Workflow for Molecular Structure Analysis of Transition Metal Complexes
ED2022-03E
Comprehensive analysis of transition metal complexes with XtaLAB Synergy-ED, JEOL MS and NMR
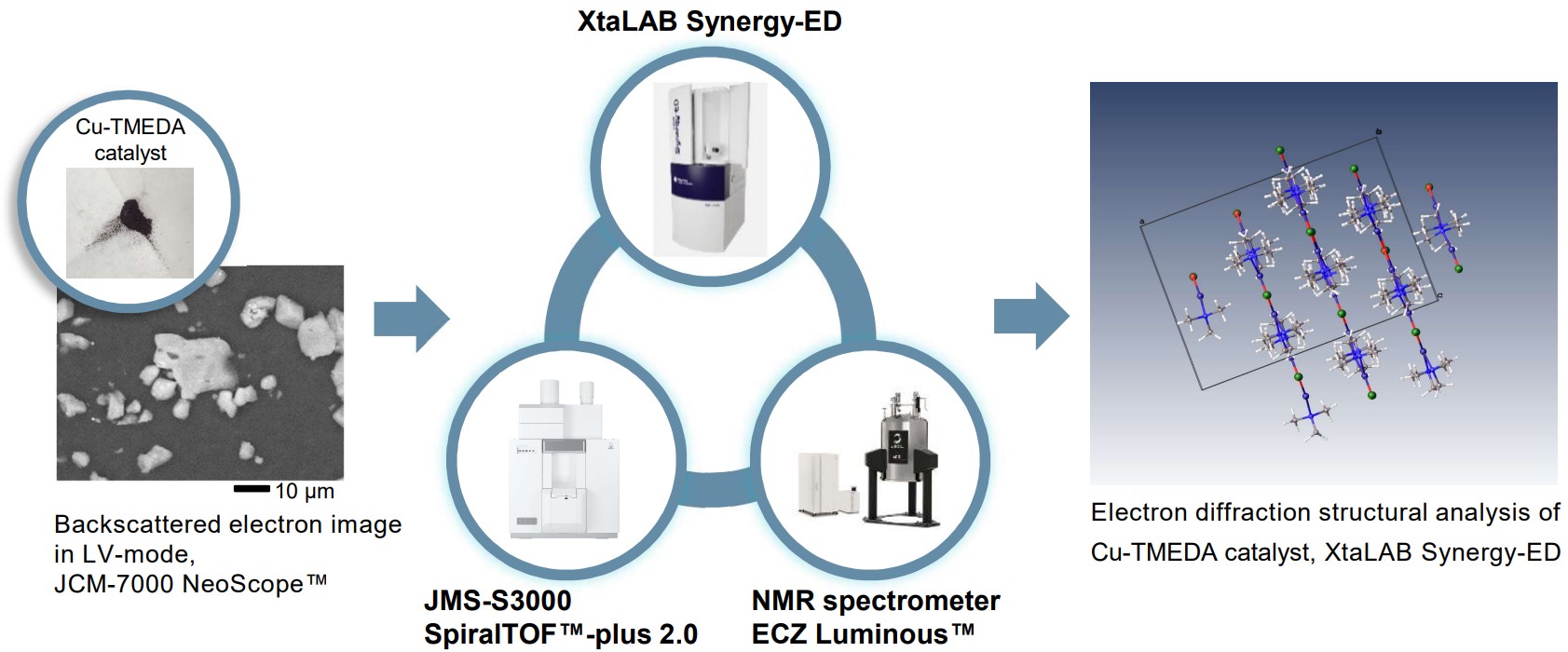
XtaLAB Synergy-ED allows molecular structure analysis of micro-crystal. This feature is quite effective in the difficult case of crystallization, such as transitional metal complexes. Furthermore, the comprehensive analysis using JEOL mass spectrometer (MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) provides detailed information for molecular structure determination.
