The National Institute of Health Sciences
The National Institute of Health Sciences was established in 1874 as the Tokyo Drug Control Laboratory to serve as the official government agency for the testing and analysis of medical pharmaceutical products, and is the oldest national research institute in Japan.
Regulatory Science: Contributing to Society and Mankind
In July 1997, following revisions to the regulatory system for pharmaceuticals and medical devices, the name was changed from the National Institute of Hygienic Health Sciences to the National Institute of Health Sciences (NIHS.)
The NIHS conducts testing, research, and studies regarding the proper evaluation of the quality, safety, and efficacy of pharmaceutical products, foods, and the numerous chemicals in the environment we live in. The results of these activities are reflected in welfare administration activities to ensure and/or improve the health and environment of Japanese citizens. NIHS plays an important role in the testing and research from an international perspective, and provides support for international cooperation in relevant fields.
The NIHS has a wide range of analytical instruments for shared use within the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW), including 6 nuclear magnetic resonance systems (NMR), 10 mass spectrometers (MS), 1 laboratory information system (LIMS), and 1 X-ray structure analyzer. This equipment is used mainly by MHLW researchers.
The NIHS is actively engaged in the activities of “regulatory science”, a field of science established to regulate the products arising from the advances in science and technology to ensure that these products provide a real benefit to the public.
For research that is directly related to the interests of the nation as a whole, the amount of time taken to provide a result is an important factor. For example, the research to identify components of so-called “designer drugs” (substances designed to circumvent existing drug laws), to discover counterfeit medications (unapproved, unlicensed pharmaceutical products), or to detect specific raw materials with allergenic properties, is always conducted with an awareness that time is critical.
For this reason, having the latest and most-advanced equipment is considered to be the highest priority in order to obtain the highest sensitivity with the shortest preparation and analysis times.
A recently acquired, state-of-the art, instrument is the JEOL RESONANCE 800 MHz NMR with the UltraCOOL cryogenic probe. Although the sensitivity for 13C is >3600 on this instrument, the “INADEQUATE” measurement that directly reveals 13C-13C coupling can be successfully acquired with a 10 mg sample, as shown in the results below.
For this sample (an active ingredient of a crude drug with a molecular weight 480) nearly all the direct coupling is observed in 43 hours. When the same measurement is performed with a conventional probe, it takes an unrealistic amount of time to accumulate the data, about 1075 hours (45 days), or 25 times longer.
Dr. Yukihiro Gohda, National Institute of Health Sciences Division of Drugs / Division of Pharmacology, Phytochemistry and Narcotics (concurrent) Division head/ Doctor of Pharmacology

National Institute of Health Sciences in Yoga
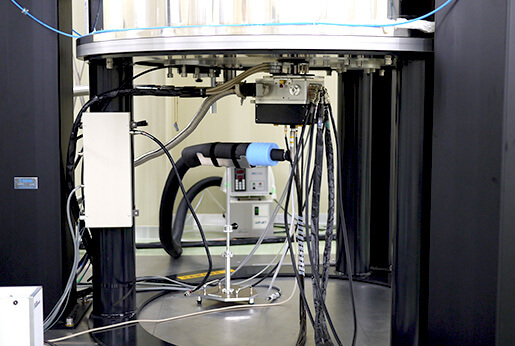
800MHz NMR system with the UltraCOOL probe installed.
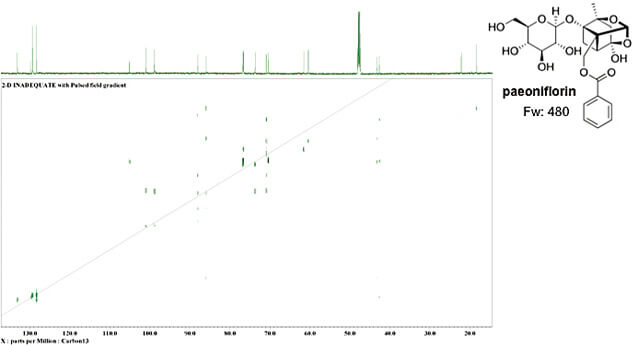
13C 2D-INADEQUATE 800MHz, 10 mg paeoniflorin in CD3OD,512 scans (about 43h)
With the introduction of highly sensitive instruments like this, it is possible to greatly reduce the time needed to identify the structure of such drugs, and then implement any notification required.
In addition, many components, like the synthetic cannabinoids that are added to some designer drugs, have an extremely high activity. From the perspective of the safety of the researchers, it is necessary to be very careful when handling relatively large quantities of these components. If the measurement equipment is more sensitive, however, it is possible to perform the work with a much smaller amount.
The NHIS is also proactively working on the application of quantitative NMR for public standards. Quantitative NMR will be adopted in Supplement II of the 16th amendment of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia.※
The case studies presented here are just a small part of the research conducted using the shared-use equipment of the NIHS. This equipment will continue to play an active role as an important tool for the regulatory science that makes a valuable contribution to society and mankind.
As at 20 Sep.,2013
Instruments from JEOL RESONANCE

NMR instruments
- ECA800 2 systems, ECA600 2 systems (as shared-use equipment)
MS instruments
- DART-TOF/MS, JMS-MS700 (as shared-use equipment)
