Shortening measurement time by multiple acquisition experiments
NM200008E
Multiple acquisition measurements have been attracting a lot of attention as a method for shortening measurement time in recent years.
These sophisticated experiments allows us to acquire multiple 1D or 2D NMR data in one measurement on an instrument equipped with a single receiver or multiple receivers. Multiple acquisition experiments can significantly shorten the total experimental time compared to acquiring data conventionally.
In addition, multiple acquisition experiments can also benefit from Non Uniform Sampling (NUS), therefore additional shortening of measurement time is possible. However, if there is a significant difference in sensitivity between the experiments combined in the multiple acquisition experiment, it is necessary to set the number of scans according to the least sensitive experiment.
① NOAH method
NOAH (NMR by Ordered Acquisition using 1H-detection) is a useful method which can acquire multiple 2D spectra at once even without using multiple receivers. Fig. 1 shows a NOAH pulse sequence which acquires 2D 1H-13C HSQC, 1H-13C HMBC and 1H-1H COSY spectra altogether.
All the 2D spectra are generated simultaneously after the experiment has finished. Fig. 2 shows results of NOAH-3 of 10% cinnamic acid cis-3-hexen-1-yl ester in CDCl3. These spectra can be obtained within 5 minutes by using NUS.
A dedicated automation was made for NOAH to improve its usability (Fig. 3). User sets the spectrum width, number of Y points, number of scans, and selects/unselects the NUS option. As individual filenames and process lists are automatically set for each data file after the measurement has completed, these data can be analyzed in the same way as traditionally acquired data.

Fig. 1: Pulse sequence of NOAH-3
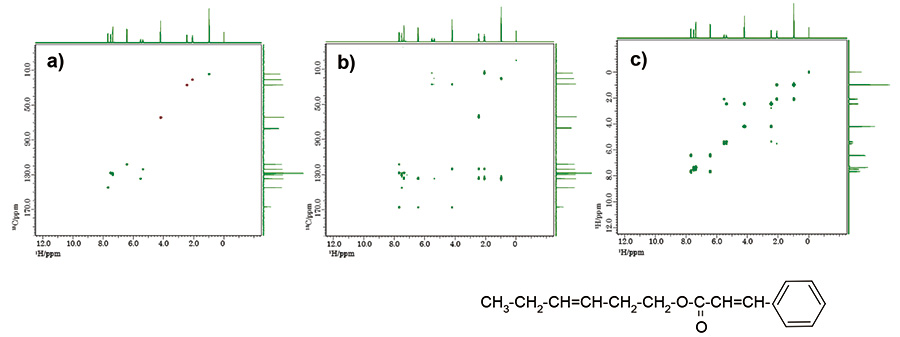
Fig. 2: NOAH-3: a) HSQC, b) HMBC, c) COSY
Number of scans: 1, Y points: 256, NUS density: 25%, exp. time: 5 min
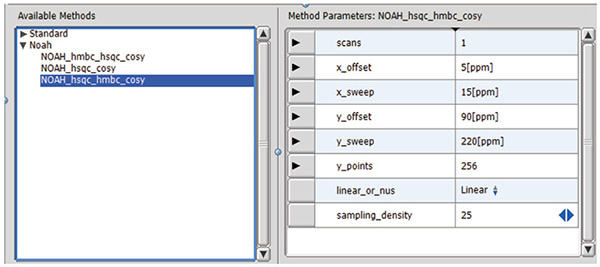
Fig. 3: Setting screen of NOAH automation
Instrument
Reference
- Eriks. Kupce and Tim D.W. Claridge, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Eng., vol.56 (39), pp. 11779-11783 (2017).
- JEOL Application Note NM190005E "NOAH-NMR Supersequences with Nested Acquisition for Small Molecules"
② Interleaved method
Interleaved experiments also have multiple acquisition blocks during one experiment. However, when compared to NOAH experiments, interleaved experiments detect different nuclei by means of multiple receivers.
Fig. 4 shows a pulse sequence of interleaved COSY. One receiver observes 1H-1H COSY and the second receiver observes 19F-19F COSY. Therefore, 1H-1H COSY and 19F-19F COSY spectra are recorded at the same time.
Fig. 5 shows results of interleaved COSY collected on 10 mg voriconazole in DMSO-d6. These spectra can be obtained within 3 minutes with NUS.