Structure analysis of acetylacetonate complex, Copper(II) acetylacetonate
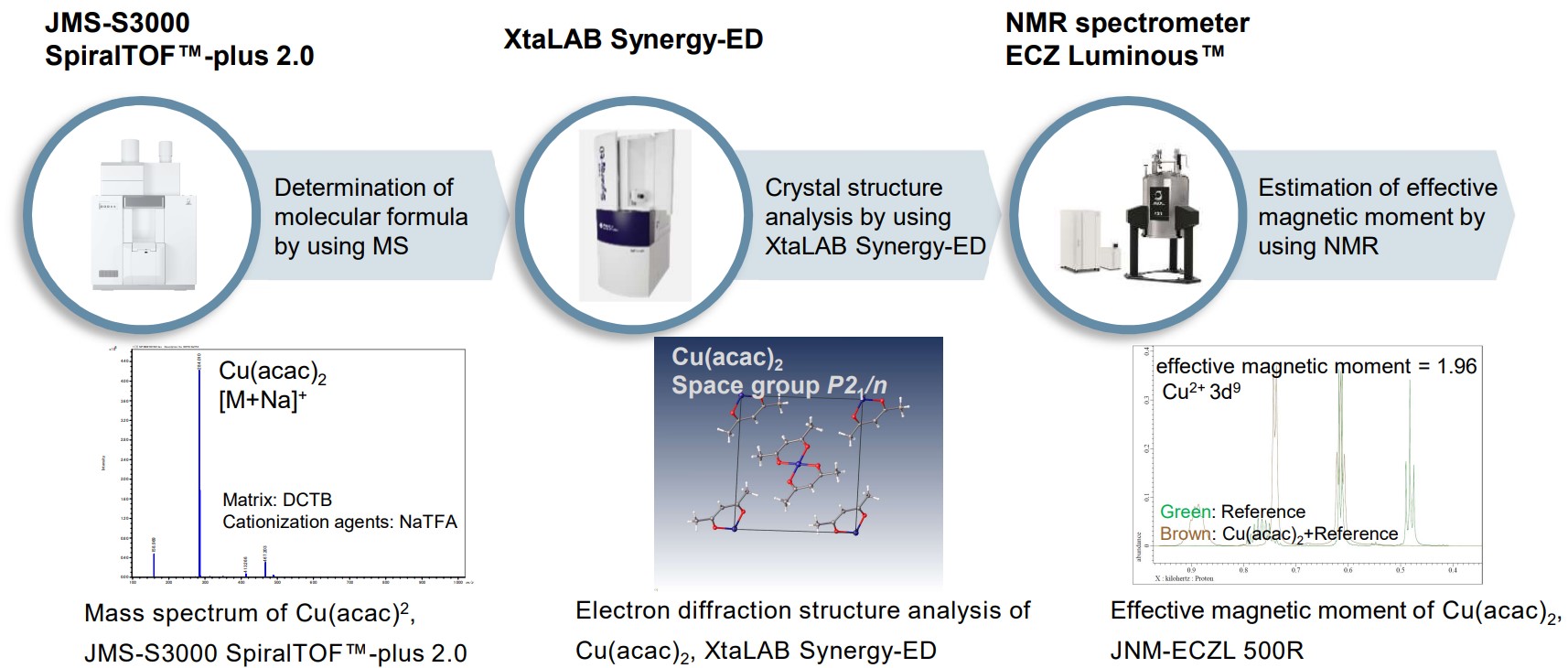
Transition metal complexes often form complicated structures, therefore it is important to analyze them from many directions with various analytical methods for molecular structure analysis. For example, the elemental composition of a sample is analyzed with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and its molecular formula is determined by using MS (shown the left). Moreover, the molecular structure is analyzed with micro-crystals by using XtaLAB Synergy-ED (shown the center). In addition, it is effective to determine the electronic structure of a metal ion of paramagnetic complexes. NMR provides the analysis of magnetic susceptibility, and then it is possible to estimate the state of unpaired electrons (shown the right). On the other hand, for diamagnetic complexes, it is also possible to analyze the details of ligands and the state of coordination with NMR.
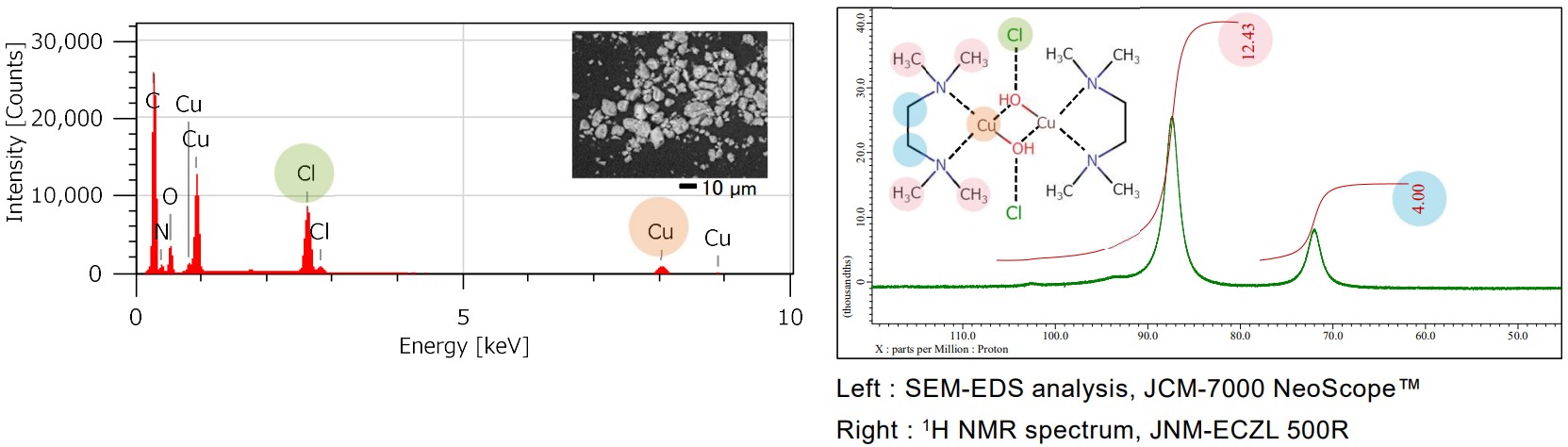
Elemental composition and ligands of Cu-TMEDA catalyst with SEM-EDS and NMR analysis
SEM-EDS provides detailed information of elemental composition, furthermore NMR allows the analysis of ligands. The chemical structures of transition metal complexes can be correctly analyzed through the comprehensive analysis of EDS and NMR. In the example below, the left-hand shows the result of the elemental composition analysis with SEM-EDS, JCM-7000 NeoScope™ and the right-hand shows the result of the ligands analysis with NMR, JNM-ECZL 500R.
