Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer (NMR)
NMR is an abbreviation for Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. An NMR instrument allows the molecular structure of a material to be analyzed by observing and measuring the interaction of nuclear spins when placed in a powerful magnetic field.
For the analysis of molecular structure at the atomic level, electron microscopes and X-ray diffraction instruments can also be used, but the advantages of NMR are that sample measurements are non-destructive and there is less sample preparation required.
Fields of application include bio, foods, and chemistry, as well as new fields such as battery films and organic EL, which are improving and developing at remarkable speed. NMR has become an indispensable analysis tool in cutting-edge science and technology fields.
NMR instrument composition

Principles of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
When a nucleus that possesses a magnetic moment (such as a hydrogen nucleus 1H, or carbon nucleus 13C) is placed in a strong magnetic field, it will begin to precess, like a spinning top.
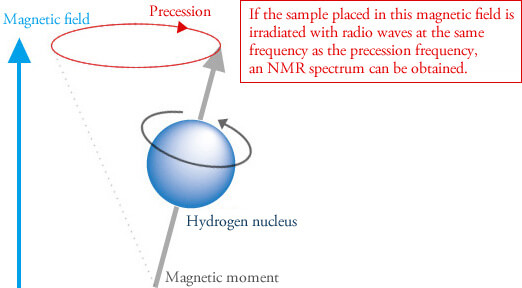
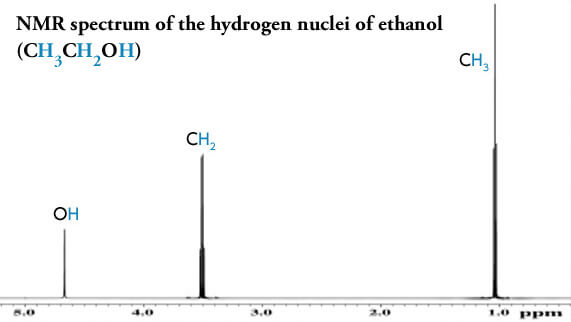
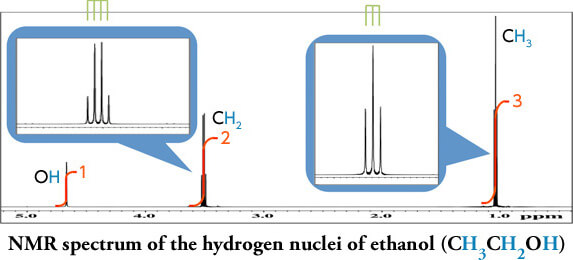
What we can learn from NMR spectra
Chemical shift: Information about the composition of atomic groups within the molecule.
Spin-Spin coupling constant: Information about adjacent atoms.
Relaxation time: Information on molecular dynamics.
Signal intensity: Quantitative information, e.g. atomic ratios within a molecule that can be helpful in determining the molecular structure, and proportions of different compounds in a mixture.
NMR application fields
Analysis of Molecular Structure and Identification of Unknown Chemical Substance
A very wide range of applications including Organic Chemistry, Inorganic Chemistry, Biochemistry, Pharmaceutical Analysis, New Materials, Petrochemistry, etc.

Quantitative Analysis
Polymer Chemistry, Quality Control of Synthetic Chemicals, Food Chemistry

Analysis of Mixtures
Food Chemistry, Biochemistry, Physiology
Dynamics(chemical reaction speed, identification of binding site, interaction)
Organic Chemistry, Inorganic Chemistry, Biochemistry

Relaxation Time (molecular mobility, interatomic distance)
Organic Chemistry, Polymer Chemistry

Diffusion Coefficient (molecular weight, conformation of polymer)
Organic Chemistry, Polymer Chemistry