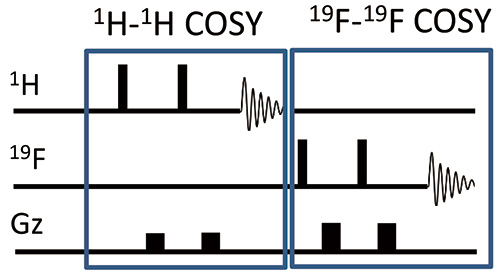
Fig. 4: Pulse sequence of Interleaved COSY
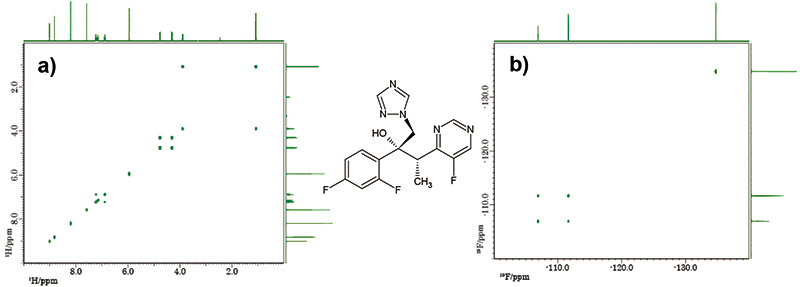
Fig. 5: Interleaved COSY: a) 1H-1H COSY, b) 19F-19F COSY
Number of scans: 1, Y points: 256, NUS density: 25%, exp. time: 3 min
Instrument
③ PANSY method
PANSY (Parallel Acquisition Nmr SpectroscopY) experiments usually acquire two FID data in parallel. These techniques also observe signal of different nuclei using multiple receivers as in the Interleaved method. On the other hand, acquisition blocks are executed at the same time, i.e. in parallel, in PANSY. Fig. 6 shows a pulse sequence of PANSY COSY which acquires 1H-1H COSY and 19F-1H HETCOR spectra.
Fig. 7 shows the results of PANSY COSY on 15 mg 1-ethoxy-2,3-difluoro-4-(trans-4-propylcyclohexyl)benzene in CDCl3.
Fig. 8 shows a pulse sequence of PANSY HMBC which collects 1H-13C HMBC and 19F-13C HMBC spectra.
Fig. 9 shows the results of PANSY HMBC of the same sample. These measurements time were reduced by NUS.
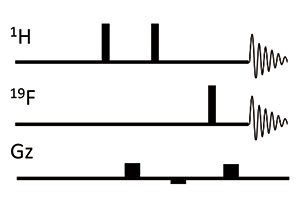
Fig. 6: Pulse sequence of PANSY COSY
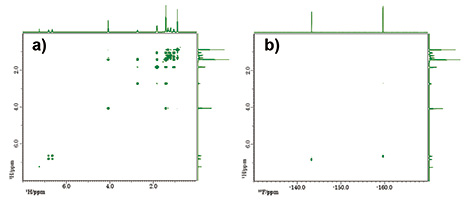
Fig. 7: PANSY COSY: a) 1H-1H COSY, b) 19F-1H HETCOR
Number of scans: 1, Y points: 256, NUS density: 25%, exp. time: 3 min
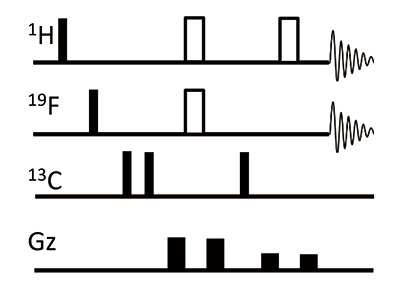
Fig. 8: Pulse sequence of PANSY HMBC
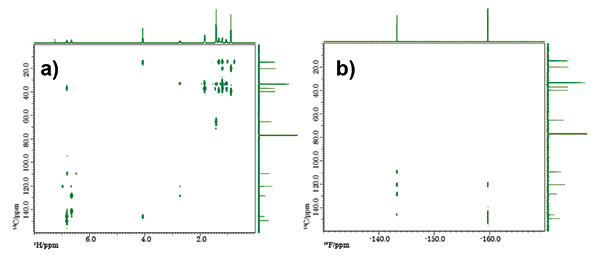
Fig. 9: PANSY HMBC: a) 1H-13C HMBC, b) 19F-13C HMBC
Number of scans: 4, Y points: 256, NUS density: 25%, exp. time: 8 min
Instrument
Reference of Interleaved and PANSY:
- Helena Kovacs and Eriks Kupce, Magn. Reson. Chem. 2016, 54, 544-560.
- Please see the PDF file for the additional information.
Another window opens when you click. 
PDF 440.4KB
SEARCH APPLICATIONS
Related Products
Solutions by field
Are you a medical professional or personnel engaged in medical care?
No
Please be reminded that these pages are not intended to provide the general public with information about the products.
