Comprehensive Analysis of Acetylacetonate Complexes
ED2022-04E
Various structural analysis methods for acetylacetonate complexes with XtaLAB Synergy-ED, JEOL MS and NMR
XtaLAB Synergy-ED allows molecular structural analysis of micro-crystals. It is quite effective for transition metal complexes in the difficult case of crystallization. Acetylacetonate (acac) anion is a bidentate ligand and shows various complex compounds. The ligand is an ion that bonds to a central transition metal to form octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar and so on. In the example below, results are shown of electron diffraction structural analysis of Chromium(III) acetylacetonate (Cr(acac)3), Vanadyl (II) acetylacetonate (Vo(acac)2) and Copper(II) acetylacetonate (Cu(acac)2) complexes by XtaLAB Synergy-ED and the schematic diagram of 3d orbital.
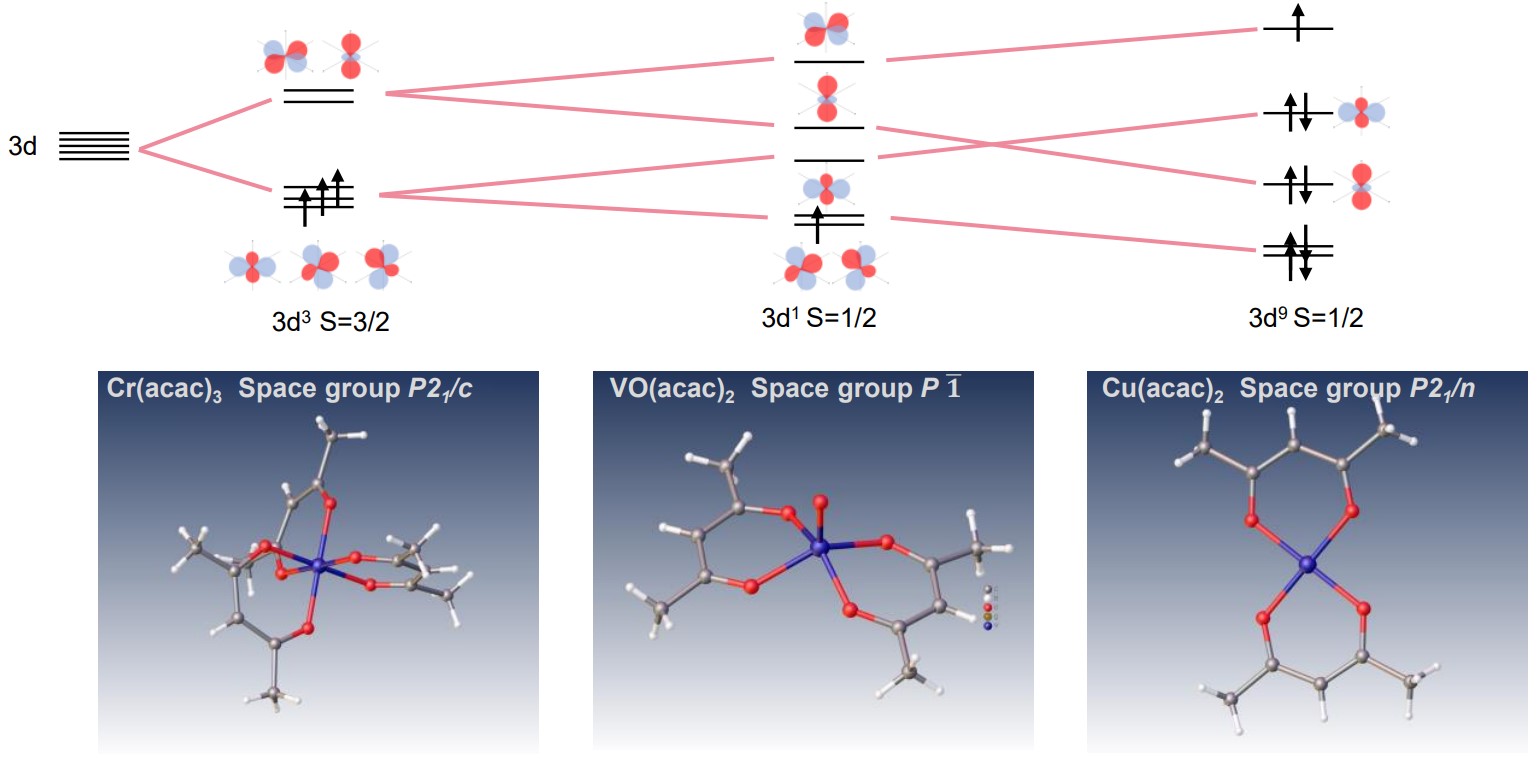
Electron diffraction structure analysis of Cr(acac)3, Vo(acac)2 and Cu(acac)2 complexes, XtaLAB Synergy-ED
Structure analysis of octahedral acetylacetonate complex, Rhodium(III) acetylacetonate
JEOL mass spectrometer (MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrometer provide details of chemical structure information of acetylacetonate complexes for molecular structure determination. In the example below, the left-hand is the result of MS and NMR analysis and the right-hand shows the resulting structural model from electron diffraction structure analysis of Rh(acac)3.
