the syringe sampling procedure, and measurement results of example compounds that are sensitive to heat and light.
Measurement
Two bis(diazo) compounds sensitive to heat and light were measured. The corresponding chemical structures are shown in Figure 1. The sample was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran to concentration of 10 mg/mL (Sample solution).
Table 1 shows the details of the measurement conditions for FD-HRMS analysis. The sampling procedure and tools are illustrated in Figure 2.
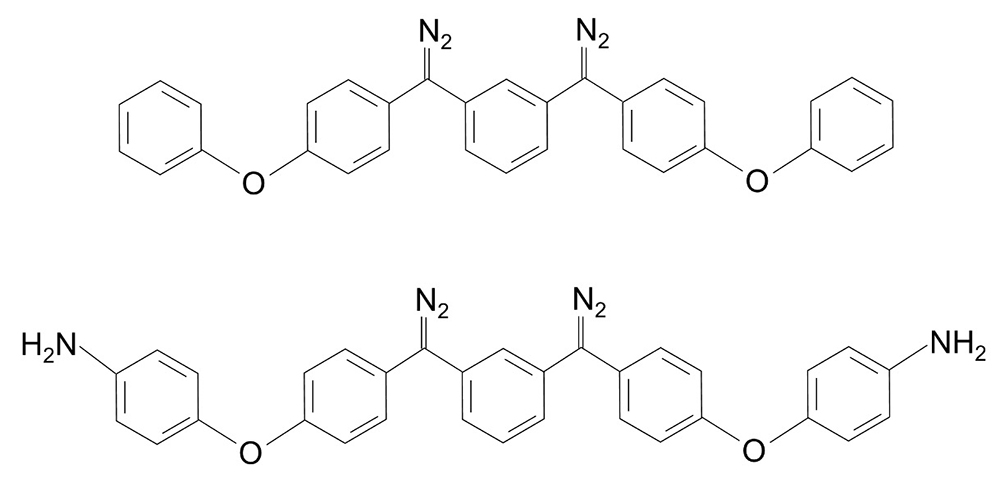
Figure 1. Chemical structures
Table 1. Measurement and analysis conditions
| HRMS | |
|---|---|
| Sampling method | Syringe |
| Sample volume | 4 μL |
| TOFMS | JMS-T2000GC (JEOL) |
| Ionization | FD+ : -10 kV, 40 mA |
| Cathode voltage | -10 kV |
| Emitter current program | 0 mA → 25.6 mA/min → 40 mA |
| Monitor ion range | m/z 35-1600 |
Sampling Procedure
- Set the probe on the probe stand.
- Pull up 4 µL of sample solution using the micro-syringe, and set the micro-syringe on the syringe stand.
- Move the tip of the micro-syringe close to the emitter.
- Push the plunger to make droplet of sample solution, then coat the emitter with the sample droplet.
Table 2. The features of syringe sampling with tool
| Sampling operability | Requires familiarity with sampling |
|---|---|
| Sample volume | Approx. 4 µL/measurement |
| Merits |
|
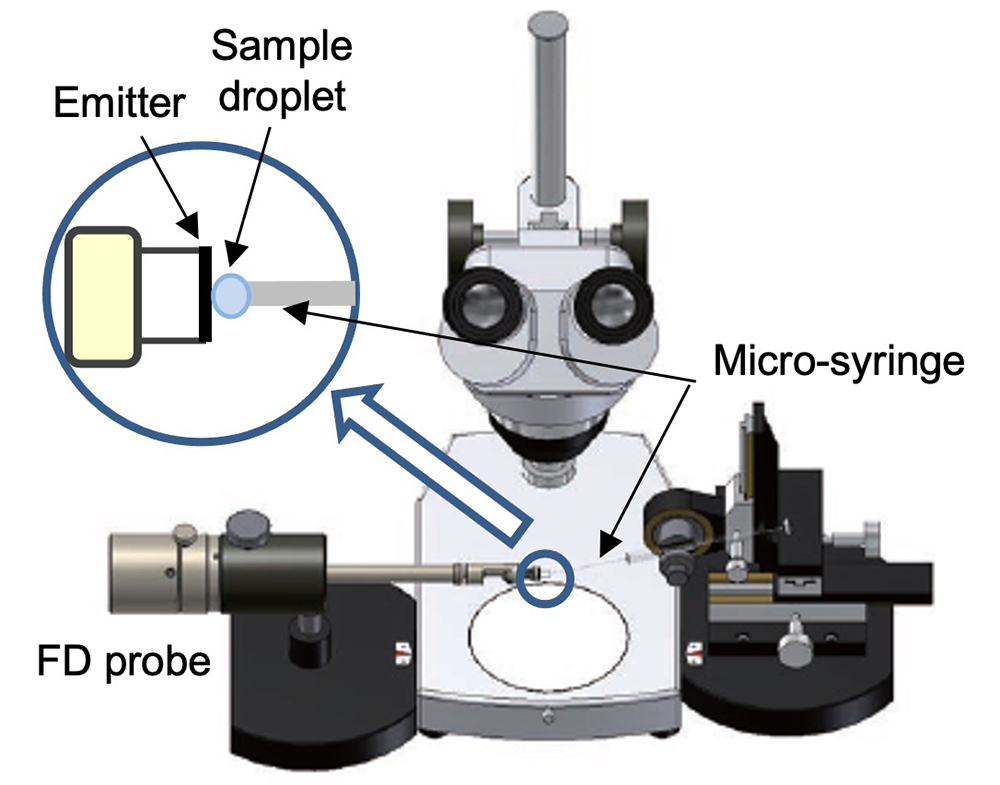
Figure 2. Scheme of syringe sampling tool
Result
FD-HRMS mass spectra were shown in Figure 3. The molecular ion [M]+・ was primary component detected from each sample. Some impurities or reacted compounds were also detected, though peak intensity was notably less than the molecular ion peak. The accuracy of the m/z measured for both molecular ions was less than 1 mDa of error.