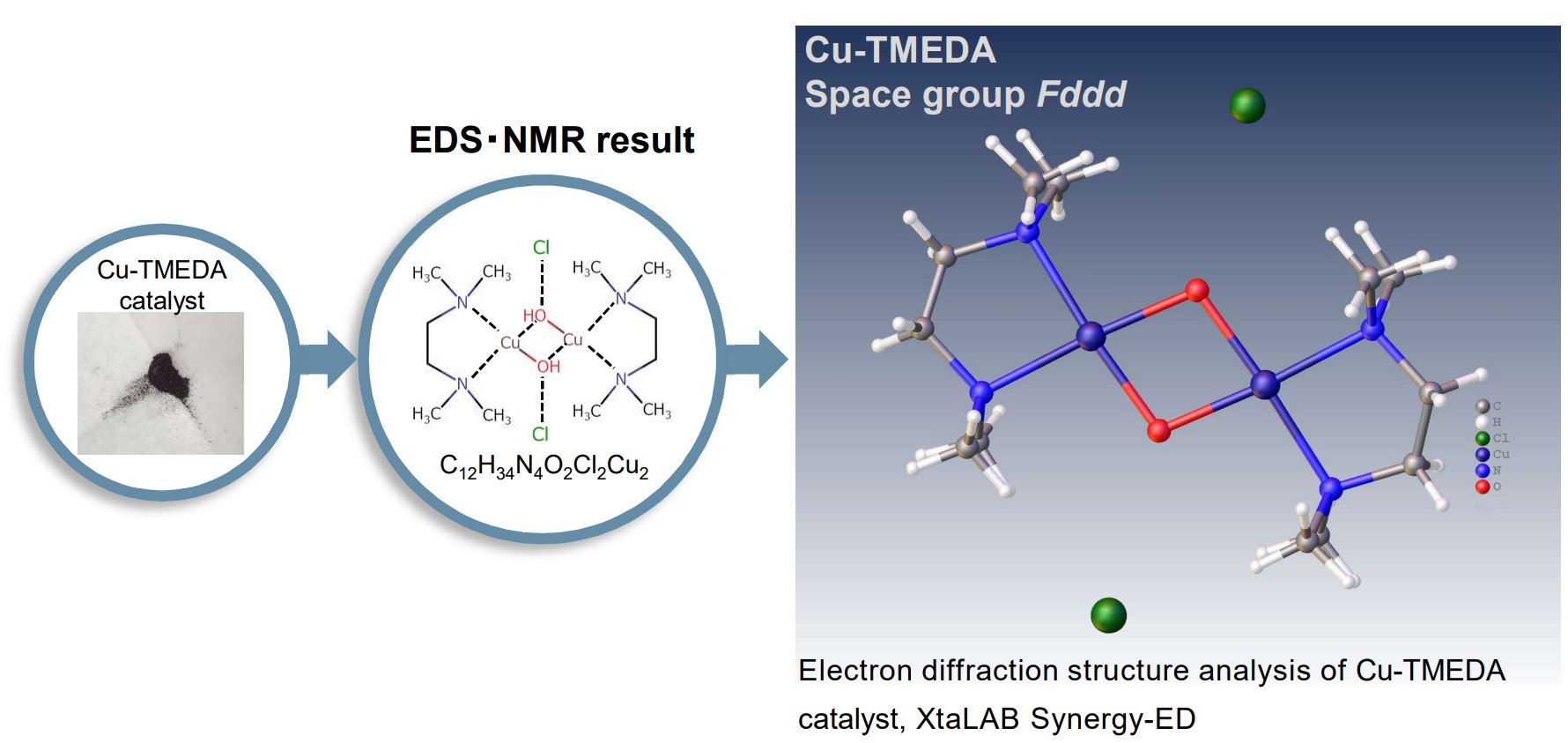
Structure determination of submicron particles of Cu-TMEDA catalyst with XtaLAB Synergy-ED
XtaLAB Synergy-ED allows single crystal electron diffraction analysis with submicron particles. The result of electron diffraction analysis is refined by using the result of EDS and NMR, finally validated to show the resulting structural model.
