13C-13C homonuclear correlations in solid-state NMR
NM120005E
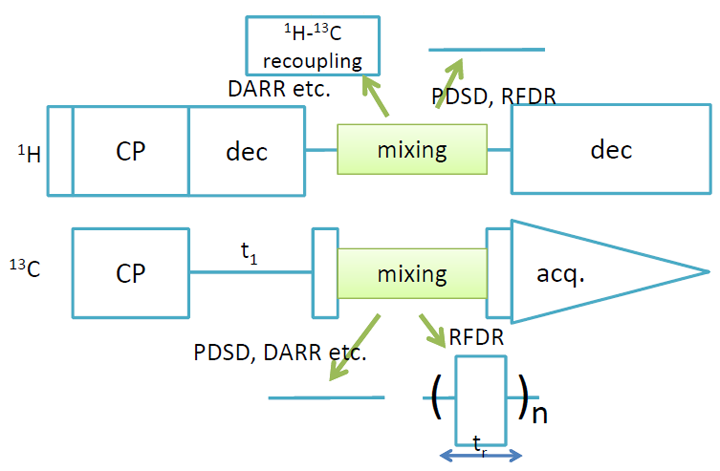
Magic angle spinning (MAS) suppresses anisotropic interactions, leading to high resolution and sensitivity. This also results in the suppression of 13C-13C spin diffusion even in uniformly 13C labeled samples. 13C-13C spin diffusion without any rf-field irradiation such as in PDSD experiments (Proton-Driven Spin Diffusion) is inefficient; a PDSD spectrum (A) was obtained with a mixing time of 10 ms. The 13C-13C dipolar interactions can be re-introduced by rotor-synchronous rf-irradiation such as in Radio Frequency Driven Recoupling (RFDR) experiments. An RFDR spectrum (B) gives 13C-13C correlations with a much shorter mixing time of 1.6 ms. Although RFDR is a very efficient method to recouple 13C-13C interactions, the dipolar truncation hampers us to obtain two-bond correlations; only directly bonded 13C-13C correlations are observed in (B). This can be overcome by second- order recoupling methods like DARR, PARIS, SHANGHAI, etc. These methods achieve higher efficiency than PDSD and give two-bond correlations as in (C) and (D). If the dipolar truncation is acceptable, RFDR gives the best efficiency; if not, second-order recoupling methods are the best.
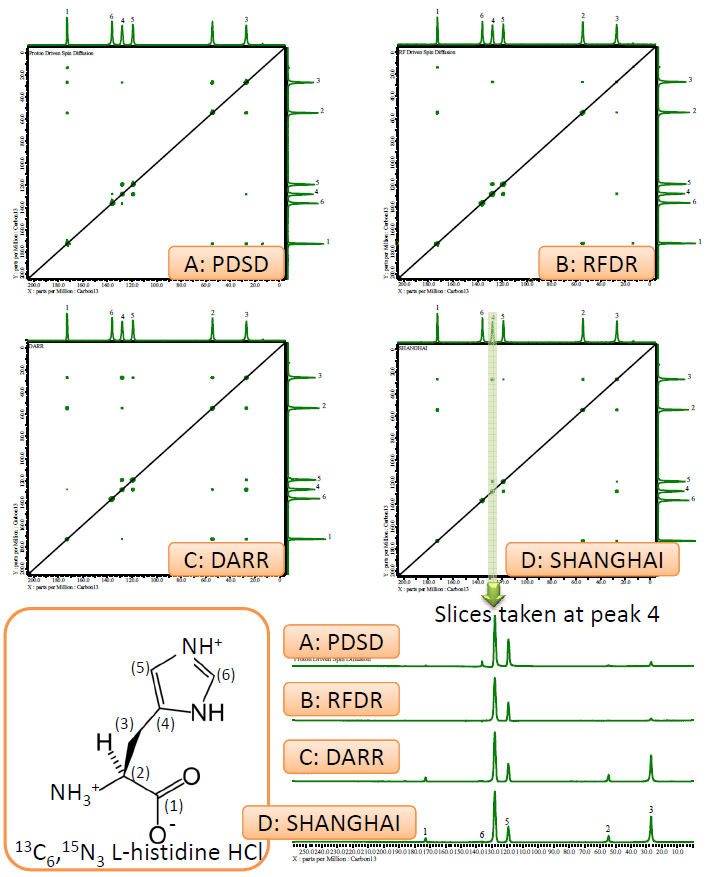
JNM-ECA500, 3.2mm HXMAS, 20 kHz MAS
Reference
DARR: Chem. Phys. Lett. 344 (2001) 631, PARIS: J. Magn. Reson. 488 (2010) 10, RFDR: J. Magn. Reson. 223 (2012) 107, SHANGHAI: J. Magn. Reson. 212 (2011) 320.
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.