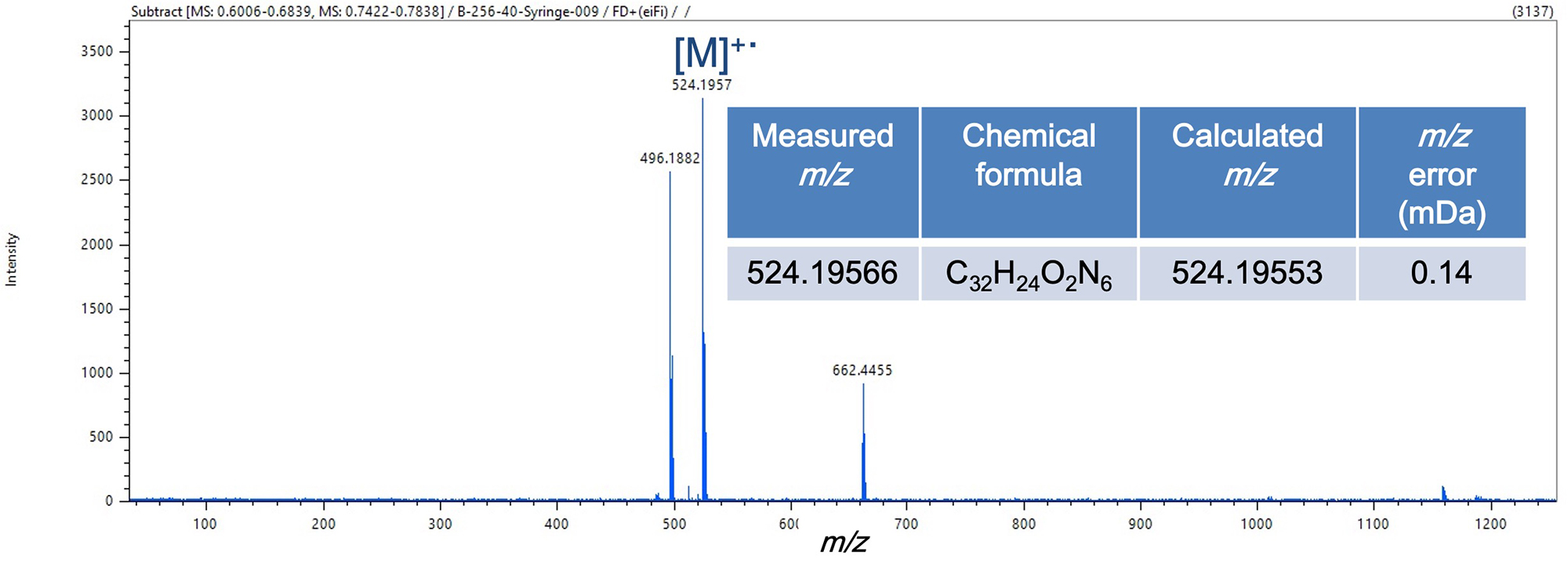
Figure 3. FD mass spectra and estimation results of chemical formula from exact mass of molecular ions
The advantages of the syringe-sampling method are shown in Table 2. Although the method requires some familiarity with the sampling operation, only a small sample volume is required, because it can be dispensed with a micro-syringe. The method can also result in less contamination at the emitter, because the sample is applied only to the emitter wire. It is also possible to get a higher concentration of sample on the emitter by repeatedly applying the sample solution. Using an air tight micro-syringe for sampling is advantageous when using highly volatile solvents.
Summary
In this application note, we reported the FD-HRMS measurement results of two heat/light sensitive compounds using a micro-syringe sampling method. Since FD measurement takes only 1 to 3 minutes from applying sample to completion of measurement, it is a useful analytical method that can help rapidly determine the chemical composition and molecular weight of sample compounds, even if the target compounds are sensitive to heat and light.
Acknowledgement
The author would like to thank Dr. Xiaosong Liu (刘晓松博士) at Oxford Suzhou Center for Advanced Research for providing the sample and for agreeing to use the data.
Solutions by field
Related products
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.
Contacts
JEOL provides a variety of support services to ensure that our customers can use our products with peace of mind.
Please feel free to contact us.