Magnetic susceptibility of Cu-TMEDA catalyst with paramagnetic NMR spectroscopy
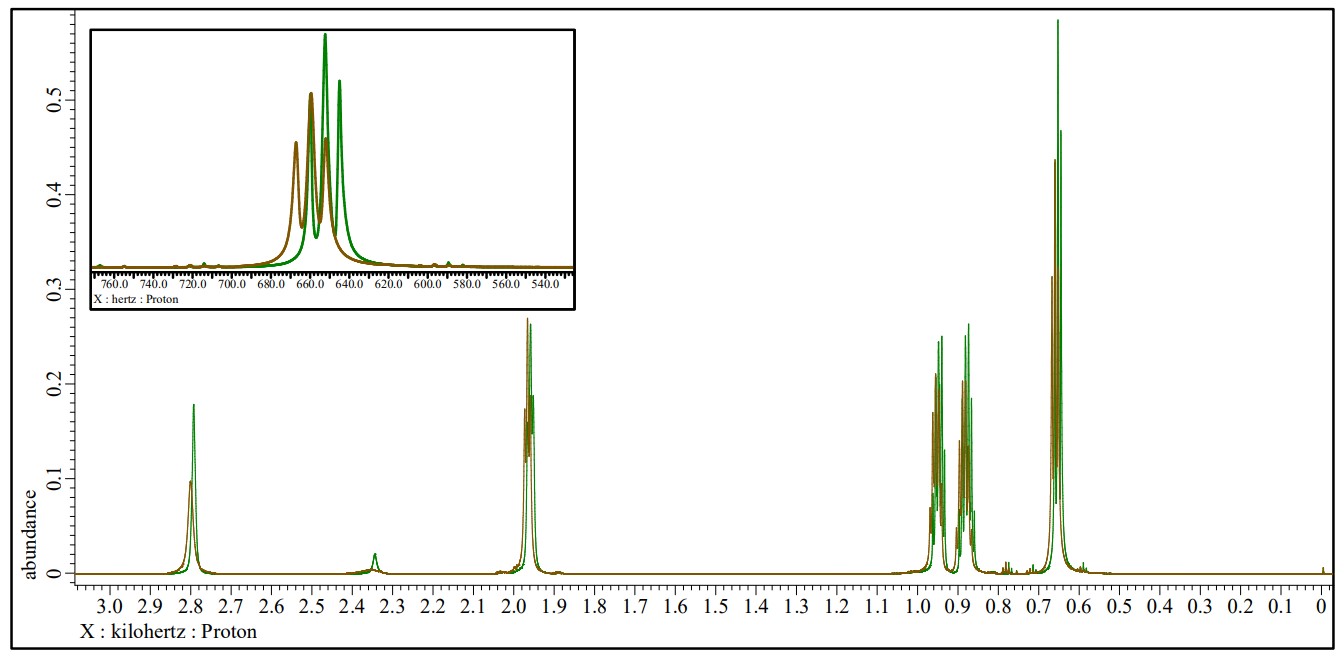
Green : 1H NMR spectrum of the reference solution (1-Butanol), JNM-ECZL 500R
Brown : 1H NMR spectrum of Cu-TMEDA catalyst dissolved in the reference solution, JNM-ECZL 500R
The presence of paramagnetic ions causes the chemical shifts of other compounds in the solution to move. This effect can be used to estimate the magnetic susceptibility of transition metal complexes and subsequently the electronic structure of transition metal ions (Evans method [1]). The results of EDS, NMR and XtaLAB Synergy-ED indicate that Cu2+ ion in Cu-TMEDA catalyst has a square planar structure with the Cu2+ ions sharing oxygen. In this structure, each Cu2+ ion has 3d9 S=1/2 for the nine d electrons of Cu2+ in a square‐planar field. Using the result of Evans method, the expected effective magnetic moment of electronic configuration is calculated to be 2.81 µB. As the effective magnetic moment is much closer to the value calculated from S=1 (2.83 µB), according to these results, it is thought that Cu-TMEDA catalyst shows paramagnetism of s=1 system for two copper ions.
Solutions by field
Related products
Related information
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.