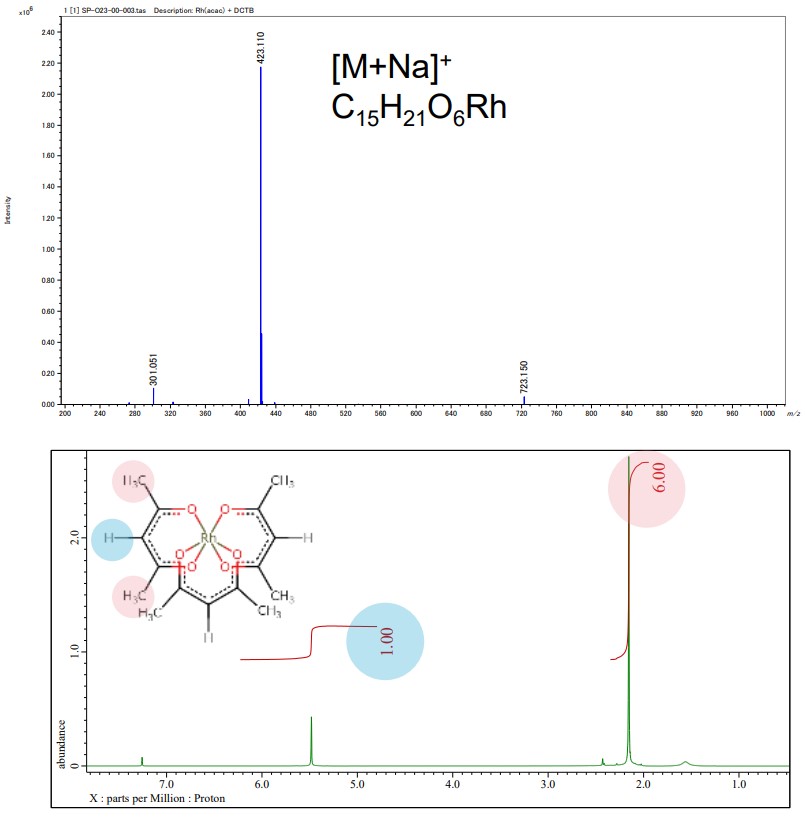
Above : Mass spectrum of Rh(acac)3, JMS-S3000 SpiralTOF™-plus 2.0
Below : 1H NMR spectrum of Rh(acac)3, JNM-ECZL 500R
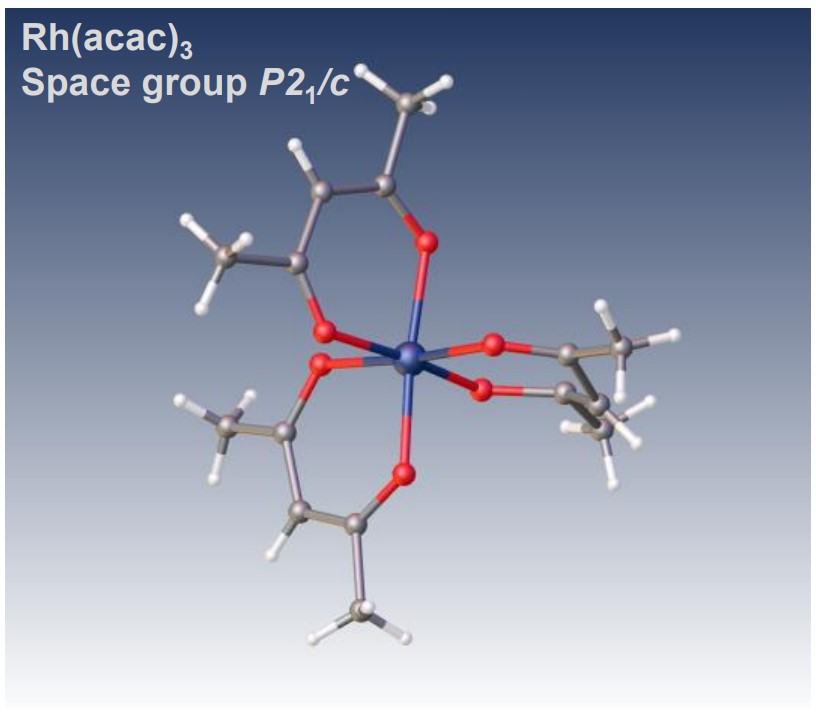
Electron diffraction structure analysis of Rh(acac)3, XtaLAB Synergy-ED
Spin state analysis of octahedral acetylacetonate complex
Rh(acac)3 has two possible electron configurations, denoted as high spin of 4d6 S=2 and low spin of 4d6 S=0. On the other hands, Cr(acac)3 has a spin state of d3 S=3/2 and shows paramagnetism. In the example below, the green line is a 1H NMR spectrum of Cr(acac)3 and the brown line is Rh(acac)3. The peaks of ligand of Cr(acac)3 spectrum are sifted and broadened with the Fermi-contact interaction of Cr3+ and the ligand. On the other hand, the spectrum of Rh(acac)3 shows that the peaks of the ligand are not sifted and its electron configuration is the low spin state 4d6 S=0.
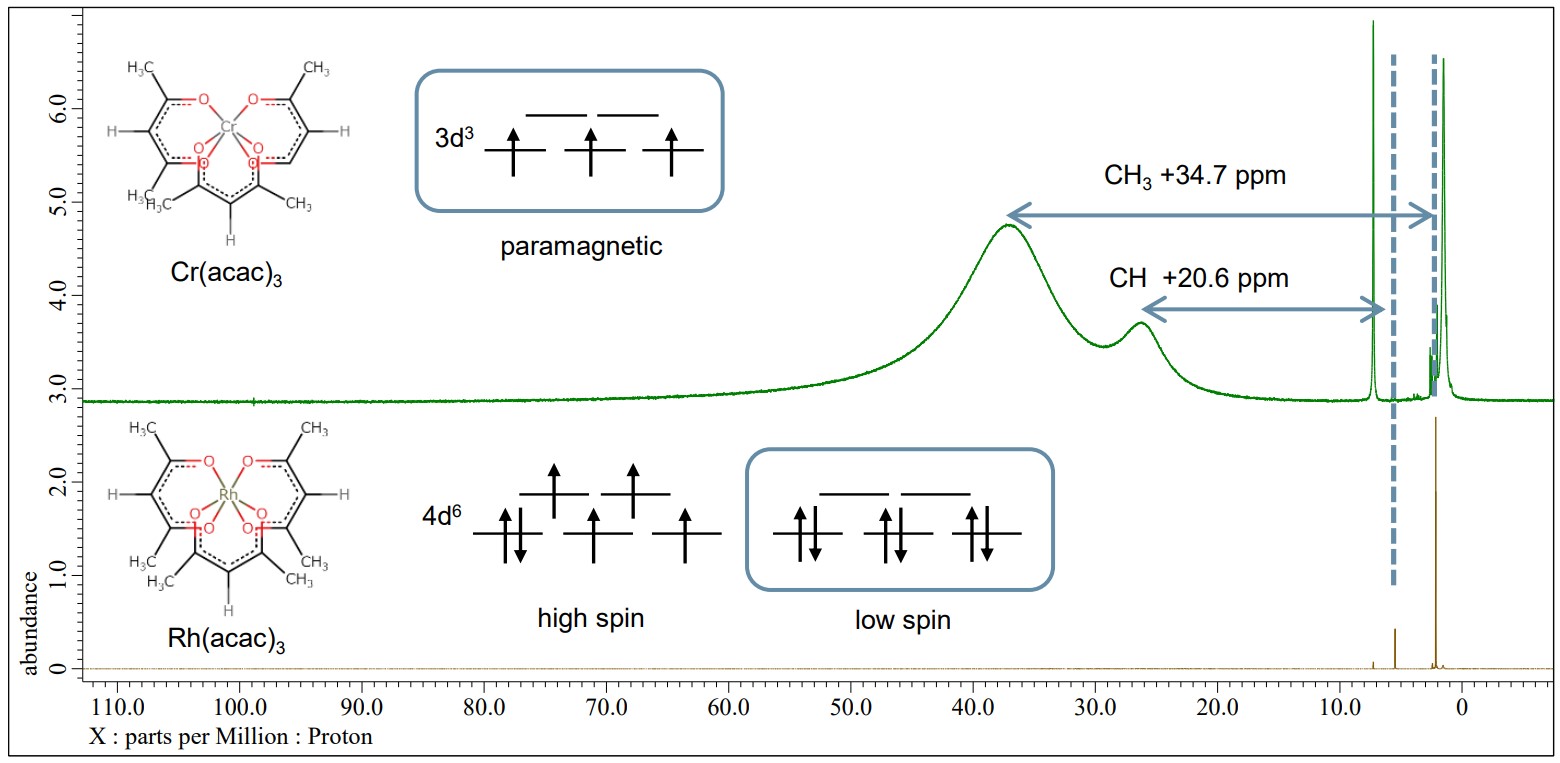
Green : 1H NMR spectrum of Cr(acac)3, JNM-ECZL 500R
Brown : 1H NMR spectrum of Rh(acac)3, JNM-ECZL 500R
Magnetic susceptibility and electron configuration of acetylacetonate complexes
The electron configuration of the transition metal is an important factor in the molecular structure of transition metal complexes. The unpaired electrons of the transition metal can be estimated by determining magnetic sensitivity. The magnetic susceptibility of complexes comes from the magnetism at the atomic level of which they are made, and is dominated by the magnetic moments of electrons. The presence of paramagnetic ions causes the chemical shifts of other compounds in the solution to move. This effect can be used to estimate the magnetic susceptibility of transition metal complexes and subsequently the electronic structure of transition metal ions (Evans method [1]). With the result of the Evans method, the effective magnetic moment is calculated to determine the electron structure of transition metal. In the example below, the table shows the effective magnetic moment of Cr(acac)3, VO(acac)2 and Cu(acac)2 complexes estimated using 1H NMR spectra.
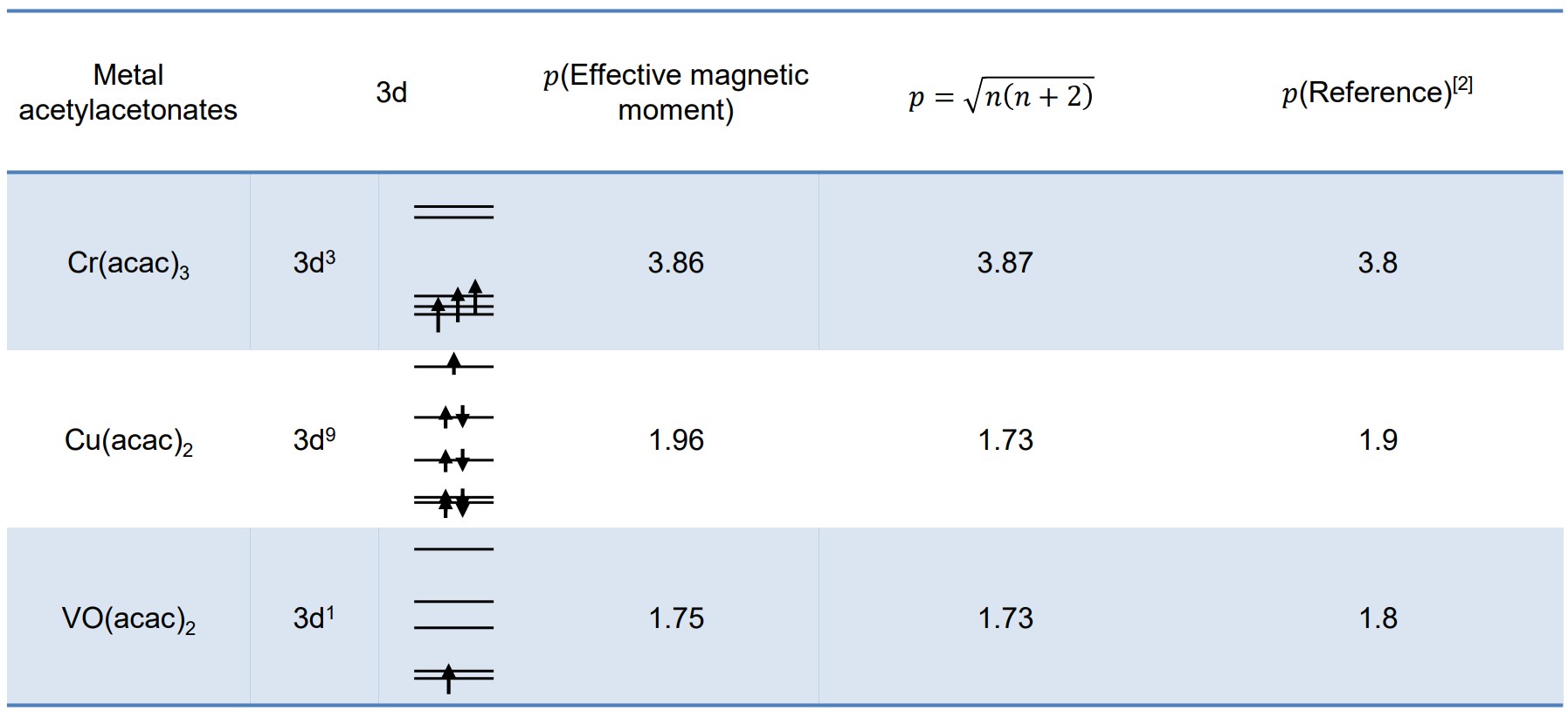
[1] D. F. Evans, J. Chem. Soc. 1959, 2003.
[2] C. Kittel, Introduction to Solid State Physics, 7th edition
Solutions by field
Related products
Related information
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.



